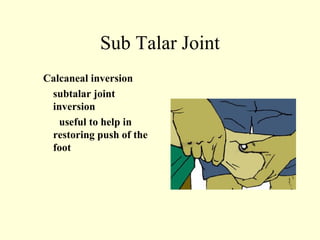
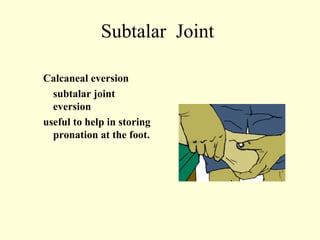
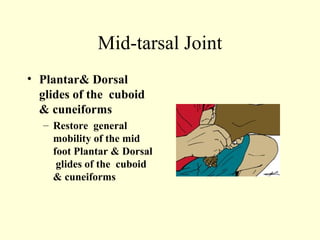
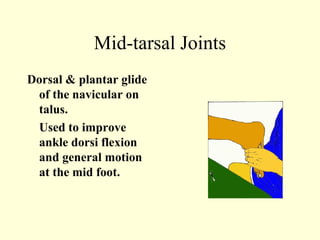
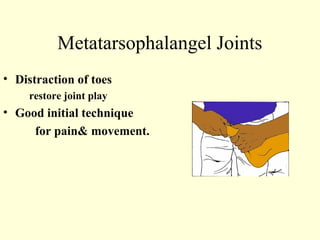
This case study describes using ankle and foot joint mobilization techniques to rehabilitate a 28-year old male who suffered a talar body fracture that was surgically repaired with lag screws. The mobilization techniques targeted the talocrural, subtalar, midtarsal, and metatarsophalangeal joints to restore range of motion, address residual loss of motion from the intra-articular fracture, and improve muscle strength in the ankle and foot. Specific techniques included distraction, glides, inversion, eversion, and distraction maneuvers applied to the relevant joints.