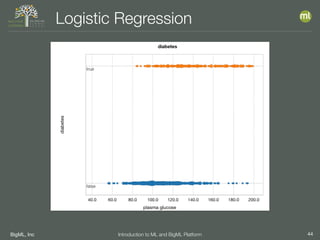
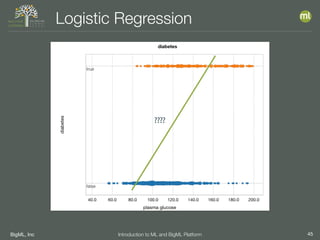
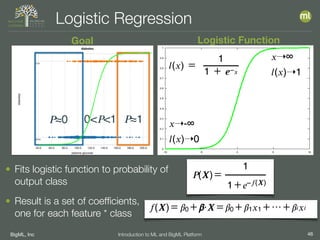
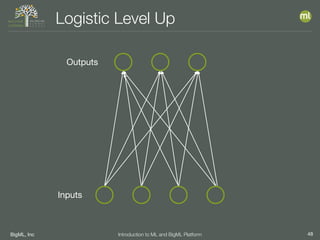
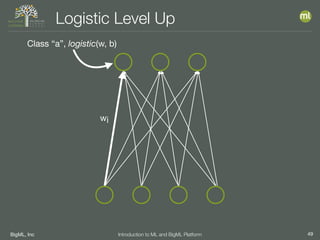
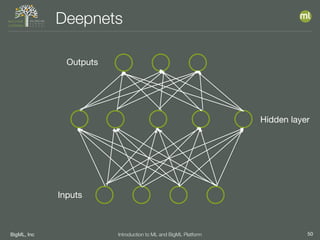
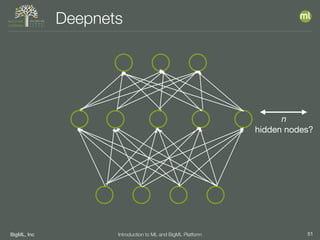
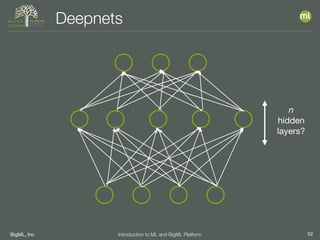
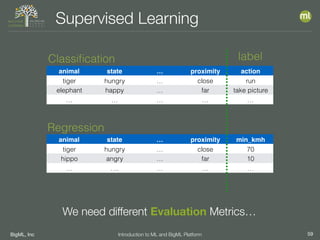
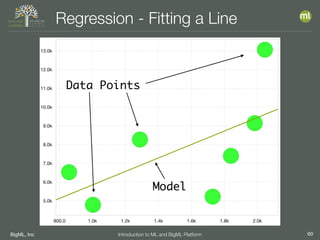
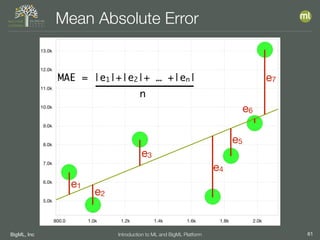
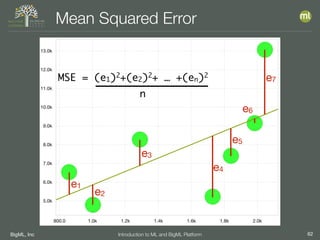
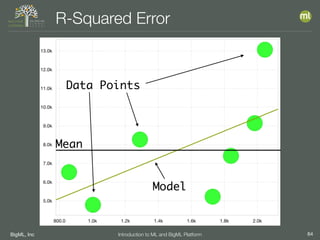
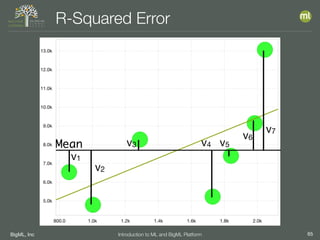
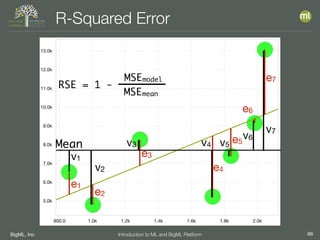
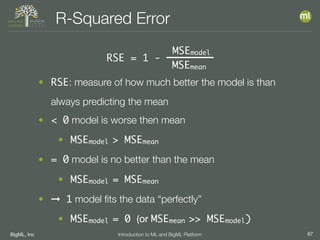
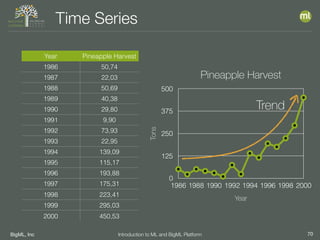
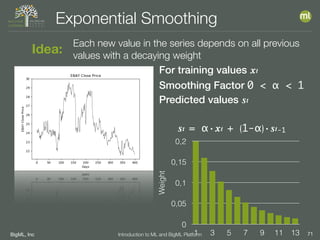
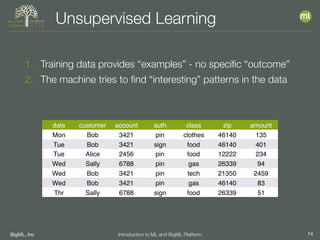
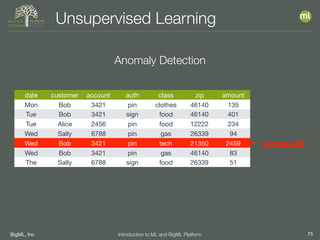
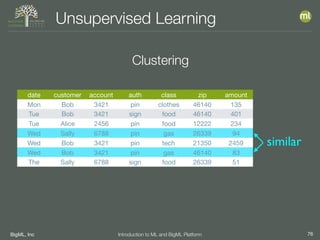
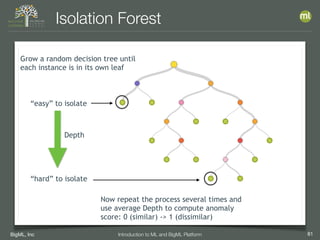
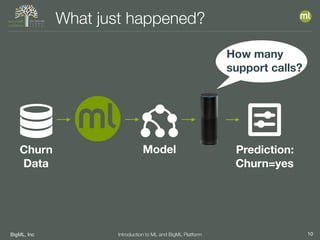
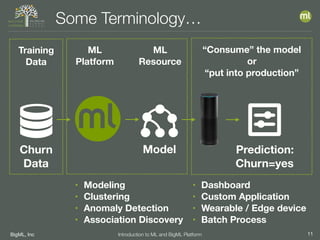
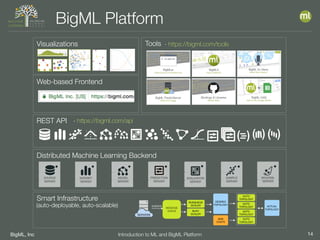
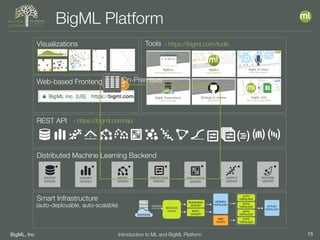
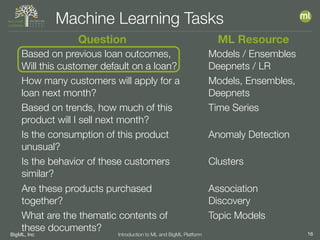
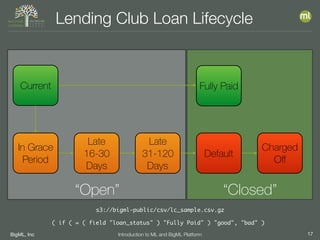
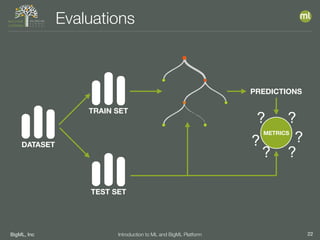
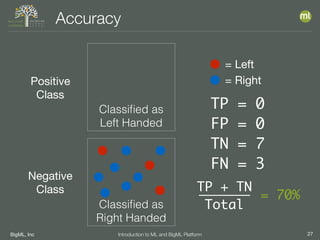
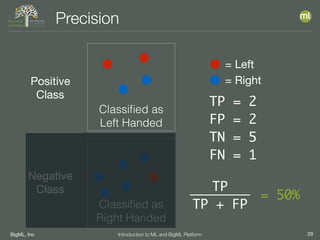
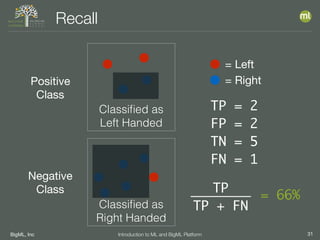
The document outlines the 4th edition of the Valencian Summer School in Machine Learning, discussing BigML's platform and its applications in machine learning. It covers various aspects such as the background of BigML, the functionalities of the platform, modeling techniques, evaluation metrics, and the importance of ensembles and fusions in improving model performance. Additionally, it emphasizes the significance of accurate evaluation and methodology in machine learning applications.











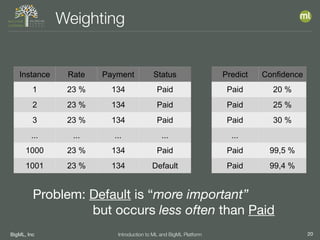








![BigML, Inc 34Introduction to ML and BigML Platform
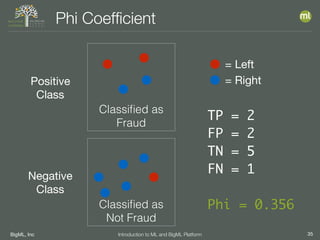
Phi Coefficient
__________TP*TN_-_FP*FN__________
SQRT[(TP+FP)(TP+FN)(TN+FP)(TN+FN)]
• Returns a value between -1 and 1
• If -1 then predictions are opposite reality
• =0 no correlation between predictions and reality
• =1 then predictions are always correct](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vssml18-intro-to-bigml-180919143446/85/VSSML18-Introduction-to-Machine-Learning-and-the-BigML-Platform-34-320.jpg)