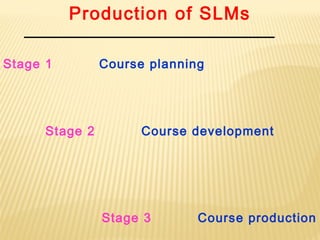
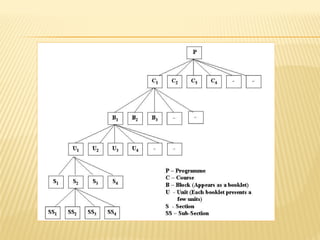
Self-learning materials (SLMs) are designed for independent learning and are divided into sections, sub-sections and interactive instructional steps. SLMs aim to stimulate self-learning by dividing content into small, logical steps and including in-text questions and activities. The production of SLMs follows three stages - planning, development and production. Effective SLMs have clear objectives, are self-explanatory, self-contained and promote self-evaluation.