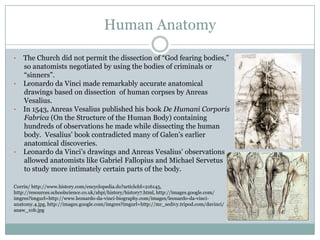
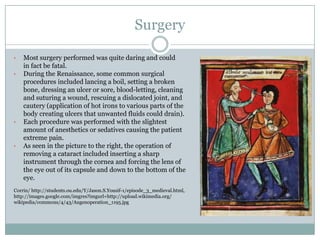
During the Renaissance, medical research progressed as physicians studied anatomy and experimented with new treatments, building on knowledge from Arabic writings. The Black Death spurred experimentation to find treatments, though it was not stopped. Anatomical understanding advanced through the work of Vesalius and da Vinci. Herbal medicines were developed to treat various diseases, though some like tobacco were found to be deadly. Hospitals began to be established separately from religious institutions.