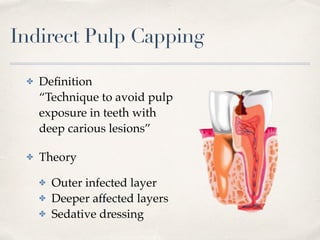
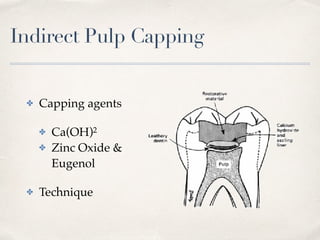
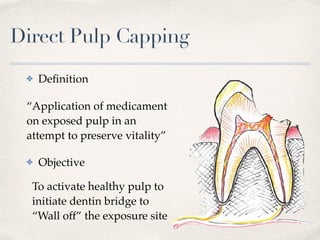
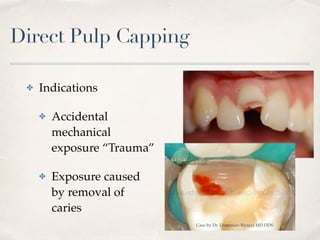
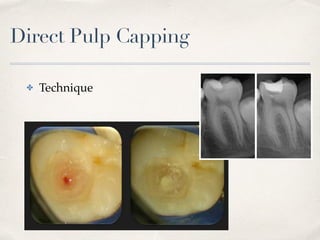
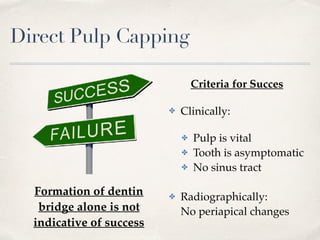
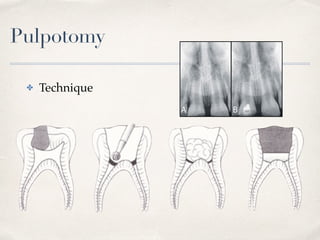
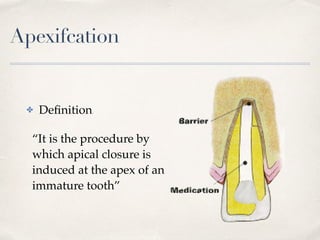
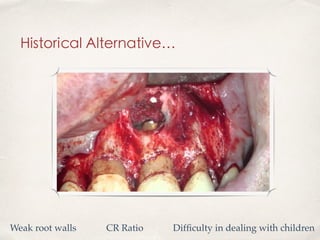
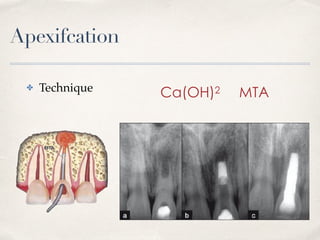
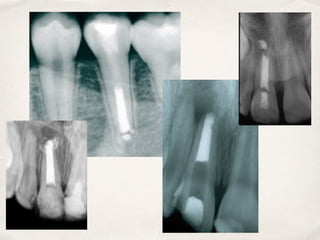
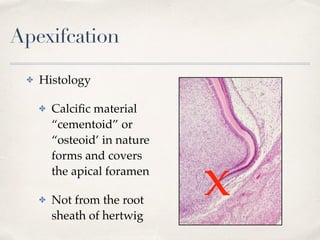
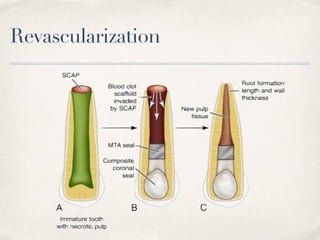
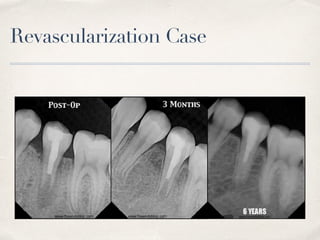
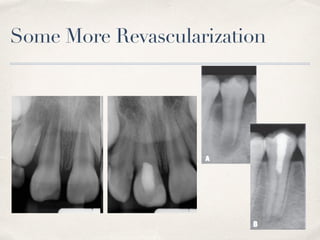
This document discusses different types of vital pulp therapy including indirect pulp capping, direct pulp capping, pulpotomy, apexogenesis, apexification, and revascularization. It provides definitions, indications, contraindications, techniques, and criteria for success or failure for each procedure. The document also includes examples of cases and references an endodontist, Dr. Ashraf Refai, who specializes in these types of vital pulp therapies.