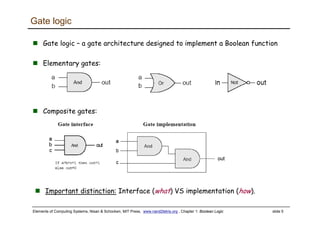
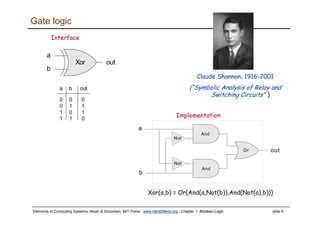
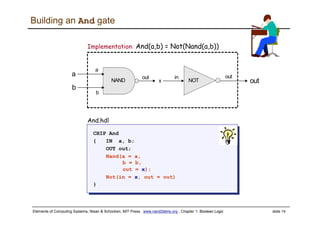
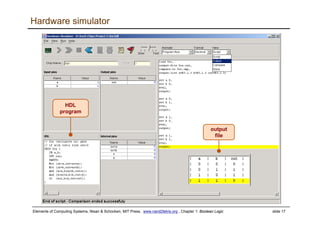
The document discusses Boolean logic and functions. It introduces Boolean algebra and some basic Boolean functions like AND, OR, and NOT. It explains that every Boolean function can be expressed using only AND, OR, and NOT. The document then discusses implementing Boolean functions using logic gates like NAND gates. It provides an example of building an AND gate from NAND gates. Finally, it discusses a hardware simulator that can be used to test HDL programs implementing Boolean functions and logic gates.