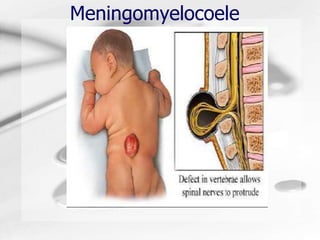
Meningomyelocoele
- 2. Introduction • Meningomyelocoele is the most severe type of SPINA BIFIDA. • Spina Bifida means "split spine” • 4 types of Spina Bifida are: – Spina bifida occulta, – Meningocele – Spina bifida cystica (Myelomeningocele) and – Lipomeningocele • Meningomyelocoele – occurs due to Failure of closure of the neural tube during the third week of gestation – abnormal differentiation of the embryonic neural tube • In Meningomyelocoele, a cystic swelling occurs over the site of the spinal defect which contains meninges, nerve roots, and the spinal cord itself which has left the vertebral canal
- 3. Spina bifida
- 4. Spinal Dysraphism Spina bifida occulta Meningocele Myelomeningocele
- 6. Incidence - Meningomyelocoele • 1-2/1000 live birth • Neural tube defects are second most common type of birth defect • Myelomeningocele is the most common form of neural tube defect. • Slightly higher in females than in males (1.2:1) • 85% occur in lumbosacral • region
- 7. Aetiology • Poor nutrition - Folic acid deficiency • Genetics (People of Northern European and Hungarian ancestry have the highest rates of the disease) • Chromosome abnormalities: – Trisomies 13 and 18 – Triploidy – Single gene mutations • Maternal obesity, hyperthermia • pregnancies complicated by diabetes at conception • Drugs: valproate, carbamazepine and drugs to induce ovulation • Maternal exposures to fumonisins, electromagnetic fields, hazardous waste sites, disinfection by-products found in drinking water and pesticides
- 8. Meningomyelocele – Clinical Features • Both meninges and spinal cord protrude into the skin of the back • Leak of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is common • Severe neurological deficits are common • Risk for bacterial meningitis • Paraplegia • Diminished control of lower limbs, bladder Hydrocephalus and bowel • Hydrocephalus often accompanies • Short stature and precocious puberty Paraplegia
- 9. Primary Functional System Congenital deficits Anomalies • Lower limb paralysis • Facial clefts • Sensory loss • Heart • Bladder and bowel malformations, and dysfunction • Genitourinary tract • Cognitive dysfunction anomalies • Cranial nerve • Urinary tract dysfunction anomalies – Ocular muscle palsies, – solitary kidney or – Swallowing andeating – malformed ureters problems and – Abnormal phonation
- 10. Arnold Chiari II in 95% of myelomeningocoele • Herniation of cerebella vermis through foramen Magnum (cerebella tonsils extend down into the spinal cord, lower CN run up instead of down) • Dislocation of the 4th ventricle towards neural canal • Associated with hydrocephalus 85% • Developmental abnormalities in CV, GI, GU systems 10%
- 11. DIAGNOSIS • Ultrasound during the second trimester • The diagnosis of myelomeningocele is certain when 3 classic central findings are present in ultrasonography – concavity of the frontal bones, – ventriculomegaly, and – Chiari II malformation. • Positive screening for maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) • Screening of the amniotic fluid for AFP, as well as for the presence of acetylcholinesterase Ultra Sound Coronal view of spine Lemon" shaped skull Sagittal view of spine
- 12. Treatment • Intrauterine surgery • Post-natal surgery:- Closure of the Myelomeningocele is performed immediately after birth if external CSF leakage is present and typically within the first 24-48 hours in the absence of CSF leakage • Multidisciplinary interventions needed to prevent progressive deterioration of multiple body systems • Treatment team consists of pediatric specialists in – Physical medicine and rehabilitation – Neurosurgery – Urology – Orthopedics along with – Pediatric nursing – Physical therapy – occupational and recreational therapy – psychology and – medical social work
- 13. Medication • Anticholinergics: - to suppress detrusor overactivity eg. Oxybutynin chloride • Tricyclic antidepressants, eg. Imipramine hydrochloride • Alpha-adrenergic antagonists: - decrease bladder outlet resistance, increase urinary flow rate, and improve bladder emptying eg. Terazosin
- 14. Locomotion improves the cognitive profile of children with Meningomyelocele? • Twenty-nine children with MMC and shunted hydrocephalus were studied. • All had motor impairment, but after physiotherapy and training, walking was possible in 23 of them (5 autonomously and 18 with an aid), while 6 had recourse to a wheelchair. • Even though global I.Q. in these MMC children was within the normal range, the characteristic splitting between verbal I.Q. (VIQ) and performance I.Q. (PIQ) was observed, but the most interesting observation was a significant performance-related difference (P=0.044 and P=0.012) between ambulatory patients (both with and without aids) and those who were dependent on wheelchairs (PIQ: 83-85 vs 63). Reference: Rendeli C. et.al; Does locomotion improve the cognitive profile of children with meningomyelocele?; Child’s Nerv Syst (2002) 18:231–234