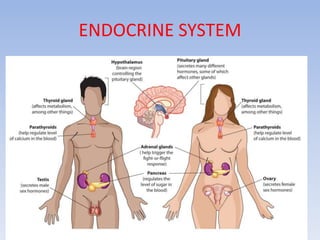
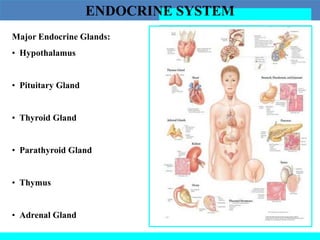
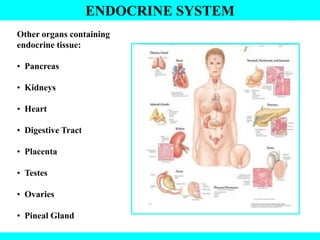
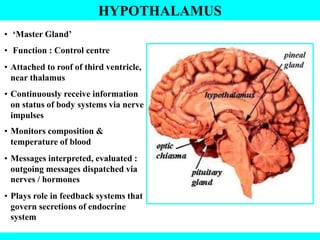
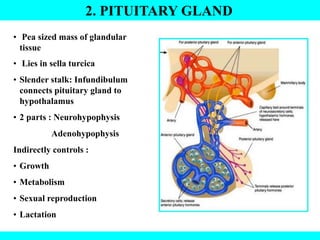
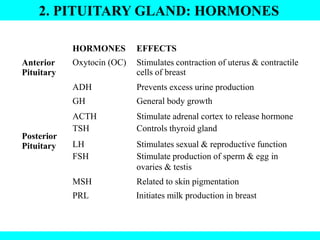
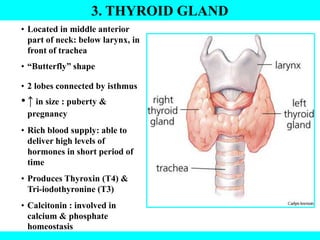
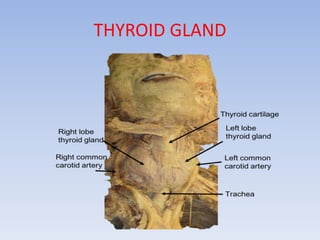
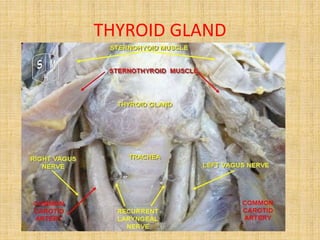
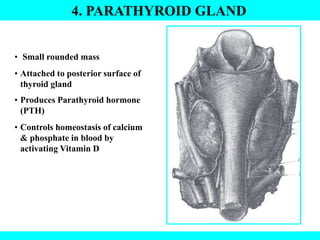
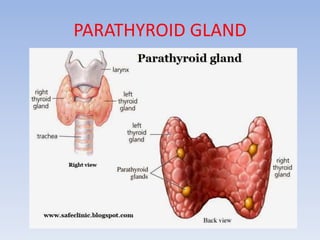
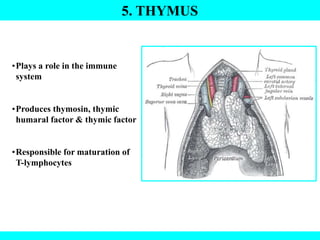
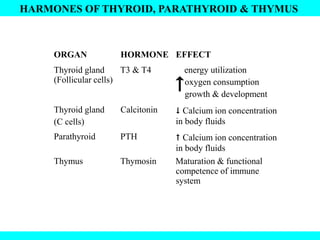
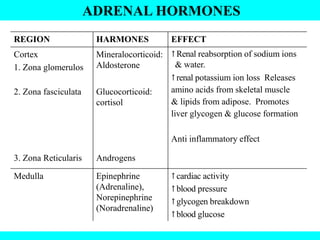
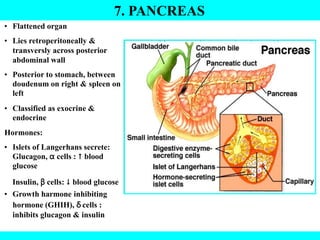
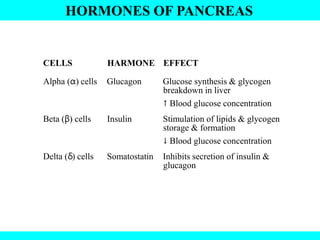
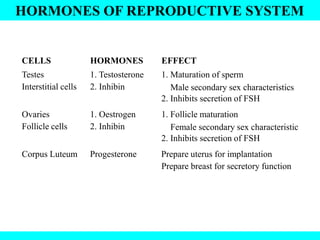
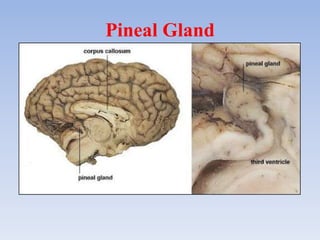
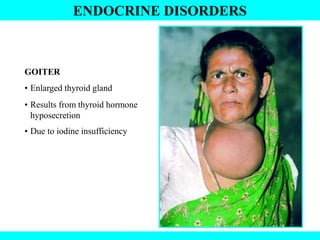
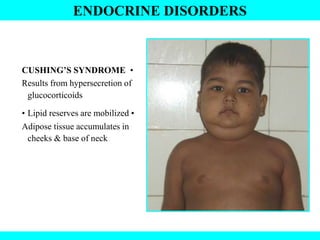
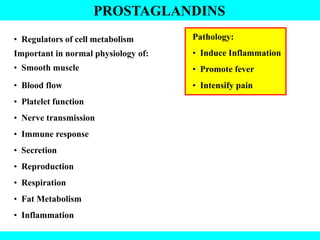
The document provides information about the endocrine system. It discusses the major endocrine glands including the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, thymus, adrenal gland, pancreas, ovaries, testes and pineal gland. It describes the hormones produced by each gland and their effects on the body. Some endocrine disorders are also mentioned like acromegaly, cretinism, goiter and Cushing's syndrome. Feedback control of hormone release is explained along with the roles of prostaglandins.