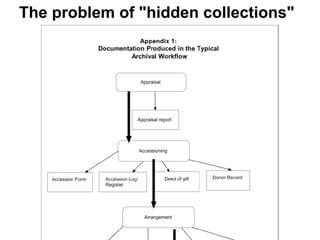
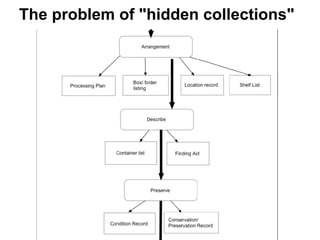
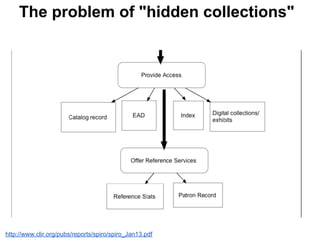
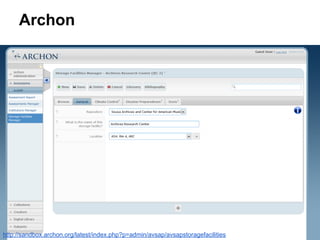
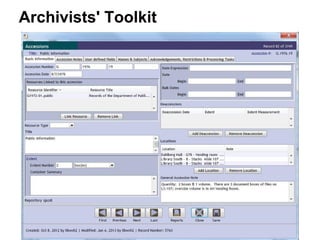
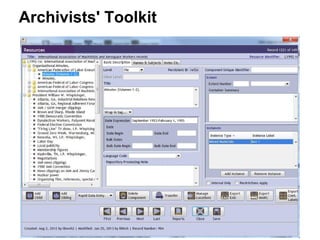
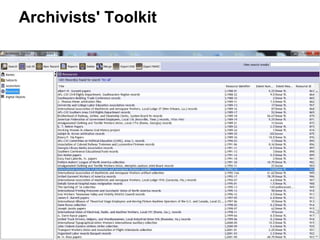
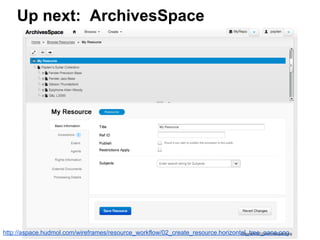
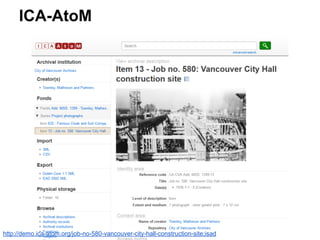
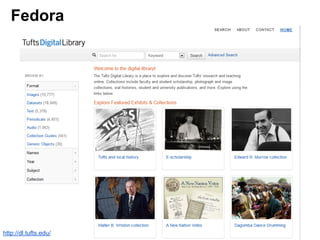
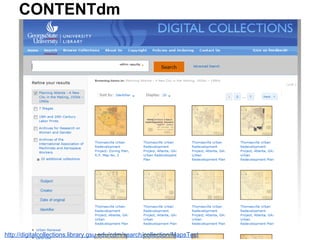
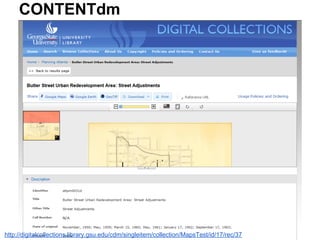
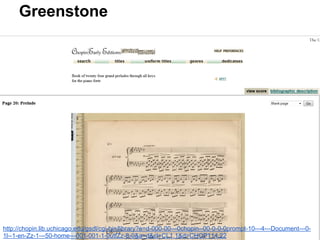
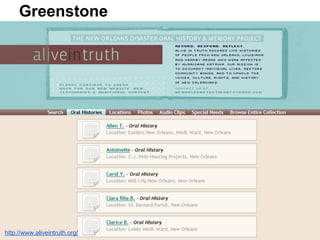
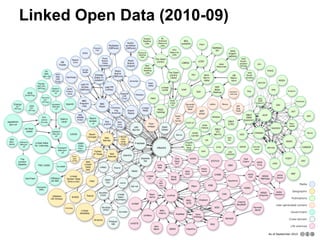
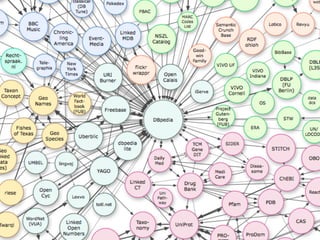
This document provides an overview of archival technologies presented at the 46th Annual Georgia Archives Institute on June 10-21, 2013. The presentation introduces various archival management tools like Archon and Archivists' Toolkit for managing archival collections. It also discusses digital collection management software such as CONTENTdm and Islandora. Emerging standards, formats and linked open data initiatives are also covered. The goal is to help archivists identify existing and new technologies that can help manage and provide access to archival materials.