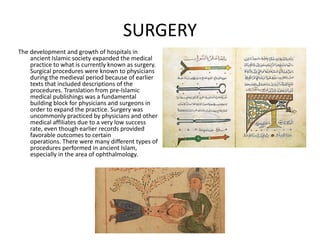
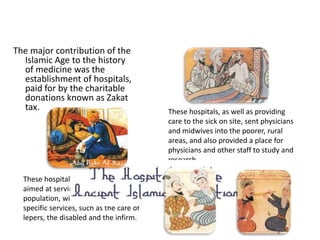
Between 700-1500 AD, the Arabic world was a center of scientific and medical knowledge, as Greek and Roman texts were translated into Arabic and studied. The establishment of hospitals funded by charitable donations expanded medical practice and surgery. Hospitals provided various services including general care, care for lepers and disabled. A major figure was Ibn Sina (Avicenna), a philosopher and physician whose most famous work "Laws of Medicine" contained sections on medicine, diagnosis, and therapies and influenced medicine for centuries after being translated to Latin.