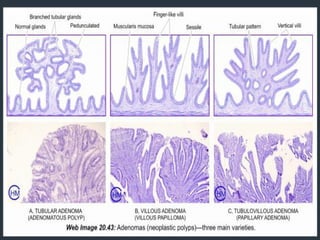
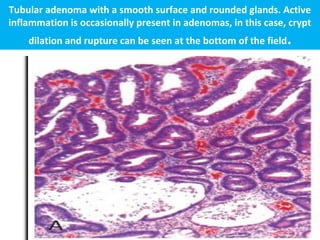
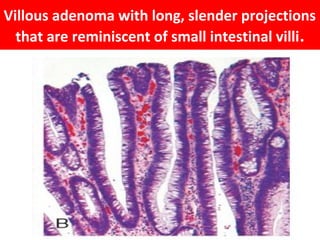
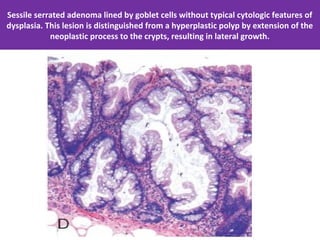
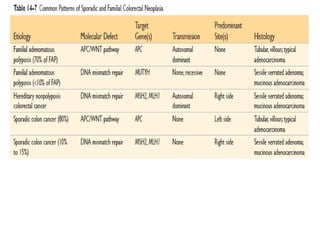
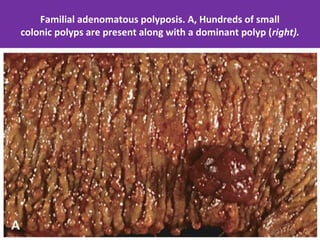
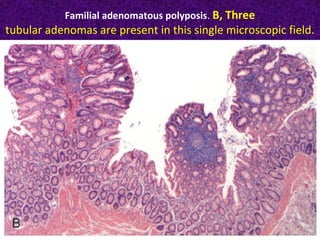
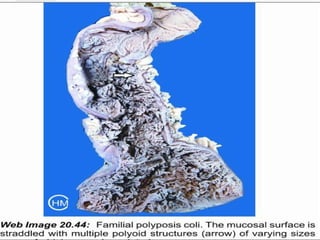
Colonic adenomas are benign epithelial tumors that can develop into colorectal cancer over time. They range in size and can be pedunculated or sessile. Microscopically, they are characterized by epithelial dysplasia and nuclear abnormalities. Certain familial polyposis syndromes, like familial adenomatous polyposis and Lynch syndrome, are associated with an increased risk of developing numerous colonic adenomas and colorectal cancer at a young age due to genetic mutations. Surveillance colonoscopy is recommended to screen for and remove adenomas to prevent cancer.