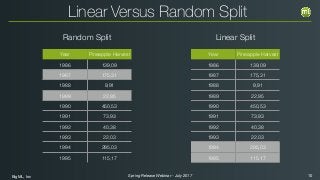
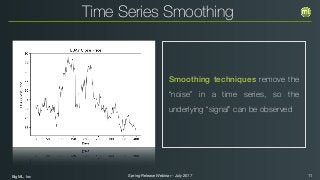
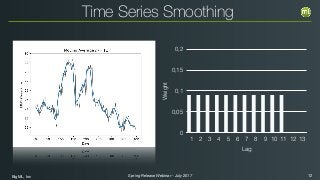
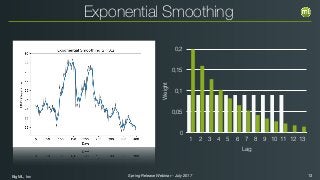
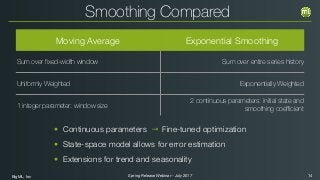
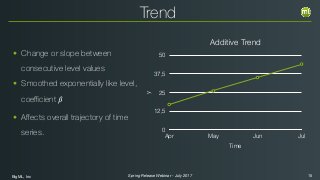
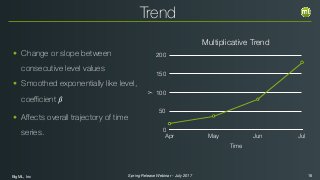
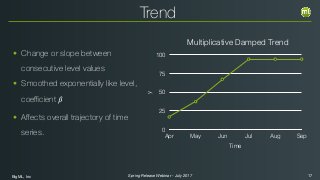
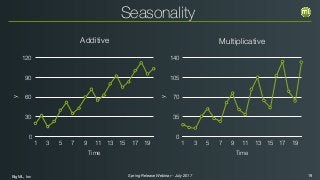
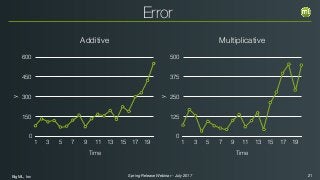
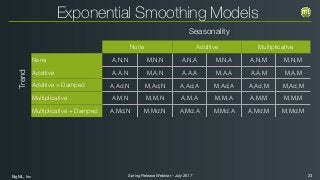
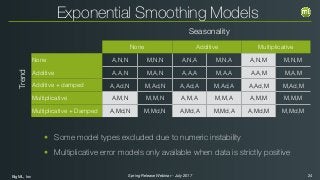
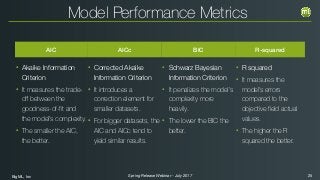
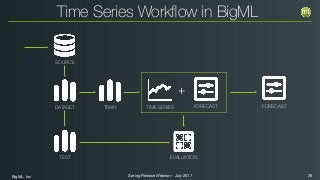
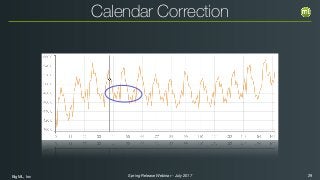
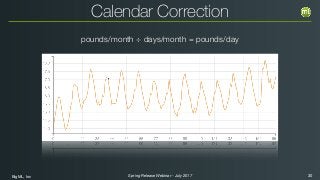
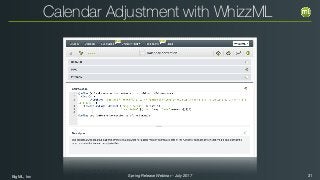
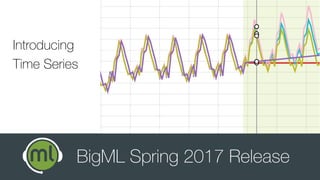
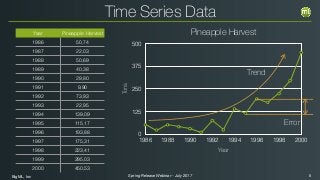
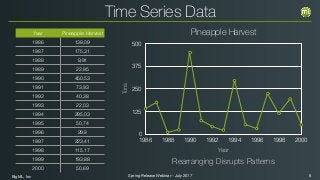
The document outlines the Spring 2017 release webinar by BigML, focusing on time series analysis and machine learning techniques. It highlights methods for discovering patterns in data, predictive modeling, seasonality, and error estimation, alongside practical applications and workflows within BigML's platform. The presentation also discusses various approaches to forecasting and the importance of metrics for evaluating model performance.


![BigML, Inc 8Spring Release Webinar - July 2017
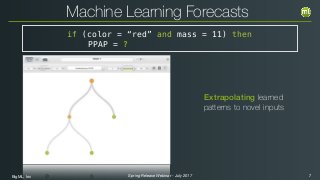
if (color = “red” and mass = 11) then
PPAP = [“apple”;34.24%]
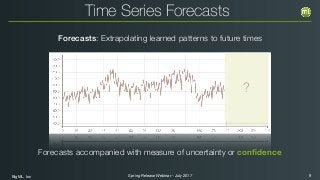
Forecasts accompanied
with measure of uncertainty
or confidence
Machine Learning Forecasts](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigmlspring2017release-test-170719163442/85/BigML-Spring-2017-Release-8-320.jpg)