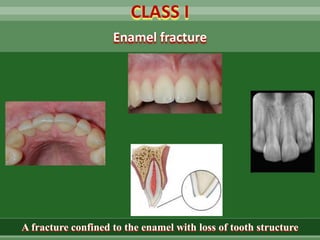
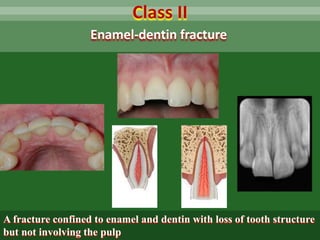
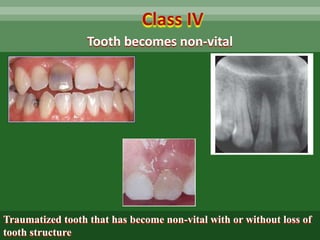
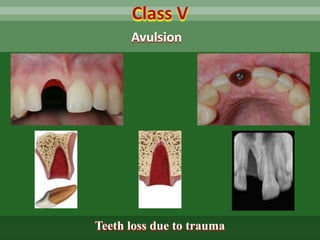
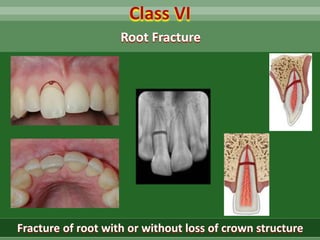
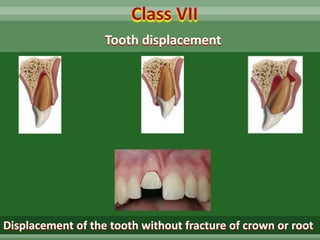
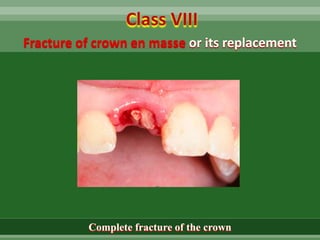
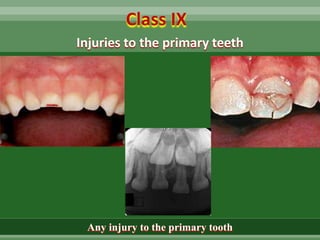
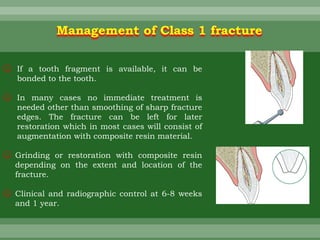
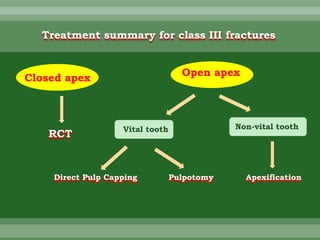
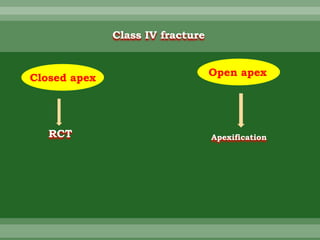
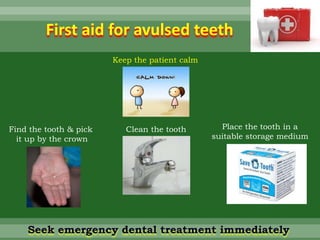
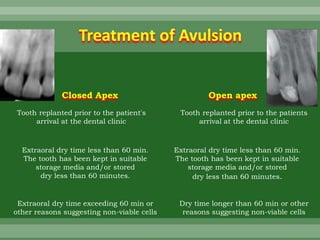
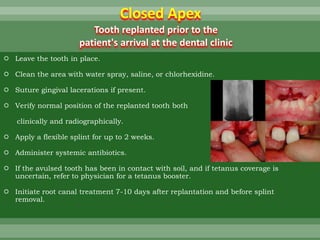
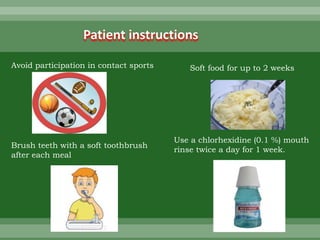
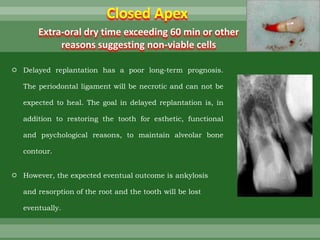
This document discusses dental trauma, including definitions, epidemiology, etiology, classification, and management of various types of dental fractures and avulsions. It notes that dental trauma is common in childhood and adolescence. The most accident-prone ages are 2-4 years for primary dentition and 7-10 years for permanent dentition. It describes the Ellis classification system for dental fractures and outlines treatment approaches for each class, including restorative procedures, endodontic treatment, splinting, and follow-up. Proper emergency management and storage of avulsed teeth is also summarized.