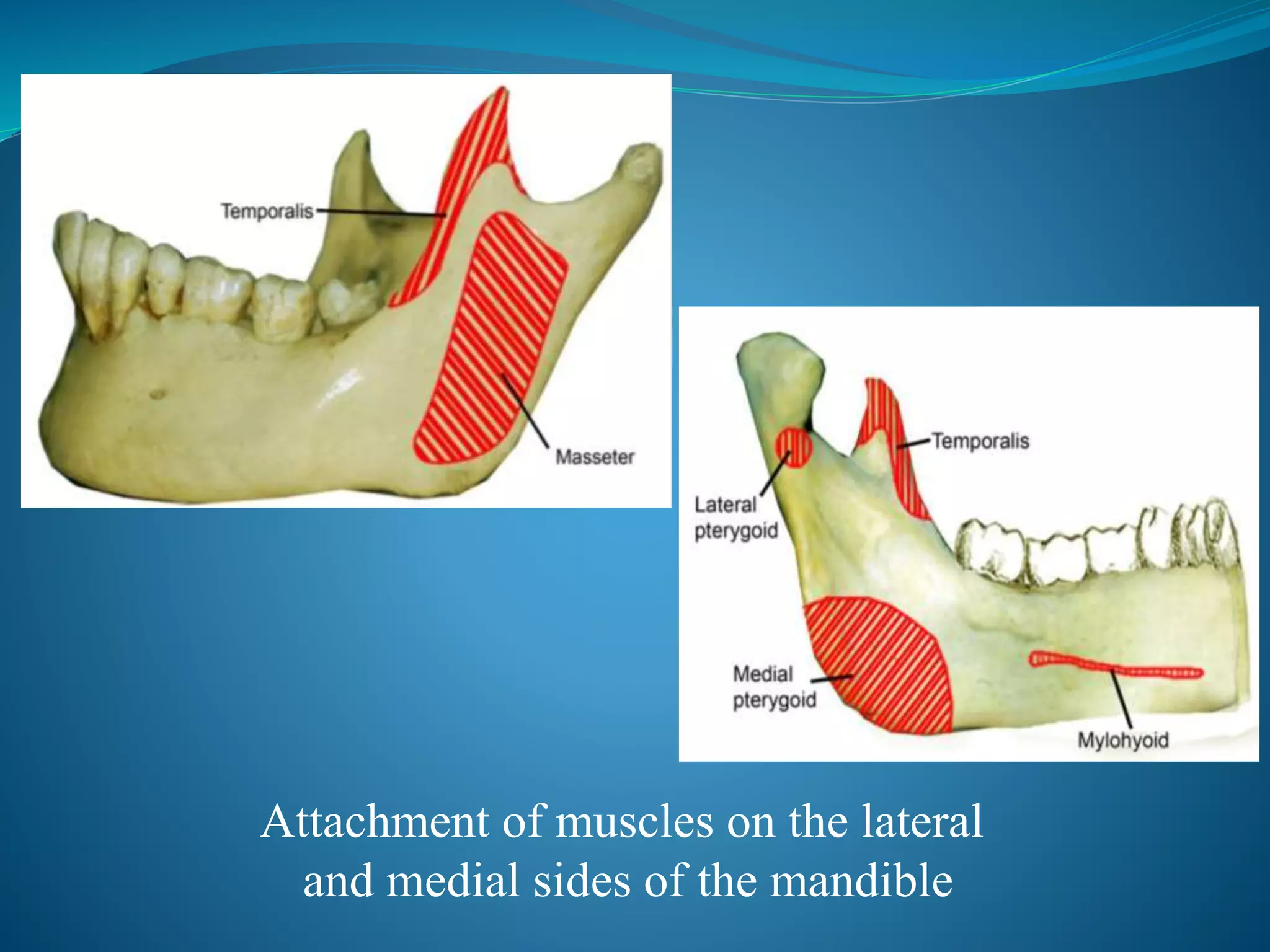
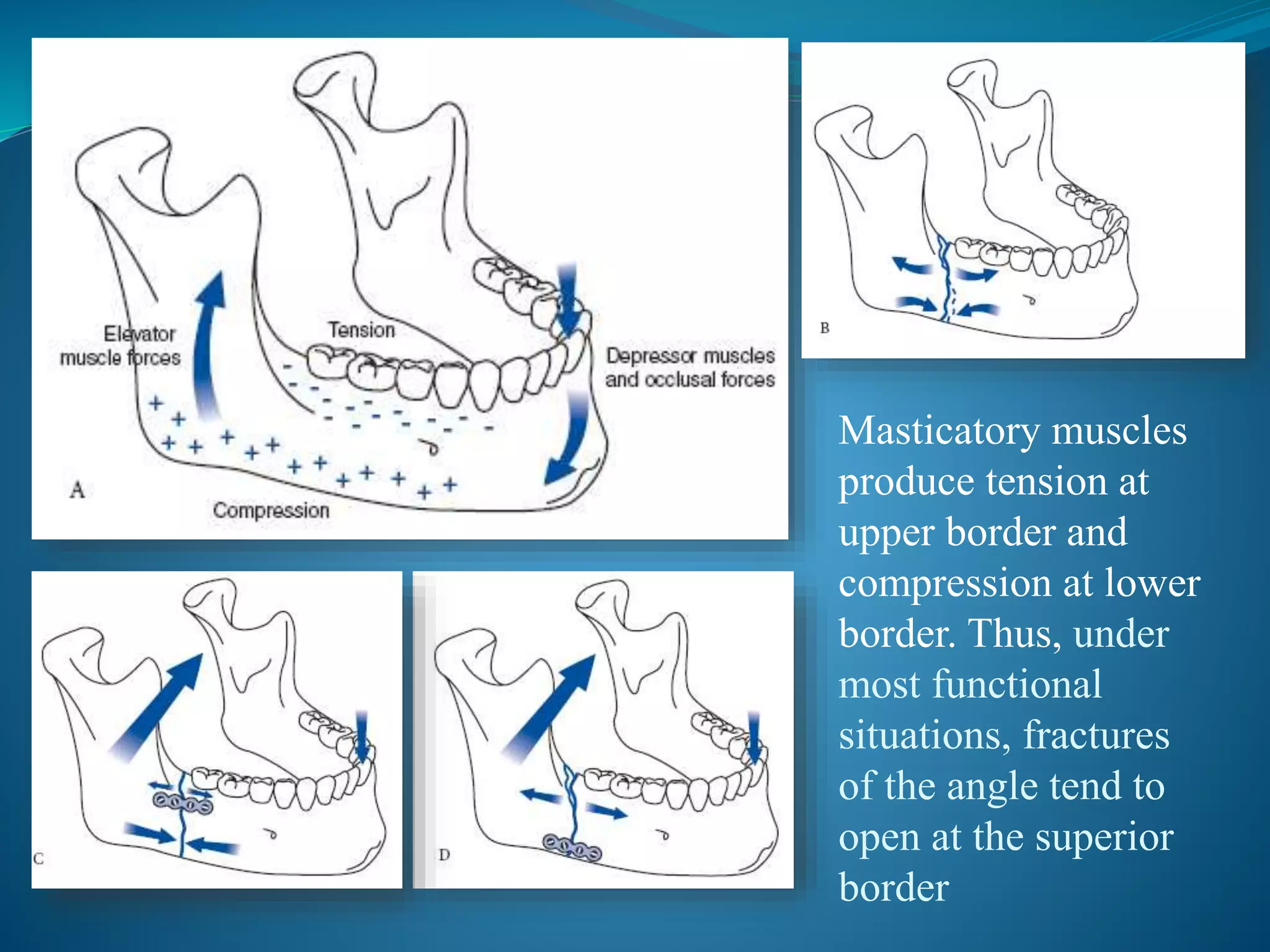
Mandibular angle fractures account for 23-42% of facial fractures and are commonly caused by motor vehicle accidents and assaults. The angle is prone to fractures due to its thin cross-section and presence of impacted third molars. Fractures are classified as vertically or horizontally favorable/unfavorable based on the direction of the fracture line and effect of muscle forces. Traditionally, rigid plate fixation and intermaxillary fixation were used but caused complications. Currently, semi-rigid fixation using a single miniplate placed along the superior border based on Champy's lines of osteosynthesis is the standard approach, allowing early function with low complications.