Poultry liver (big organ with big role)
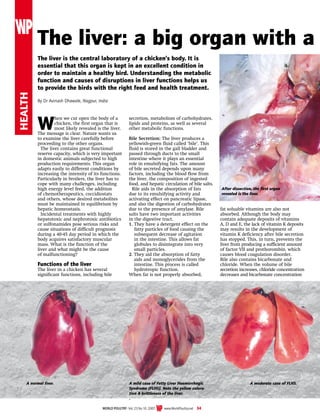
- 1. health WORLD POULTRY - Vol. 23 No 10. 2007 www.WorldPoultry.net 34 The liver: a big organ with a The liver is the central laboratory of a chicken’s body. It is essential that this organ is kept in an excellent condition in order to maintain a healthy bird. Understanding the metabolic function and causes of disruptions in liver functions helps us to provide the birds with the right feed and health treatment. By Dr Avinash Dhawale, Nagpur, India W hen we cut open the body of a chicken, the first organ that is most likely revealed is the liver. The message is clear. Nature wants us to examine the liver carefully before proceeding to the other organs. The liver contains great functional reserve capacity, which is very important in domestic animals subjected to high production requirements. This organ adapts easily to different conditions by increasing the intensity of its functions. Particularly in broilers, the liver has to cope with many challenges, including high energy level feed, the addition of chemotherapeutics, coccidiostats and others, whose desired metabolites must be maintained in equilibrium by hepatic homeostasis. Incidental treatments with highly hepatotoxic and nephrotoxic antibiotics or sulfonamides pose serious risks and cause situations of difficult prognosis during a 40-45 day period in which the body acquires satisfactory muscular mass. What is the function of the liver and what might be the cause of malfunctioning? Functions of the liver The liver in a chicken has several significant functions, including bile secretion, metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids and proteins, as well as several other metabolic functions. Bile Secretion: The liver produces a yellowish-green fluid called ‘bile’. This fluid is stored in the gall bladder and passed through ducts to the small intestine where it plays an essential role in emulsifying fats. The amount of bile secreted depends upon many factors, including the blood flow from the liver, the composition of ingested food, and hepatic circulation of bile salts. Bile aids in the absorption of fats due to its emulsifying activity and activating effect on pancreatic lipase, and also the digestion of carbohydrates due to the presence of amylase. Bile salts have two important activities in the digestive tract. 1. They have a detergent effect on the fatty particles of food causing the subsequent decrease of agitation in the intestine. This allows fat globules to disintegrate into very small particles. 2. They aid the absorption of fatty aids and monoglycerides from the intestine. This process is called hydrotropic function. When fat is not properly absorbed, fat soluable vitamins are also not absorbed. Although the body may contain adequate deposits of vitamins A, D and E, the lack of vitamin K deposits may results in the development of vitamin K deficiency after bile secretion has stopped. This, in turn, prevents the liver from producing a sufficient amount of factor VII and prothorombin, which causes blood coagulation disorder. Bile also contains bicarbonate and chloride. When the volume of bile secretion increases, chloride concentration decreases and bicarbonate concentration After dissection, the first organ revealed is the liver. A normal liver. A mild case of Fatty Liver Haemorrhagic Syndrome (FLHS). Note the yellow colora- tion brittleness of the liver. . A moderate case of FLHS.
- 2. WORLD POULTRY - Vol. 23 No 10. 2007 www.WorldPoultry.net 35 big role increases, thereby producing a higher pH. The bile, on entering the duodenum, then helps neutralise the acid chyme of the stomach. Metabolism of carbohydrates: The main function of all ingested carbohy- drates is to provide energy immediately required by the host. The mono- saccharides coming from the intestine to the liver (fructose and galactose) are transformed into glucose, which can undergo three processes. a. It can be stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles. b. It can be oxidised in the tissues to become CO2 and H2 O. c. It can be converted into fat and stored in fatty deposits. The liver is the most important organ for the regulation of glycemia. It makes glucose from carbohydrate or non-carbohydrate elements and the occurring glyconeogenesis transforms the glucose, fructose and galactose absorbed in the intestine into glycogen, which is then stored. When glycemia levels decrease, the liver turns glycogen into glucose and also makes glucose out of non-carbohydrate sources, particularly certain amino acids. When glycemia levels increase, the liver transforms glucose into glycogen and a small amount of fatty acids. This regulation process is called hepatic homeostasis. Metabolism of lipids: The liver is, more than any other organ, actively involved in the metabolism of lipids. Its main functions include: a. Synthesis of fatty acids from carbohydrates and certain amino acids, and cholesterol from acetyl coenzyme A, plasma lipoproteins and ketone bodies. b. Degradation of fatty acids derived from deposited and dietary tri- glycerides in order to meet energy requirements. c. Removal of phospholipids and free and esterised cholesterol from the blood. d. Lengthening and shortening the chain of fatty acids. e. Saturation and unsaturation of fatty acids. f. Controlling the storage of hepatic and deposited fats. Metabolism of proteins: The dietary proteins are digested through the action of hydrolytic enzymes (protease), which break down the peptide bonds and release amino acids. These are absorbed by the intestinal cells and passed into the portal vein. They then enter the liver and are transported via systemic circulation to other tissues and organs. The liver helps the protein metabolism by deamination of amino acids and the formation of urea for ammonia suppression in bodily fluids. Other functions of the liver: The liver also has several other metabolic functions. a. Storage of iron: most of the iron in the liver is stored as ferritin. b. Storage of vitamins: the liver is an excellent source of vitamins. Vitamin A is stored in higher amounts than others; it can also store great amounts of vitamins D B12 . c. Blood coagulation: the liver produces many substances used in blood coagulation, including fibrinogen, prothombin, accelerated globulin, factors VII etc. Furthermore, the liver also stores vitamin B12 , an anti-anaemic factor necessary for maturation of erythrocytes. d. Conjugation and excretion of steroid hormones: practically all steroid hormones are at least partially conjugated in the liver and eliminated in the bile. When the liver is impaired, a great amount of these hormones often accumulate in the bodily fluid, producing symptoms of hormonal imbalances. e. Detoxification: the liver transforms poisonous substances produced by the body into harmless metabolites An extreme case of FLHS. A complete liver tonic The liver performs many complex functions to maintain homeostasis (harmony among all the systems of body). When the liver is affected due to any reason, efficiency of the liver comes down in detoxification and metabolic processes. This, in turn, affects the overall performance of the bird, whether it be a broiler, breeder or layer. The combination of lipotropic agents, liver stimulants, antioxidants, mould inhibitors and toxin binders can work as a complete liver tonic. Ingredient Function Liver stimulants Potentiating the liver function Tricholine citrate Mobilising fat from liver Inositol Mobilising fat from liver Vit B12 DNA synthesis and rejuvenation of the liver Biotin Better utilisation of fats Protein hydrolysate Ready source of amino acids for hepatic regeneration Methyl donors Facilitate detoxification and liver cell rejuvenation Vit E and selenium Natural defence against free radicals causing cell damage, including that of the liver Mould inhibitors and toxin binders Minimises mycotoxin formation, adsorption, and protects (organic acids, HSCAS and MOS) vital organs
- 3. health WORLD POULTRY - Vol. 23 No 10. 2007 www.WorldPoultry.net 36 by way of oxidation and conjugation. These metabolites are later easily excreted via the kidneys. f. Maintenance of hormonal balance. g. Helps the body resist infection. h. Removal of ammonia from the blood. Liver diseases The liver is one of the most important organs for maintaining the internal environment of the body. However, important damage can occur before clinical signs become apparent. The clinical silence of the hepatic lesions is due its significant reserve of functional capacity, its complex and multiple function capacity, and its extraordinary capacity for regeneration. In the literature we recognise several syndromes, of which not all have been well documented in birds. One of them is hepatoencephalopathy. This is not a disease in itself, but a medical condition characterised by neurologic symptoms caused by intoxication of the brain by products of protein digestion, namely ammonia. A tentative diagnosis of hepatoencephalopathy is often made when neurologic signs are seen in birds with liver disease. Hemochromatosis is another liver syndrome of which we know little about. It is a disease of excessive storage of hemosiderin (hemosiderosis) in various body tissues. Hemosiderin is an iron-containing pigment derived from hemoglobin. The principle site of iron accumulation is the liver. The aetiology at present is unknown, but a high dietary iron has been suggested. Fatty Liver Syndrome Fatty Liver Haemorrhagic Syndrome (FLHS) occurs primarily in birds kept in cages, but has also been recognised as a less significant problem in birds kept on litter. It is associated with birds fed high energy diets and is most often seen during the summer months. The first sign of the syndrome is an increase in mortality of the flock with birds in full production being found dead with pale heads. Mortality usually does not reach 50%, but there is often a sudden drop in production. Hens may be overweight with large pale combs and wattles. Dead birds have large blood clots in the abdomen arising from the liver. The liver is generally enlarged, pale and friable. Large amounts of fat are present in the abdominal cavity and around the viscera. Most of the birds have active ovaries and often have an egg in the oviduct. The suffering birds have an increased concentration of AST, LDH, GLDH, estadiol, calcium and phos- phorus in the plasma compared to the unaffected birds. The cause and origin of the disease is associated with high laying intensity, excess energy, high energy/protein ratio, energy source (sub-clinical FLHS is more present in corn-based diets than in wheat-based diets), low level of dietary calcium, protein source (FLHS incidence is more present in soya-based diets than in fish-based diets), deficiency of lipotropic compounds (choline, methionine etc. and vitamins, such as vitamin C and E and minerals like zinc, copper, iron and manganese), stress (this induces liberation of corticosteroides which enhances lipogenesis and leads to FLHS), temperature (high temperature leads to increased hepatic fatty acid synthesis) and mycotoxins. Treatment The incidence of FLHS can be reduced by restricting energy intake either by feed restriction or by lowering the metabolisable energy content of the diet. The carbohydrate content of feed is decreased by increasing the amount of fat, which is rich in linoleic acid. Extra lipotropes like lecithin, choline, inositol, betaine and methionine also contribute to a healthy liver as do vitamins like B1 and biotin, which play an essential role in the metabolism of carbohydrates. Vitamin E in combina- tion with selenium has a positive effect on the synthesis and transport of fats. Impact of fatty liver on antibiotics In a study, the concentrations of five antibiotics were determined in chicken serum before and after they were induced into fatty liver. The measured peak concentrations were higher for lincomycin (LMC) and erythromycin (ERM) and lower for penicillin (PCL) and oxytetracyclin (OTC), while strepto- mycin (SMC) remained unchanged. The peak concentration of streptomycin appeared earlier and the peak of OTC later than in the normal chickens. The eliminated half lives were shorter for ERM, LMC and SMC and increased for PCL and OTC. It is clear from this study that the efficacy of some antibiotics is altered in FLHS. Bile acids as an indicator of Hepatobiliary disease Plasma bile acids (BA) and there salts are formed in the liver from cholesterol and are excreted in the intestine where they assist in the digestion of fats. Via the enterohepatic circulation, over 90% bile is reabsorbed in the jejunum and ileum. Plasma BA concentrations including their salts and corresponding glycine and taurine conjugates (BA) are a reflection of the clearing capacity for bile acids of the liver. All liver functions (such as extraction, conjugation and excretion) are involved in this process, and the BA provides information on the combined effects of these functions. It is now known that BA is a sensitive constituent for evaluating liver function and is widely used in man and domestic animals, including birds. In experimental liver disease, a 5-10 fold increase of BA over the upper limit of the reference range is common. Liver enzymes Liver enzymes are proteins that help to speed up a chemical reaction in the liver. Under normal circumstances, these enzymes reside within the cells of the liver. But when the liver is injured, these enzymes are spilled into the blood. The enzymes produced in the liver are: aspertate ammino transeferage (AST), alanine amino transeferage (ALT), lactic dehydrogenage (LDH), glutamate dehydrogenage (GLDH) and alkaline phosphatage. Of these five, the first three are produced in the cytoplasm while the fourth and fifth are produced in the mitochondrion and the membrane respectively. Generally, increased enzyme concen- trations are a measure of recent organ damage rather than decreased organ function. Cytoplasmic enzymes will be released early in the cell degeneration, while mitochondreal enzymes are released after advanced cell damage. Increased plasma GLDH activities are associated with large necrotic areas in the liver. Summary The liver performs a number of metabolic functions in the body. Since this organ receives almost all the substance absorbed from the small intestine, it always needs to be maintained in the state of ‘rocket engine’. Avoidance of excess fats and mycotoxicosis shall always receive top priority because the resultant impaired fat metabolism could lead to serious economic losses. Certain nutritional alterations with the use of HSCAS and MOS help protect the liver - undoubtedly the central laboratory of a chicken’s body. ■ Hepato-protective herbs 1) Capparis spinosa 2) Chicorium intybus 3) Solanum nigrum 4) Terminalia arjuna 5) Cssia occidentalis 6) Achillea millofolium 7) Tamarix gallica 8) Cynarascolymus 8) Escholtzia californica 9) Matricaria chamomilla 10) Taraxacum 11) Glycyrrhiza glabra 12) Grfloa frpndosa 13) Mentha piperata 14) Rosemarinus officinalis 15) Glycine soja
