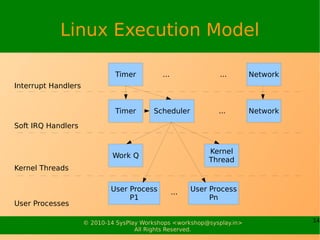
The document discusses interrupts in Linux systems. It defines interrupts as interventions that allow devices to get the CPU's attention when there is a mismatch between device and CPU speeds. It describes how interrupts work through interrupt lines, an interrupt controller, and registered interrupt handlers. It covers interrupt request numbers, programming interfaces for requesting and freeing interrupts, the responsibilities of interrupt handlers, and additional features like message signaled interrupts and soft interrupts, which are used to break up interrupt handling work.