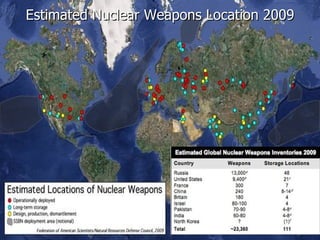
1. The document discusses nuclear non-proliferation, disarmament, and the Indo-US nuclear deal. It provides information on horizontal and vertical nuclear proliferation and defines disarmament.
2. It summarizes various international treaties and agreements aimed at limiting nuclear weapons such as the NPT, SALT, START, and CTBT. It also discusses regional nuclear weapon free zones.
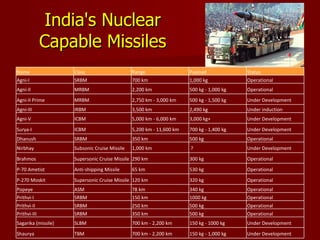
3. The document then provides details on India's nuclear weapons program and missiles, and summarizes the key aspects of the Indo-US nuclear deal.