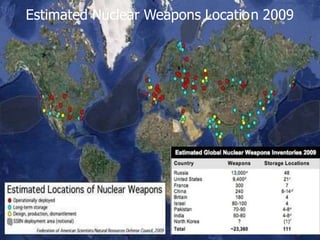
The document discusses the international regime of nuclear non-proliferation and disarmament. It defines proliferation, horizontal and vertical proliferation, and disarmament. It outlines the key components of the non-proliferation regime including the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT), United Nations Security Council, International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) safeguards, and bilateral US-Soviet/Russian arms control treaties. Over 24,000 nuclear weapons currently exist worldwide among nine nuclear states. The goal of the non-proliferation regime is to prevent the further spread of nuclear weapons and ultimately achieve their total elimination.