Embed presentation
Downloaded 49 times









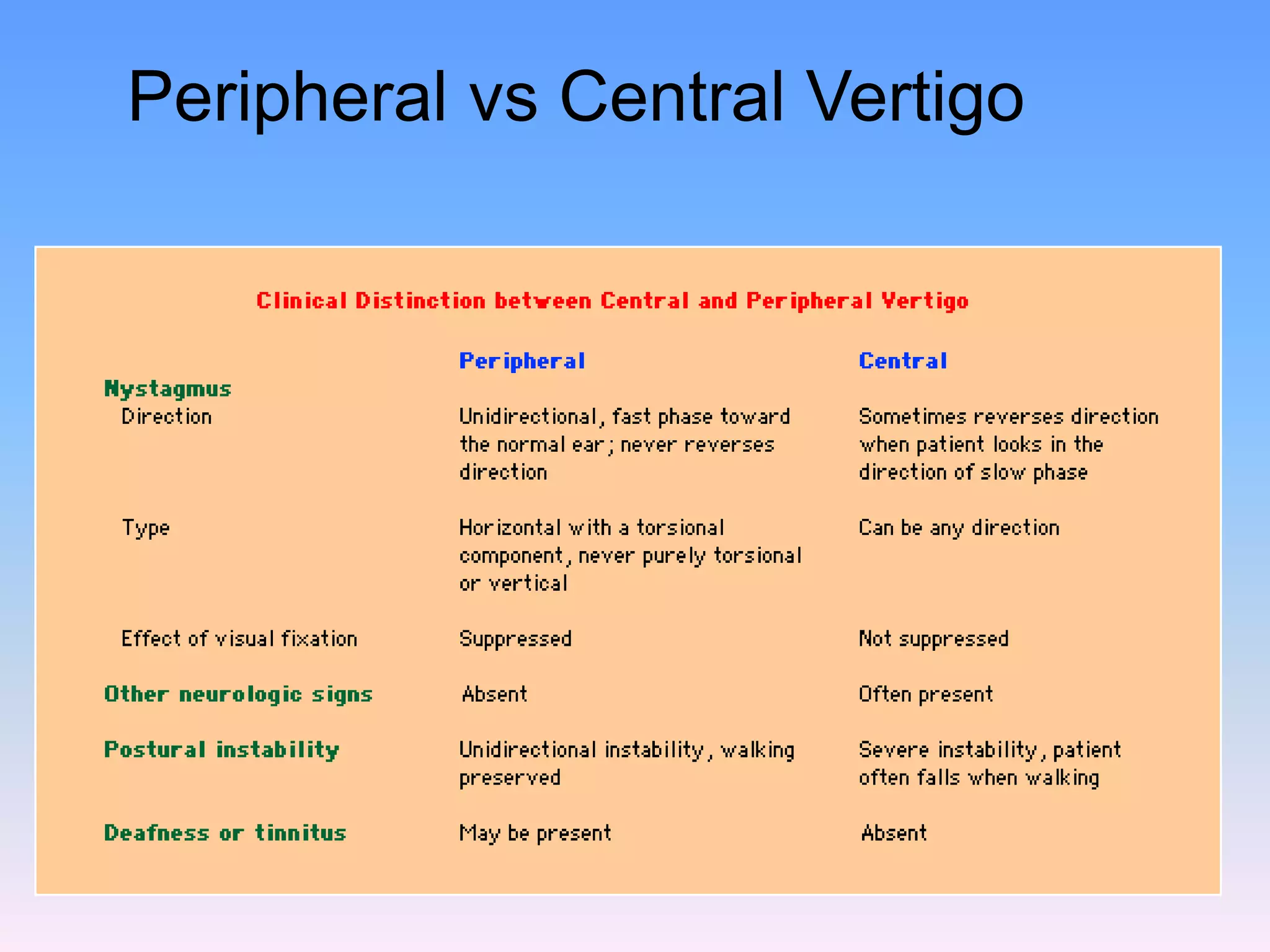
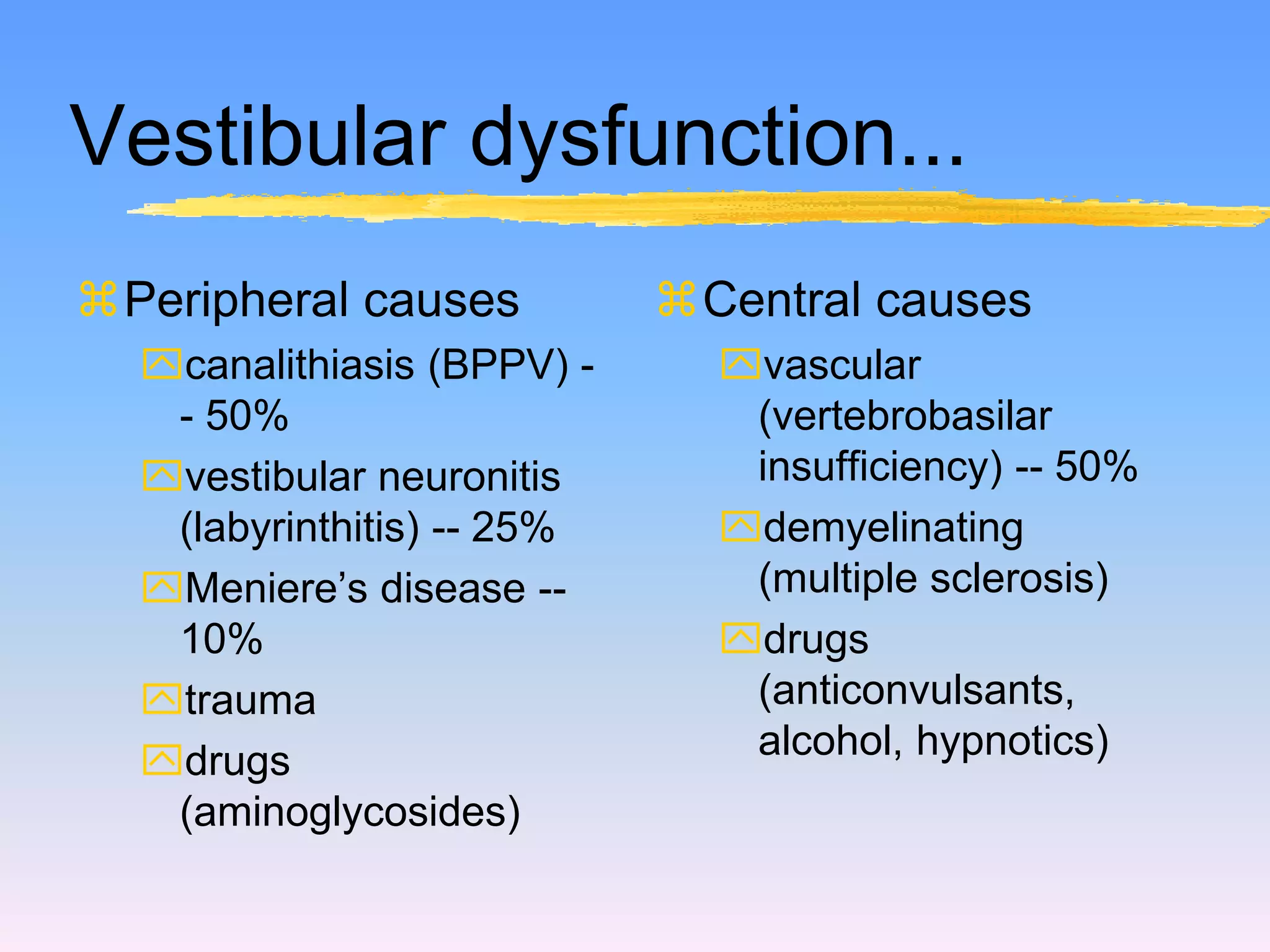
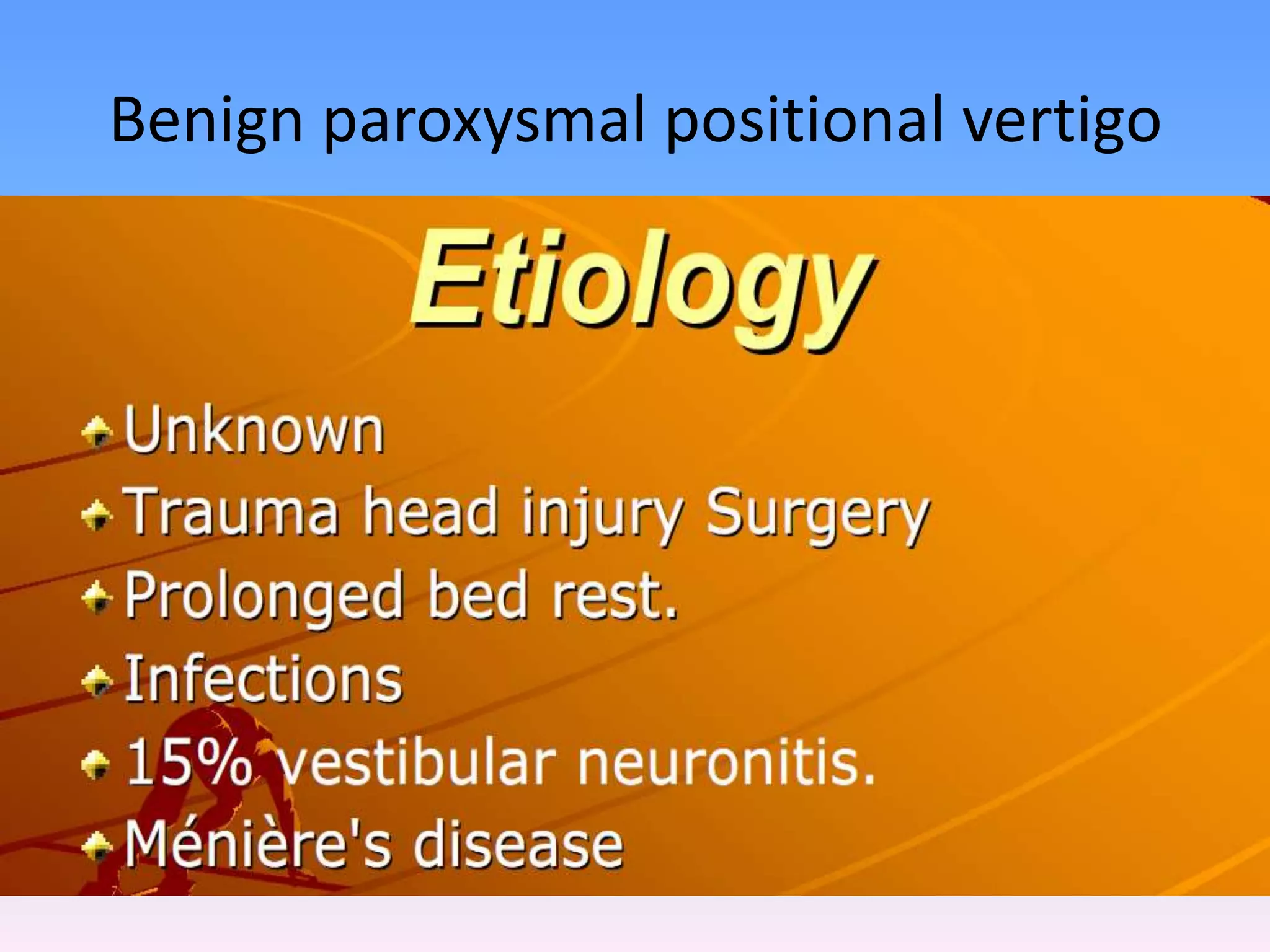
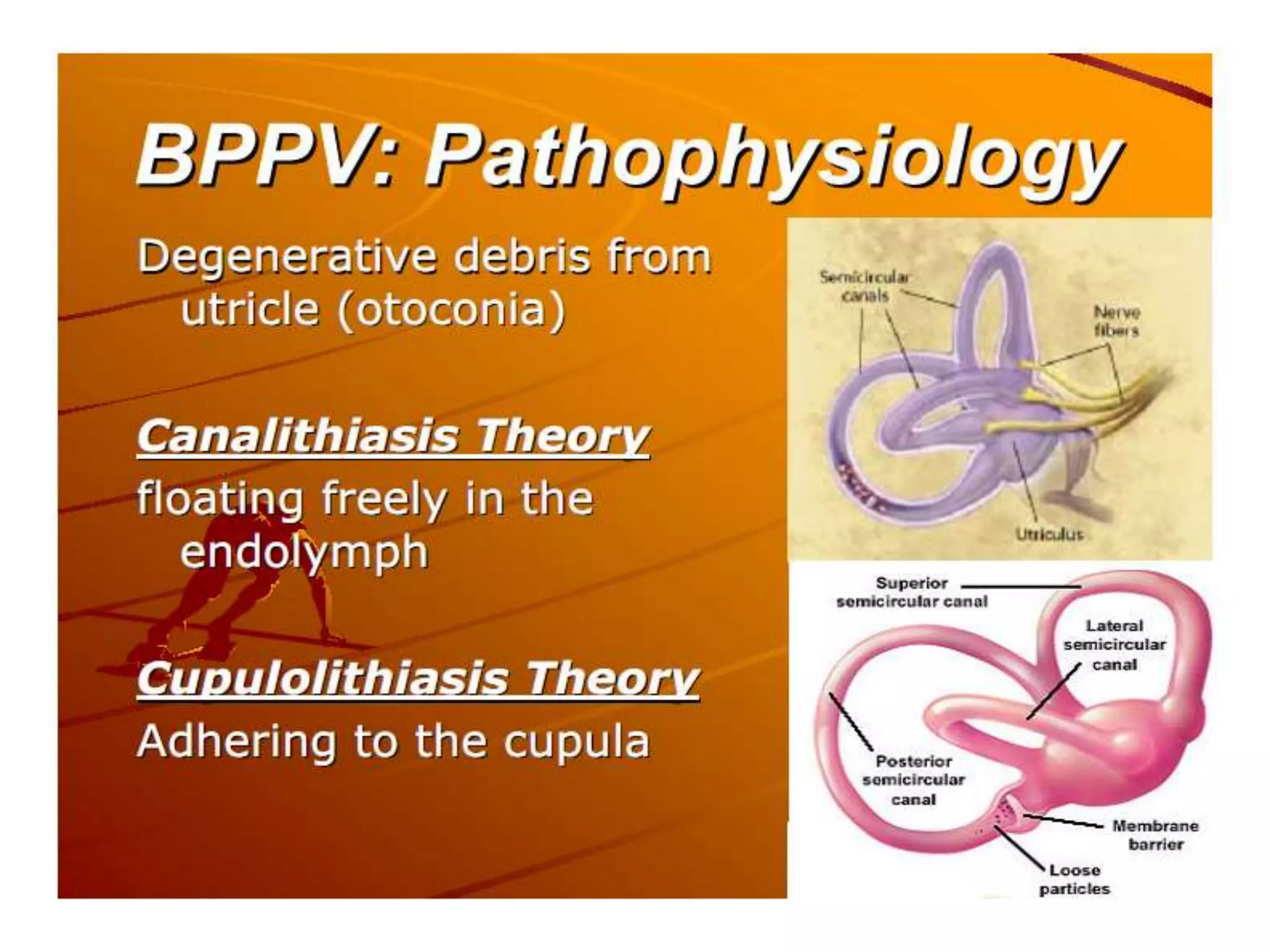


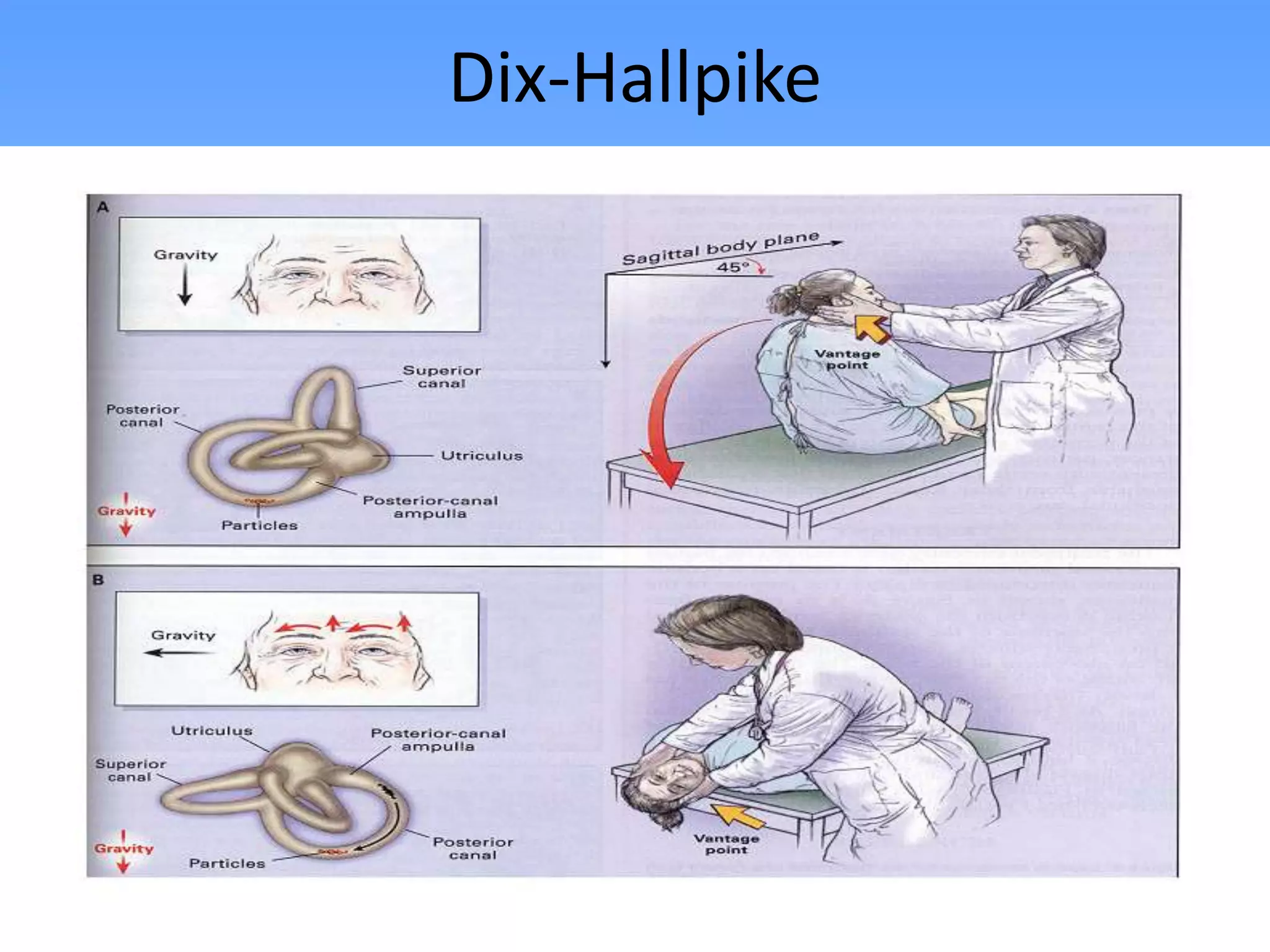



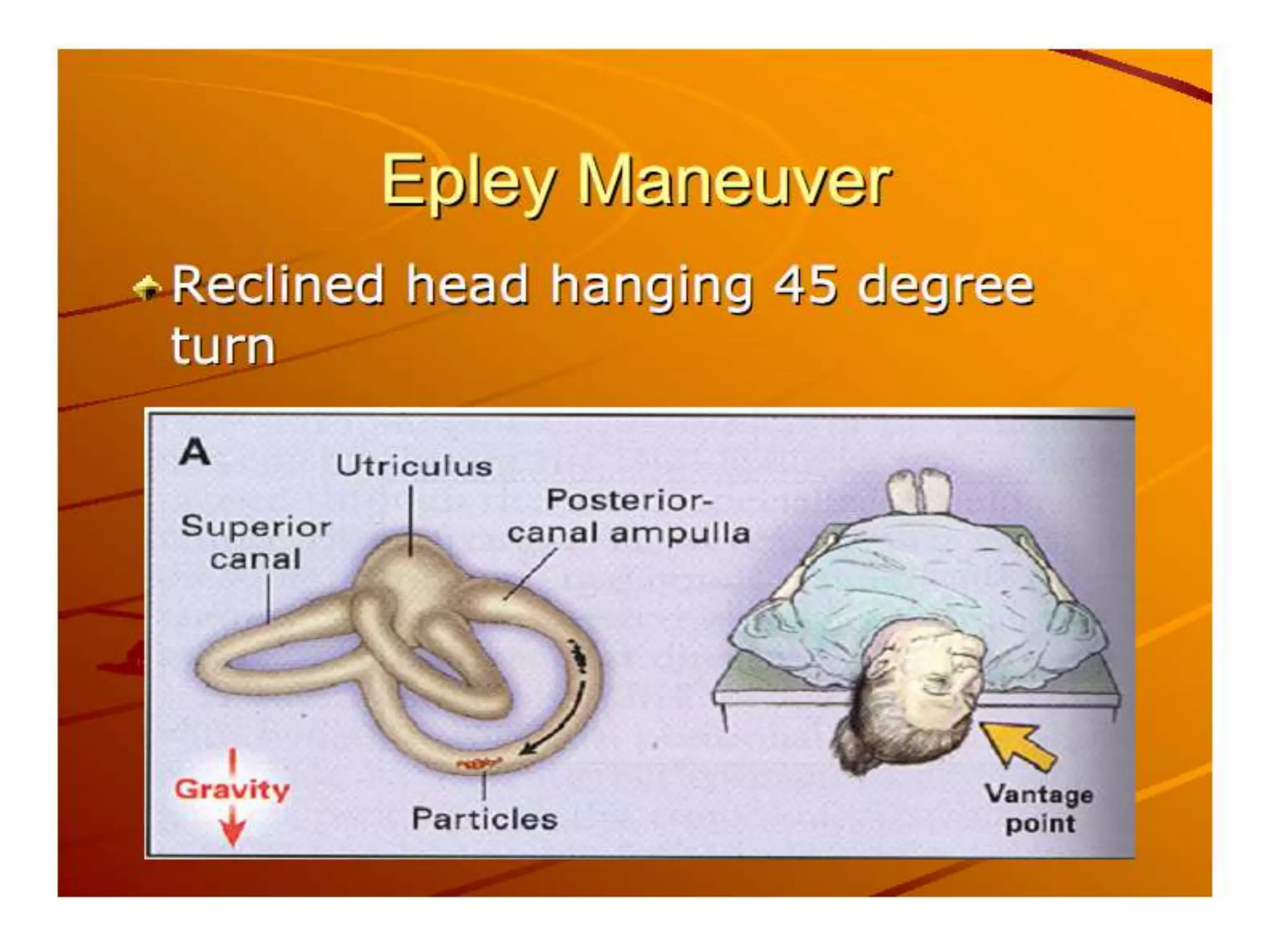
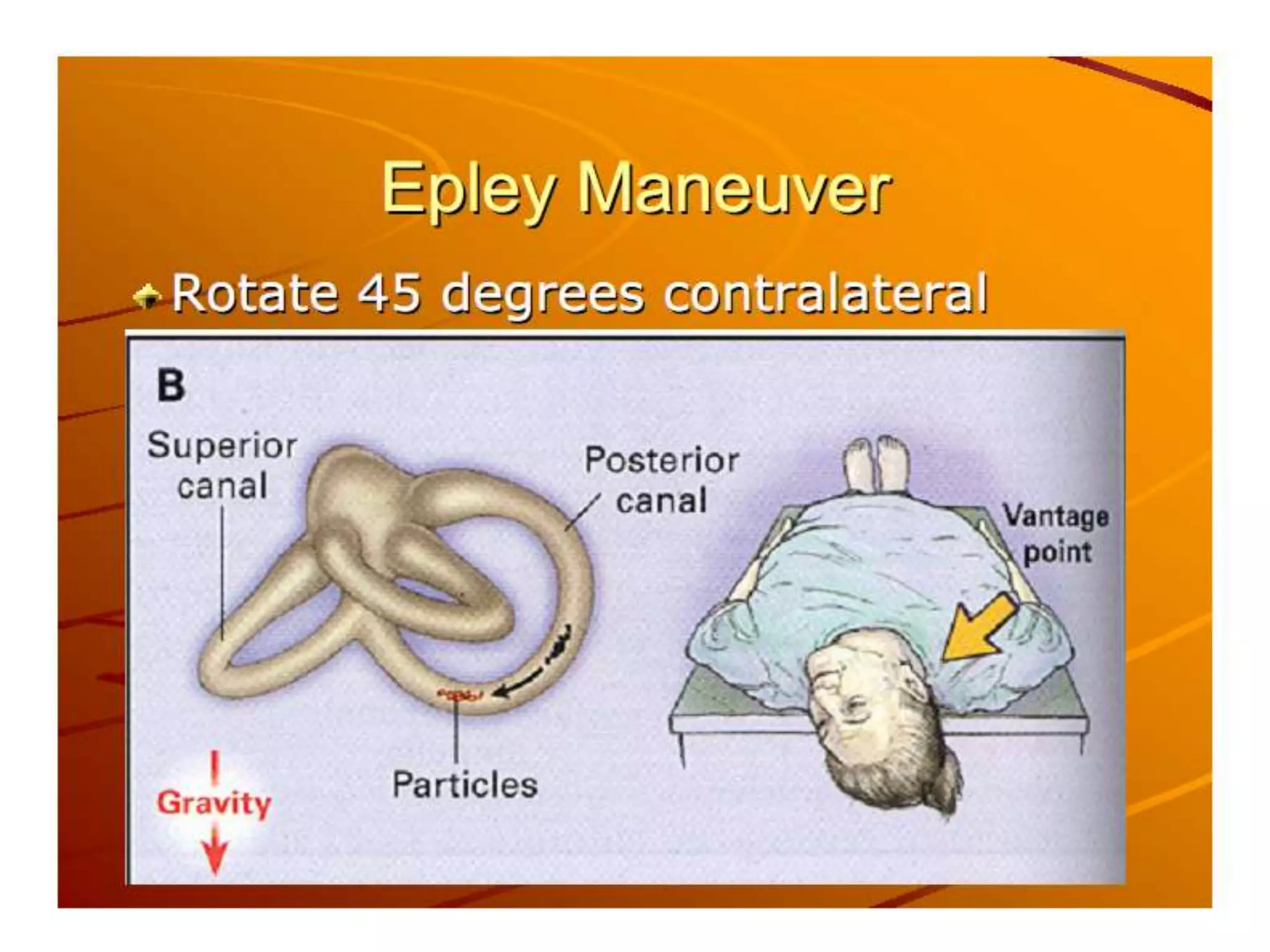
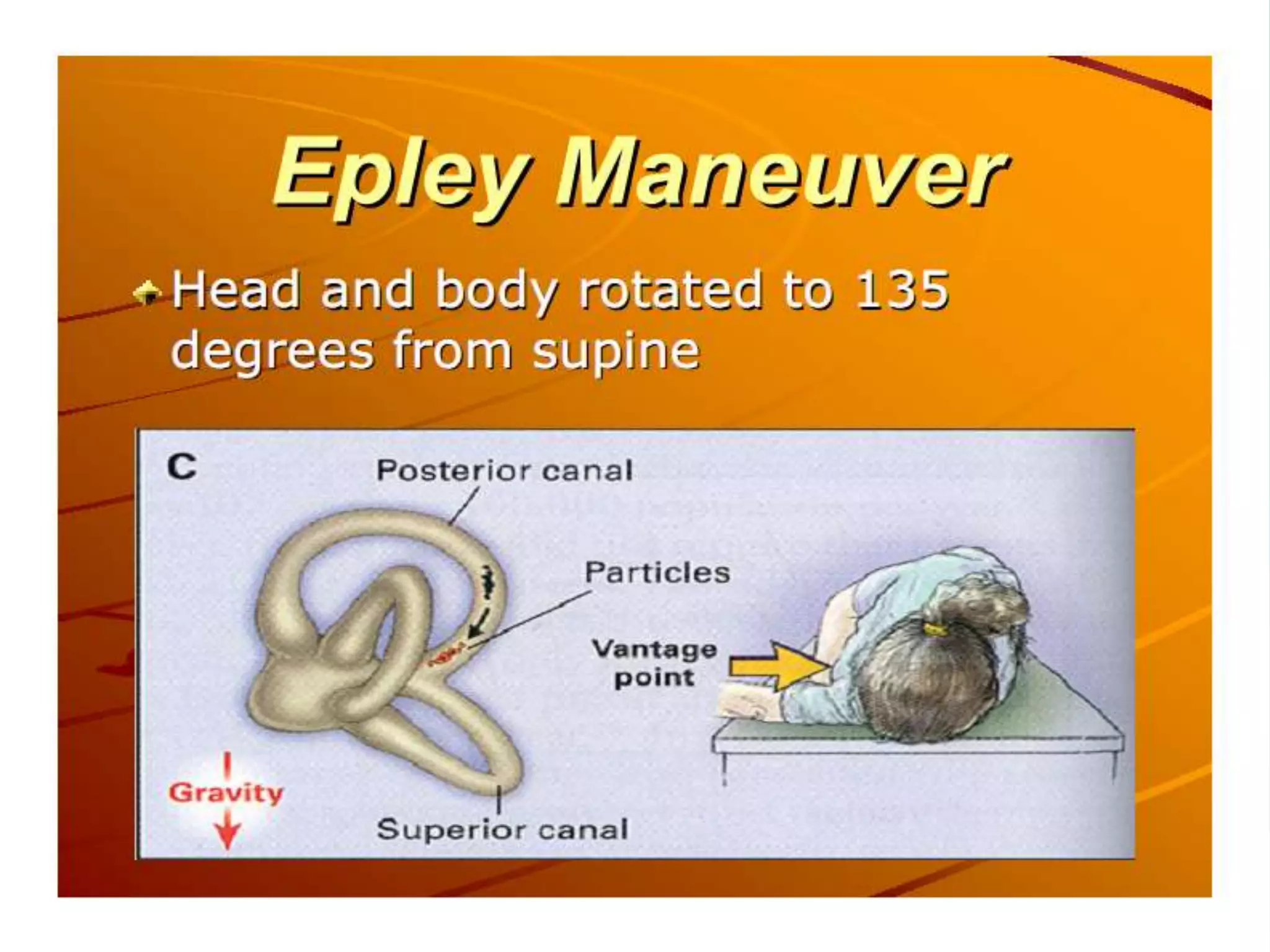
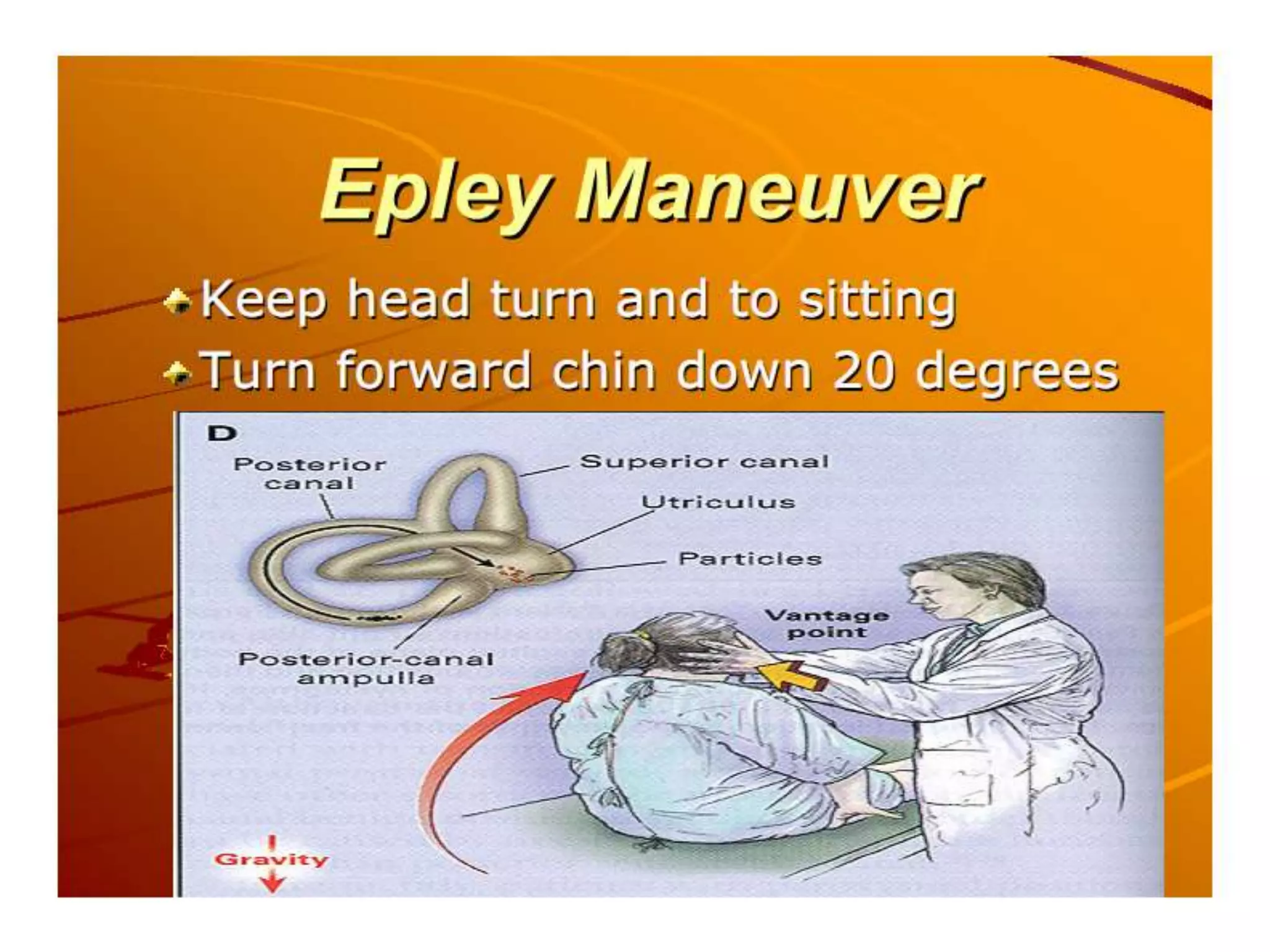
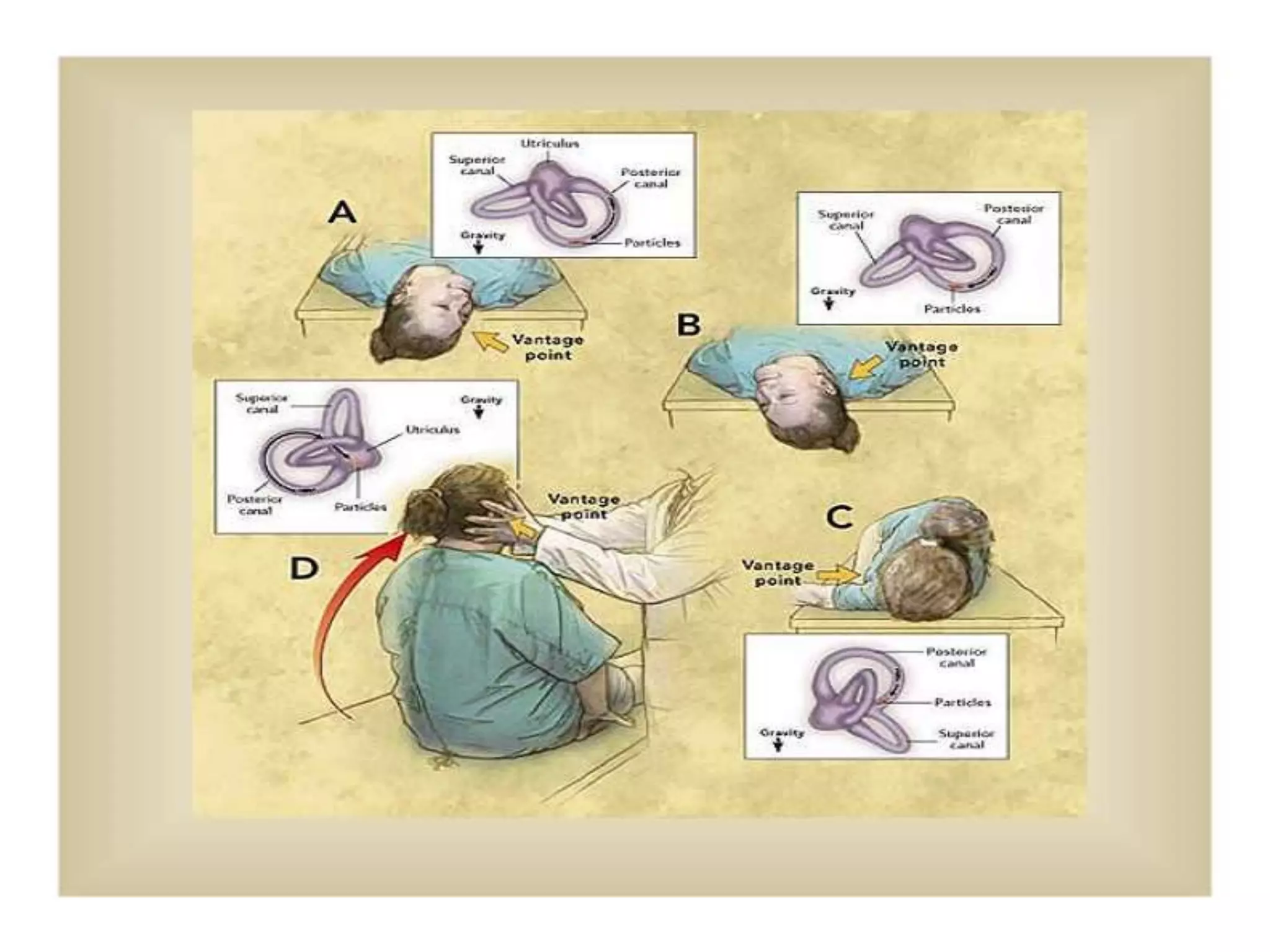


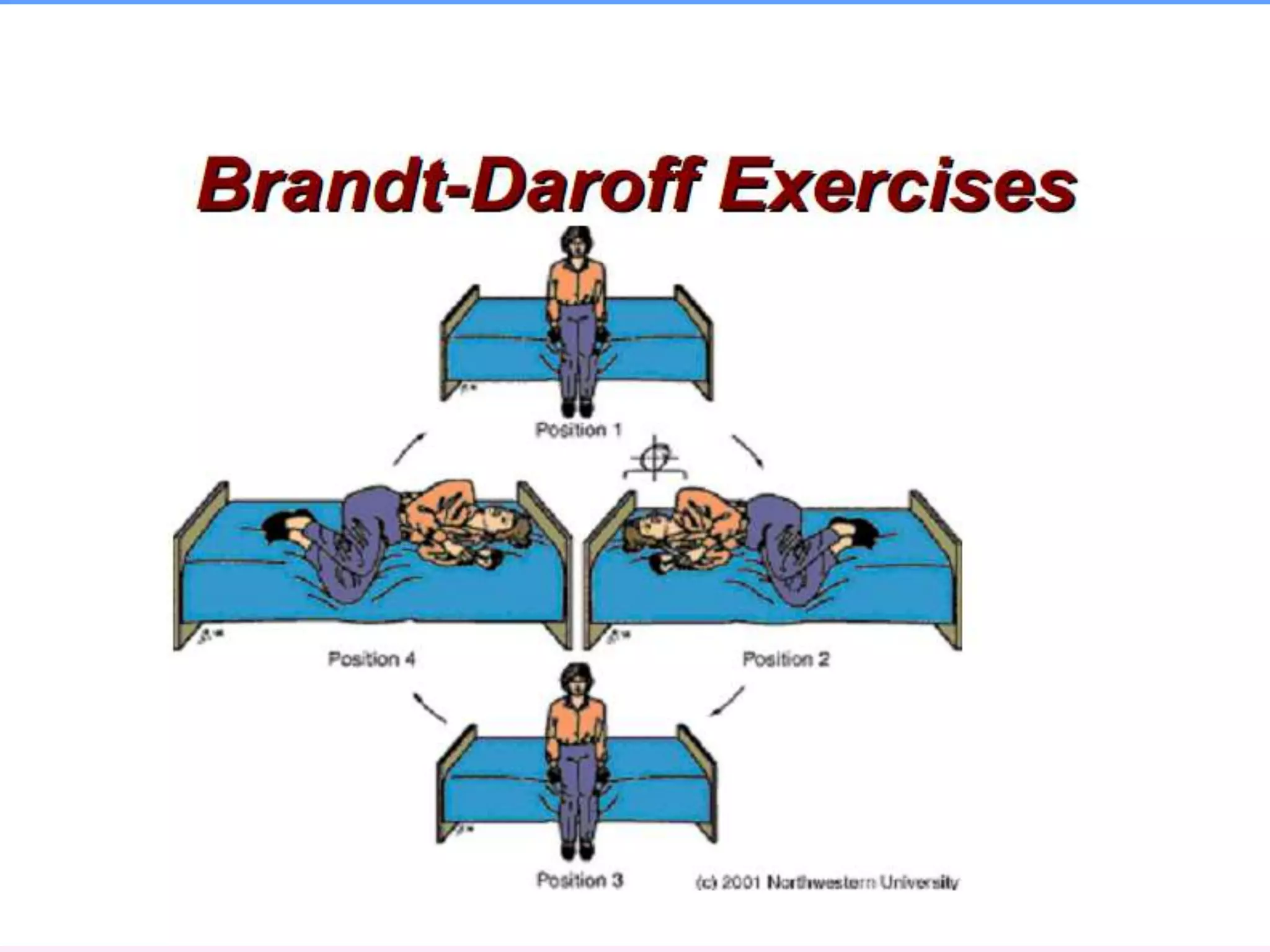


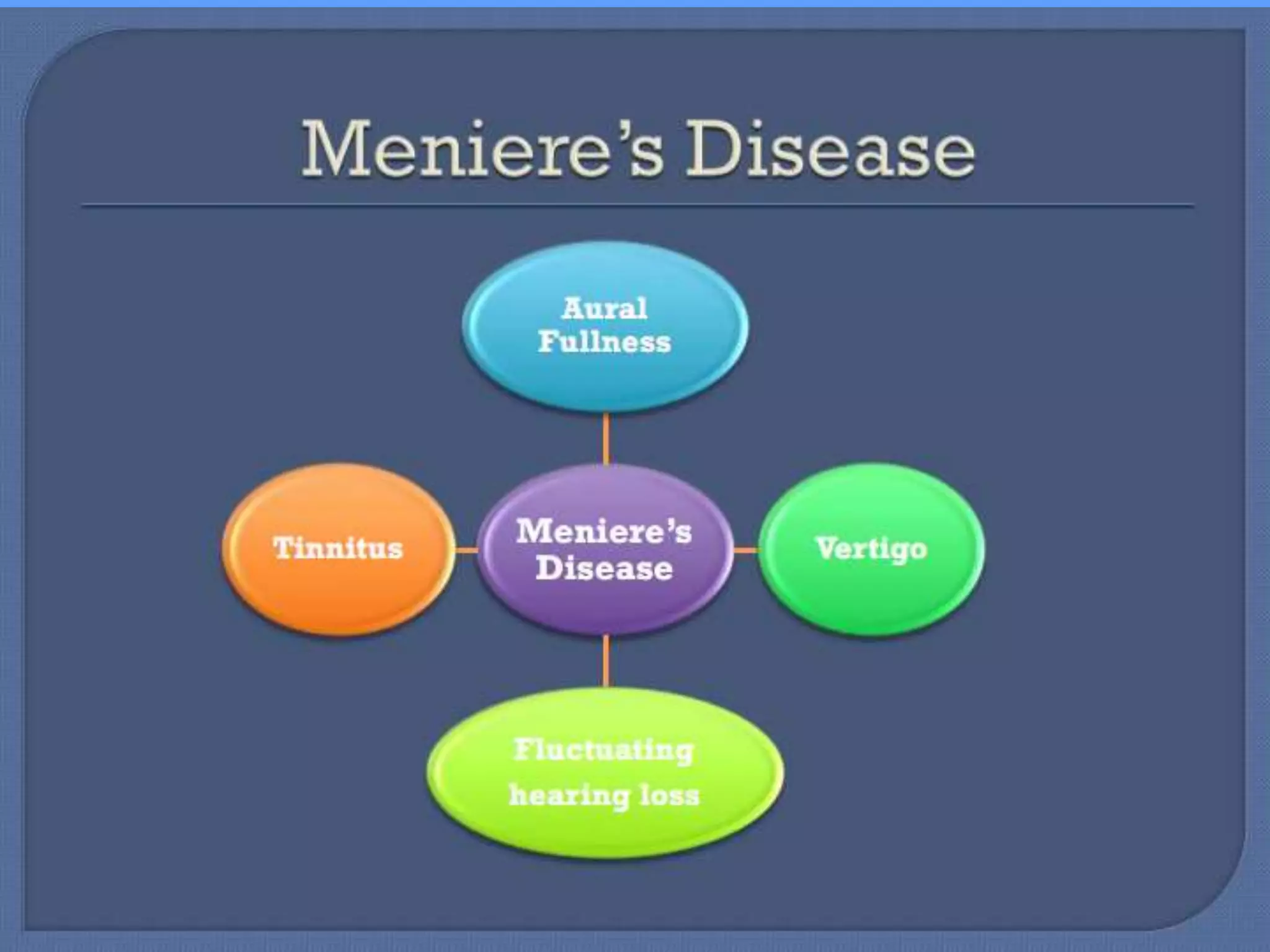











This document discusses vertigo, providing information on: 1) Differential diagnoses for vertigo including peripheral vestibular dysfunction, central brainstem lesions, presyncope, psychiatric disorders, and unknown causes. 2) Peripheral vs central causes of vertigo based on factors like onset, severity, positional nature, intermittency, and presence of nystagmus, otologic, or neurologic findings. 3) Common peripheral causes of vertigo including BPPV (canalithiasis), vestibular neuronitis, Meniere's disease, and trauma. Common central causes include vascular issues and demyelinating diseases.









































