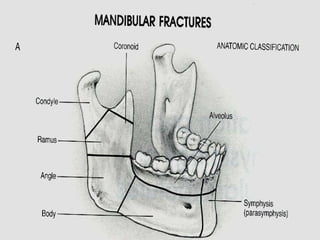
Mandible fractures are common facial injuries that can be treated with either closed or open reduction methods depending on the severity and location of the fracture. Closed reduction using maxillomandibular fixation is preferred for non-displaced or favorable fractures in children and adults. Open reduction with rigid internal fixation using plates, screws, or external fixation is used for displaced, unfavorable, or comminuted fractures. Condylar fractures may be treated with closed reduction for children but often require open reduction in adults due to higher risk of complications from malunion. Immediate postoperative mobilization after open reduction has been shown to have similar outcomes to traditional maxillomandibular fixation.