Thermocouple temperature measurement principle and common faults
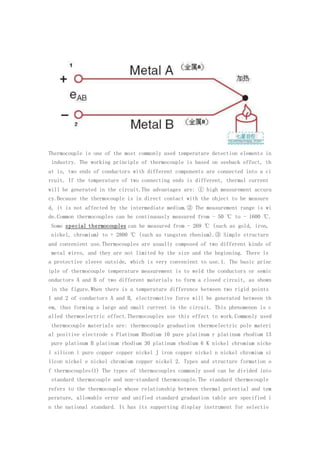
- 1. Thermocouple is one of the most commonly used temperature detection elements in industry. The working principle of thermocouple is based on seeback effect, th at is, two ends of conductors with different components are connected into a ci rcuit. If the temperature of two connecting ends is different, thermal current will be generated in the circuit.The advantages are: ① high measurement accura cy.Because the thermocouple is in direct contact with the object to be measure d, it is not affected by the intermediate medium.② The measurement range is wi de.Common thermocouples can be continuously measured from - 50 ℃ to - 1600 ℃. Some special thermocouples can be measured from - 269 ℃ (such as gold, iron, nickel, chromium) to + 2800 ℃ (such as tungsten rhenium).③ Simple structure and convenient use.Thermocouples are usually composed of two different kinds of metal wires, and they are not limited by the size and the beginning. There is a protective sleeve outside, which is very convenient to use.1. The basic princ iple of thermocouple temperature measurement is to weld the conductors or semic onductors A and B of two different materials to form a closed circuit, as shown in the figure.When there is a temperature difference between two rigid points 1 and 2 of conductors A and B, electromotive force will be generated between th em, thus forming a large and small current in the circuit. This phenomenon is c alled thermoelectric effect.Thermocouples use this effect to work.Commonly used thermocouple materials are: thermocouple graduation thermoelectric pole materi al positive electrode s Platinum Rhodium 10 pure platinum r platinum rhodium 13 pure platinum B platinum rhodium 30 platinum rhodium 6 K nickel chromium nicke l silicon t pure copper copper nickel J iron copper nickel n nickel chromium si licon nickel e nickel chromium copper nickel 2. Types and structure formation o f thermocouples(1) The types of thermocouples commonly used can be divided into standard thermocouple and non-standard thermocouple.The standard thermocouple refers to the thermocouple whose relationship between thermal potential and tem perature, allowable error and unified standard graduation table are specified i n the national standard. It has its supporting display instrument for selectio
- 2. n.The non-standard thermocouple is not as good as the standard thermocouple in the scope of use or order of magnitude, and generally there is no unified scal e, which is mainly used in some special occasions.Since January 1, 1988, all th ermocouples and thermal resistances in China have been produced in accordance w ith IEC international standards, and seven kinds of standardized thermocouples (s, B, e, K, R, J, t) have been designated as unified design thermocouples in C hina.(2) In order to ensure the reliable and stable operation of the thermocoup le, the structural requirements of the thermocouple are as follows: ① the weld ing of the two thermoelectric poles that make up the thermocouple must be firm; ② the two thermoelectric poles should be well insulated from each other to pr event short circuit; ③ the connection between the compensation wire and the fr ee end of the thermocouple should be convenient and reliable;④ The protective sleeve shall be able to ensure that the thermoelectric pole is fully isolated f rom the harmful medium.3. The temperature compensation of the cold end of the t hermocouple is generally expensive (especially when the precious metal is use d), and the distance from the temperature measuring point to the instrument is far. In order to save the thermocouple material and reduce the cost, the compen sation wire is usually used to extend the cold end (free end) of the thermocoup le to the control room with relatively stable temperature and connect it to the instrument terminal.It must be pointed out that the function of thermocouple c ompensation wire is only to extend the thermoelectric pole and move the cold en d of thermocouple to the instrument terminal in the control room. It can not el iminate the influence of the cold end temperature change on the temperature mea surement, and it does not play a compensation role.Therefore, it is necessary t o use other correction methods to compensate for the influence of cold end temp erature t0 ≠ 0 ℃.When using thermocouple compensation wire, the model must be matched, the polarity cannot be connected wrongly, and the temperature between compensation wire and thermocouple connection end cannot exceed 100 ℃. Cold junction compensation principle of thermocouple http://www.tiankangcable.com When measuring the temperature of a thermocouple, the temperature of its cold end (the measuring end is the hot end, and the end connected with the measuring circuit through the lead wire is called the cold end) is required to remain unchanged, and its thermal potential is proportional to the measured temperature.If the temperature of cold end (environment) changes during measurement, it will affect the accuracy of measurement seriously.It is called the cold junction compensation of thermocouple to take some measures to compensate the influence caused by the change of cold junction temperature.The cold junction compensation of thermocouples usually uses a thermal resistance bridge connected in series at the cold junction.The three arms of the bridge are standard resistors, and the other arm is made of (copper) thermistor.When the cold end temperature changes (for example, increases), the thermoelectric potential generated by the thermocouple will also change (decrease), and the thermoelectric resistance
- 3. value in the series bridge will also change and the voltage at both ends of the bridge will also change (increase).If the parameters are selected well and the wiring is correct, the voltage generated by the bridge is exactly equal to the amount of thermoelectric potential changing with the change of temperature, and the total output voltage (potential) of the whole thermocouple measuring circuit exactly reflects the measured temperature value.This is the cold junction compensation principle of thermocouple. Thermocouple thermometer is the most widely used thermometer at present. Thermocouple thermometer is a kind of temperature electrical measuring instrument. It usually consists of three parts: thermocouple, thermocouple cold end temperature compensation device (or element) and display instrument. The three parts are connected by wires. Principle of thermocouple temperature measurement Thermocouples are formed by welding one end of two different conductors or semiconductor linear materials a and B. A and B are called thermoelectric poles (or thermocouple wires).The welded end is placed at the temperature T to be measured, which is called the hot end (or measuring end, working end) of the thermocouple; the non welded end is called the cold end (or reference end, free end), and the cold end is placed in the environment with the temperature t0 outside the tested object. If the two cold ends of the thermocouple are also connected to form a closed circuit, as shown in Figure 2-1, when the temperature of the hot end and the temperature of the cold end are not equal, i.e. t ≠ to, there is current flowing through the circuit, which means that the electromotive force is generated in the circuit. The electromotive force generated due to the temperature difference between the two contacts of the thermocouple is called thermoelectric (dynamic) force, and the above-mentioned theory is called thermoelectric effect, orCalled the Seebeck effect.Thermocouple is to use thermoelectric effect to measure temperature.Further study shows that thermoelectric potential is composed of contact potential and thermoelectric.
- 4. 1.Contact potential When two kinds of homogeneous conductors A and B contact, due to the different density of free electrons in a and B (set free electron density Na > NB), conductor a will diffuse free electrons to conductor B through the contact, then a loses electrons, and B accumulates electrons, so that potential difference is generated on both sides of the contact, and the electrostatic field E is established, as shown in Figure 2-2, the left side of electrostatic field E will prevent free electrons from continuing to diffuse.When the interaction of diffusion force and electric field force is balanced.The diffusion of electrons stops relatively, and the potential is finally generated between two sides of the contact. This potential is called contact potential, which is represented by the symbol EAB (T), where t is the temperature of the contact. The contact potential is related to the temperature of the contact surface and the properties of the two conductors. The direction is shown in Figure 2- 2, from the electrode with small electronic density to the electrode with large electronic density http://www.tksiliconerubbercable.com. 2.Thermoelectric potential Because the free electron density of conductor will increase with the increase of temperature, when the temperature of both ends of the same conductor is different (as shown in Figure 2-
- 5. 3), the free electron density of the end with high temperature will be higher than that of the end with low temperature, so there will be a similar spontaneous electron diffusion process in contact potential between the two ends, and finally a potential difference will be generated between the two ends of conductor to establish the potentialThe potential is called thermoelectric potential, which is expressed by the symbol EA (T, to). Its size is related to the temperature T, to and conductor properties at both ends of the conductor, as shown in Figure 2-3, from the low temperature end to the high temperature end.For the convenience of analysis, the thermoelectric potential is sometimes written in the form of EA (T, to) = EA (T) - EA (to). 3.Thermal potential To sum up, in the thermocouple circuit shown in Figure 2-1, when t > T0, Na > Nb, two contact potentials (T) and EAB (to), two temperature difference potentials (T, to) and EB (T, to) will be generated in the circuit.The direction of each potential is shown in the figure. At this time, the total potential of the loop, i.e. the thermal potential EAB (T, to), is the algebraic sum of these contact potentials and the thermoelectric potential, i.e EAB(t,to)= eAB(t) - eA(,to) - eAB(to) + eB(t,to) = eAB(t)-[eA(t) - eA(to)] - eAB(to) + [eB(t) - eB(to)] = [eAB(t) - eA(t) + eB(t)] - [eAB(tO) - eA(to) + eB(to)] = fAB(t) – fAB(to) Because the thermoelectric potential is smaller than the contact potential and T > to, the contact potential EAB (T, to) accounts for the largest percentage in the total potential EAB (T, to). Therefore, the direction of the total potential EAB (T, to) depends on the direction of EAB (T).Because of the high electron density of a, a is the positive electrode and B is the negative electrode. In the positive hot electrode, the direction of the potential is from the hot end to the cold end. The above formula shows that when the materials of the two thermoelectric poles are selected, the thermoelectric potential is the difference between the two functions related to the contact
- 6. temperature respectively.If the cold end temperature to remains the same, then FAB (to) = C (constant), then EAB (T, to) = FAB (T) - C, the thermoelectric potential and the hot end temperature t have a one-to-one correspondence.Therefore, when the thermoelectric potential EAB (T, to) is measured, the value of the measured temperature T can be determined, which is the principle of thermocouple temperature measurement. For the convenience of use, the corresponding relationship between the hot end temperature and the thermoelectric potential of the standardized thermocouple can be found in the function table.This kind of function table is made by experiment under the condition of cold end temperature of 0 ℃, which is called thermocouple graduation table.The thermocouple scale can be used to express the thermoelectric characteristics of thermocouples.See table 1-5 for the graduation table of several common thermocouples.It should be noted that when to is not equal to 0 ℃, the index table cannot be used to directly check the value of EAB (T, to) or EAB (T, to) Attached table 1: graduation table of Pt Rh 10 Pt thermocouple (graduation s; reference end temperature 0 ℃; MV) Attached table 2: platinum rhodium 13 platinum thermocouple graduation table (graduation R; reference end temperature 0 ℃; MV)
- 7. Attached table 3: Pt Rh 30-pt RH 6 thermocouple graduation table (graduation B; cold end temperature 0 ℃; MV) Attached table 4: graduation table of Ni Cr Ni Si thermocouple (graduation number is K; cold end temperature is 0 ℃; MV)
- 8. Attached table 5: graduation table of Ni Cr Cu Ni (Constantan) thermocouple (graduation No. E; cold end temperature 0 ℃; MV)
- 9. (S-type thermocouple) Platinum Rhodium 10 platinum thermocouple Platinum Rhodium 10 platinum thermocouple (S-type thermocouple) is a precious metal thermocouple.The diameter of the coupling wire is specified as 0.5mm, and the allowable deviation is - 0.015mm. The nominal chemical composition of the positive electrode (SP) is platinum rhodium alloy, including 10% rhodium, 90% platinum, and the negative electrode (SN) is pure platinum, so it is commonly known as single platinum rhodium thermocouple.The maximum operating temperature of the thermocouple is 1300 ℃ in the long term and 1600 ℃ in the short term.S-type thermocouples have the advantages of the highest accuracy, the best stability, wide temperature measurement range and long service life.It has good physical and chemical properties, thermoelectric stability and oxidation resistance at high temperature. It is suitable for oxidation and inert atmosphere.As S-type thermocouple has excellent comprehensive performance and conforms to the international temperature standard, it has been used as the interpolation instrument of international temperature standard for a long time. "ITS-90" stipulates that it will not be used as the internal inspection instrument of international temperature standard in the future, but the international temperature Advisory Committee (CCT) recognizes that S-type thermocouple can still be used to approximate the international temperature standard.The disadvantages of S-type thermocouples are thermal potential, small thermoelectric potential rate, low sensitive reading, low mechanical strength at high temperature, very sensitive to pollution, expensive precious metal materials, so a large one-time investment.(R type thermocouple) platinum rhodium 13 platinum thermocouple platinum rhodium 13 platinum thermocouple (R type thermocouple) is a precious metal thermocouple.The diameter of the coupling wire is 0.5mm and the allowable deviation is - 0.015mm. The nominal chemical composition of the positive electrode (RP) is platinum rhodium alloy, including 13% rhodium, 87% platinum, and the negative electrode (RN) is pure platinum. The maximum long-term service temperature is 1300 ℃ and the maximum short- term service temperature is 1600 ℃.The R-type thermocouple has the advantages of the highest accuracy, the best stability, the wide temperature range and the long service life.It has good physical and chemical properties, thermoelectric potential stability and oxidation resistance at high temperature. It is suitable for oxidation and inert atmosphere.As the comprehensive performance of R-type thermocouple is similar to that of S-type thermocouple, it is difficult to popularize in China. Except for the application of temperature measurement on imported equipment, it is rarely used in China.From 1967 to 1971, NPL in the UK, NBS in the US and NRC in Canada carried out a cooperative study. The results show that the stability and reproducibility of R-type thermocouple are better than that of S-type thermocouple. At present, no research has been carried out in China.The disadvantages of R-type thermocouple are thermal potential, small thermoelectric potential rate, low sensitive reading, low mechanical strength at high temperature, very sensitive to pollution, expensive precious metal materials, so a large one-time investment.(type B thermocouple) platinum rhodium 30 - platinum rhodium 6 thermocouple platinum rhodium 30 - platinum rhodium 6 thermocouple (type B thermocouple) is precious metal thermocouple.The diameter of the coupling wire is specified as 0.5mm, and the allowable deviation is - 0.015mm. The nominal chemical composition of its positive electrode (BP) is platinum rhodium alloy, including 30% rhodium, 70% platinum, and the negative electrode
- 10. (BN) is platinum rhodium alloy, containing 6% rhodium. Therefore, it is commonly known as double platinum rhodium thermocouple.The maximum operating temperature of the thermocouple is 1600 ℃ in the long term and 1800 ℃ in the short term.B-type thermocouple has the advantages of the highest accuracy, the best stability, wide temperature measurement range, long service life, high temperature upper limit, etc.It can be used in oxidizing and inert atmosphere, or in vacuum for a short time, but not in reducing atmosphere or atmosphere containing metal or non-metal vapor.An obvious advantage of B-type thermocouple is that it does not need compensation wire, because the thermal potential is less than 3 μ V in the range of 0 ~ 50 ℃.The disadvantages of B-type thermocouple are thermal potential, small thermoelectric potential rate, low sensitive reading, low mechanical strength at high temperature, very sensitive to pollution, expensive precious metal materials, so a large one-time investment.(K- type thermocouple) Ni Cr Ni Si thermocouple Ni Cr Ni Si thermocouple (K-type thermocouple) is the most widely used low-cost metal thermocouple at present, and its consumption is the sum of other thermocouples.The nominal chemical composition of the positive electrode (KP) is Ni: Cr = 90:10, the nominal chemical composition of the negative electrode (KN) is Ni: Si = 97:3, and the service temperature is - 200 ~ 1300 ℃.K-type thermocouple has the advantages of good linearity, large thermoelectric potential, high sensitivity, good stability and uniformity, strong oxidation resistance, low price, etc. it can be used in the oxidizing inert atmosphere.Widely used by users.K-type thermocouple can not be directly used in the atmosphere of sulfur, reducibility or reduction, oxidation alternation and vacuum at high temperature, nor is it recommended to be used in the atmosphere of weak oxidation.(n-type thermocouple) Ni Cr Si Ni Si thermocoupleNi Cr Si Ni Si thermocouples (n-type thermocouples) are low-cost metal thermocouples. They are the latest internationally standardized thermocouples. They were developed by the laboratory of the Australian Ministry of defense in the early 1970s. They overcome two important shortcomings of K-type thermocouples: the instability of thermoelectric potential caused by the short-range ordering of Ni Cr alloy lattice in the range of 300-500 ℃; the instability of thermoelectric potential caused by the short-range ordering of Ni Cr alloy lattice in the range of 800 ℃Thermoelectric potential instability caused by preferential oxidation of Ni Cr alloy.The nominal chemical composition of the positive electrode (NP) is Ni: Cr: Si = 84.4:14.2:1.4, the nominal chemical composition of the negative electrode (NN) is Ni: Si: Mg = 95.5:4.4:0.1, and the service temperature is - 200 ~ 1300 ℃.The n-type thermocouple has the advantages of good linearity, large thermoelectric potential, high sensitivity, good stability and uniformity, strong oxidation resistance, low price, not affected by short-range ordering, and its comprehensive performance is better than the K-type thermocouple,N-type thermocouple can not be directly used in the atmosphere of sulfur, reducibility or reduction, oxidation alternation and vacuum, nor in the atmosphere of weak oxidation.(E-type thermocouple) nichrome copper nickel thermocouple (E-type thermocouple), also known as nichrome constantan thermocouple, is also a kind of low-cost metal thermocouple. The positive electrode (EP) is: nichrome 10 alloy, the chemical composition is the same as KP, the negative electrode (EN) is copper nickel alloy, the nominal composition is: 55% copper, 45% nickel and a small amount of manganese, cobalt, iron and other elements.The temperature
- 11. of the thermocouple is - 200 ~ 900 ℃.The thermoelectric force and sensitivity of e-type thermocouple are the highest among all thermocouples. It is suitable to make thermopile to measure small temperature change.It is not sensitive to the corrosion of high humidity atmosphere, so it is suitable for the environment with high humidity.E thermocouple also has the advantages of good stability, better oxidation resistance than copper constantan, iron constantan thermocouple, low price, etc., which can be used in oxidizing and inert atmosphere and widely used by users.E-type thermocouple can not be directly used in sulfur at high temperature, reducing atmosphere, thermal potential uniformity is poor.(J-type thermocouple) Fe Cu Ni thermocouple (J-type thermocouple), also known as fe-constantan thermocouple, is also a cheap low-cost low-metal thermocouple.The nominal chemical composition of its positive electrode (JP) is pure iron, and its negative electrode (JN) is copper nickel alloy, which is often vaguely called constantan. Its nominal chemical composition is 55% copper and 45% nickel, as well as a small amount of very important elements such as manganese, cobalt and iron. Although it is called constantan, it is different from that of nickel chromium constantan and copper constantan, so it cannot be replaced by en and TN.The temperature range of iron constantan thermocouple is - 200 ~ 1200 ℃, but the commonly used temperature range is 0 ~ 750 ℃.J-type thermocouples can be used in vacuum, oxidation, reduction and inert atmosphere, but the positive iron oxidizes faster at high temperature, so the use temperature is limited, and it can not be directly used in sulfurization atmosphere at high temperature without protection.(T-type thermocouple) copper copper copper nickel thermocouple copper nickel thermocouple (T-type thermocouple) is also known as copper constantan thermocouple, which is also the best low-temperature low-cost metal thermocouple.Its positive electrode (TP) is pure copper, its negative electrode (TN) is copper nickel alloy, often constantan. It is common with constantan en of nichrome constantan, but not with constantan jn of iron constantan. Although they are all called constantan, the measuring temperature range of the cover of copper copper nickel thermocouple is - 200 ~ 350 ℃.T-type thermocouple has the advantages of good linearity, large thermoelectric potential, high sensitivity, good stability and uniformity, low price, etc., especially in the temperature range of - 200 ~ 0 ℃, better stability, annual stability can be less than ± 3 μ V, which can be used as the second-class standard for low-temperature value transfer after low-temperature verification.The oxidation resistance of positive copper of T-type thermocouple is poor at high temperature, so the upper limit of use temperature is limited. The basic knowledge of thermocouples - the causes of common faults of thermocouples and their solutions
- 12. 4、 Causes of common faults of thermocouples and Solutions See table 4-1 for common fault causes and treatment methods of thermocouples Table 4-1 common fault causes and treatment methods of thermocouples Fault phenomenon Possible reasons processing method The thermoelectric potential is smaller than the actual value (the indicated value of the display instrument is lower) Thermoelectric short circuit Find out the cause of short circuit. If it is caused by humidity, dry it; if it is caused by insulator damage, replace the insulator Dust accumulated at the terminal of thermocouple, causing short circuit Ash cleaning Short circuit between compensating wires Find out the short circuit point, strengthen the insulation or replace the compensation wire Thermocouple thermal electrode deterioration If the length allows, cut out the metamorphic section and weld again, or replace the thermocouple with a new one Compensation conductor and thermal dipole connected reversely Reconnect correctly Compensation wire is not matched with thermocouple Replace the matching compensation lead The installation position of thermocouple is not recorded or the insertion depth does not meet the requirements Re install as required Temperature compensation of thermocouple cold end does not meet the requirements Adjust the cold end compensator Thermocouple is not matched with display instrument More thermocouple or display instrument to match The thermoelectric potential is larger than the actual value (the indicated value of the display instrument is higher) Thermocouple is not matched with display instrument More thermocouple or display instrument to match Compensation wire is not matched with thermocouple Replace the compensation lead to match There is DC interference signal entering Eliminate DC interference Poor contact between thermocouple terminal and thermoelectric pole Tighten the terminal screws
- 13. Unstable thermoelectric potential output The insulation of thermocouple measuring line is damaged, causing intermittent short circuit or grounding Find out the fault point and repair the insulation Thermocouple installation is not firm or external vibration Fasten thermocouple, eliminate vibration or take shock absorption measures The thermoelectric pole will not break Repair or replace thermocouple External interference (AC leakage, electromagnetic induction, etc.) Find out the interference source and take shielding measures Thermal potential error of thermocouple is large Thermoelectric pole metamorphism Replace the hot electrode Improper installation position of thermocouple Change installation position Surface area of protective pipe grey Ash removal Correct use of thermocouples Xue Fu Lian The correct use of thermocouples can not only accurately get the temperature value, ensure the product is qualified, but also save the material consumption of thermocouples, save money and ensure the product quality.Incorrect installation, thermal conductivity and time lag are the main errors of thermocouple in use. 1. Error caused by improper installation For example, the installation position and insertion depth of thermocouples cannot reflect the real temperature of furnace, in other words, thermocouples should not be installed too close to doors and heating places, and the insertion depth should be at least 8-10 times of the diameter of the protective tube; the gap between the protective sleeve and the wall of thermocouples is not filled with insulation material, which causes the hot overflow or cold air intrusion in the furnace, so the thermocouple protective tube and the wall holeThe gap between them shall be blocked with insulating materials such as fire-resistant mud or asbestos rope to avoid the influence of cold and hot air convection on the accuracy of temperature measurement; the cold end of thermocouple shall be too close to the furnace body to make the temperature exceed 100 ℃; the installation of thermocouple shall avoid strong magnetic field and strong electric field as far as possible, so the thermocouple and power cable shall not be installed in the same conduit to avoid interference and error; thermocouple cannot be installedIn the area where the measured medium rarely flows, when measuring the gas temperature in the tube with thermocouple, the thermocouple must be installed against the flow direction and fully contacted with the gas. 2. Error caused by insulation variation
- 14. For example, if the thermocouple is insulated, the dirt or salt slag between the protective tube and the stay wire plate are too much, resulting in poor insulation between the thermal dipole and the furnace wall, which is more serious under high temperature. This will not only cause the loss of the thermal potential, but also introduce interference, resulting in errors sometimes up to Baidu. 3. Error introduced by thermal inertia Because of the thermal inertia of the thermocouple, the indicating value of the instrument lags behind the change of the measured temperature, especially in the rapid measurement.Therefore, thermocouples with thin thermoelectric pole and small diameter of protective tube should be used as far as possible.When the temperature measurement environment permits, the protective pipe can even be taken away.Because of the measurement lag, the amplitude of temperature fluctuation detected by thermocouple is smaller than that of furnace temperature fluctuation.The larger the measurement lag is, the smaller the amplitude of thermocouple fluctuation is, and the greater the difference with the actual furnace temperature is.When a thermocouple with a large time constant is used to measure or control the temperature, although the temperature displayed by the instrument fluctuates very little, the actual furnace temperature may fluctuate a lot.In order to measure temperature accurately, thermocouple with small time constant should be selected.The time constant is inversely proportional to the heat transfer coefficient and directly proportional to the diameter of the hot end of the thermocouple, the density of the material and the specific heat. To reduce the time constant, in addition to increasing the heat transfer coefficient, the most effective way is to minimize the size of the hot end.In use, the protective casing with thin wall and small inner diameter is usually made of materials with good thermal conductivity.In the more precise temperature measurement, the bare wire thermocouple without protective sleeve is used, but the thermocouple is easy to be damaged, so it should be corrected and replaced in time. 4. Thermal resistance error In case of high temperature, if there is a layer of coal ash on the protective tube and dust is attached to it, the thermal resistance will increase and block the heat conduction. At this time, the temperature indication is lower than the true value of the measured temperature.Therefore, the outside of the thermocouple protection tube should be kept clean to reduce the error. Remember not to connect the thermocouple compensation wire reversely Li Qiang (Longkou metrological verification and Measurement Institute) All the comrades who are engaged in temperature measurement know the working principle of thermocouples - two different conductors form a closed circuit. When the temperature at both ends of the circuit is equal, the thermoelectric potential of the circuit is zero.When the temperature of the working end and the overstock end of the thermocouple is not equal, the heat generated in the rebel loop is potential.The thermoelectric potential is related to the temperature difference between the two ends.The free end temperature of the thermocouple is not a constant value.All manufacturers use thermocouple special wire compensation wire.By extending the thermocouple to a constant temperature, the thermoelectric potential of the thermocouple is compensated. In the process of daily inspection, many electricians do not know the function of compensation wire, only know that compensation wire is the special wire connecting thermocouple and instrument.It is wrong to connect the compensation wire with thermocouple and instrument at will, which will cause great error.Take a machining factory in our city as an example. At that time, the process of
- 15. workpiece required 920 ℃.The operator also set the value according to the process requirements, and the instrument indication is normal.After the liquid fire, the workpiece appears striation, which makes a furnace of workpiece scrapped.In the analysis of the accident, it is found that the compensation wire is connected reversely. After correction, the temperature in the furnace is 973 ℃.At that time, the free end temperature of the mass transformer couple was 45 ℃, and the indoor temperature was 18 ℃.The temperature error caused by reverse connection is as follows: =1.817mV =0.718mV Equivalent to 53.13 ℃.The above example shows that the thermocouple compensation wire can cause considerable temperature error after being connected reversely.Therefore, do not connect the compensation wire in reverse. 1. Principle of thermocouple temperature measurement Two conductors (or semiconductors) of different materials form a closed circuit. When the temperature of two contacts is different from 0, electromotive force will be generated in the circuit. This phenomenon is called thermoelectric effect, and the electromotive force is called thermoelectric potential.The combination of conductors or semiconductors of these two different materials is called thermocouple, and conductors A and B are called thermoelectric poles.Two contacts, one is called hot end, also known as measuring end or working end. When measuring temperature, it is placed in the measured medium; the other is called cold end, also known as reference end or free end, which is connected with display instrument through wire.TT Contact potential is the electromotive force formed at the contact due to the different free electron density of two different conductors.When two kinds of conductors contact, the free electron diffuses from the conductor with high density to the conductor with low density, and one side of the free electron loses positive charge at the contact, and the other side of the free electron has negative charge.
- 16. When the diffusion reaches dynamic balance, a stable contact potential is formed at both sides of the contact surface.The value of contact potential depends on the properties of two different conductors and the temperature of the contact point.The contact potentials AB (T) and ab (0) of the two contacts can be expressed asEET Where: K - Boltzmann constant; - electric quantity per unit charge; NAT, and at0, BT0 - electronic density of the two materials when the temperature is and 0, respectively.ENBTNNTTA, B Thermoelectric potential is a kind of electromotive force produced by the difference of temperature between two ends of the same conductor.When the temperature at both ends of the same conductor is different, the electronic energy at the high temperature end is greater than that at the low temperature end, so the number of electrons from the high temperature end to the low temperature end is more than that from the low temperature end to the high temperature end. As a result, the high temperature end is positively charged due to the loss of electrons, and the low temperature end is negatively charged due to the gain of redundant electrons. Therefore, the contact potential is formed at both ends of the conductor, and its size is determined by the following factorsThe formula is: Where, NAT and are the electronic density of conductor and conductor respectively, which are functions of temperature.NBtAB The total thermal potential generated in the thermocouple loop is EAB(T, T0)=eAB(T)+eB(T,T0)-eAB(T0)-eA(T,T0) In the total thermal potential, the thermoelectric potential of the thermocouple is much smaller than that of the contact potential, which can be
- 17. ignored. Then the thermoelectric potential of the thermocouple can be expressed as: (T, t0) = EAB (T) - EAB (T0)EAB For the selected thermocouple, when the reference terminal temperature is 0 constant, (t0 = C) is constant, then the total thermoelectric EMF is only a function of temperature, that is, (T, t0 = EAB (T) - C = f (T)TEABTEAB This relation is very useful in practical measurement, that is, as long as the magnitude of (, t0) is measured, the measured temperature can be obtained, which is the principle of using thermocouple to measure temperature.EABTT 2、 Basic law of thermocouple 1Law of homogeneous Conductor: The thermoelectric EMF of a thermocouple composed of two kinds of homogeneous conductors is only related to the temperature of two materials and two contacts, but not to the size, shape and temperature distribution along the electrode.That is, if the material is not uniform, when there is a temperature gradient on the conductor, there will be additional electromotive force.This theorem shows that thermocouples must be composed of two homogeneous materials with different properties.Inside 2, law of intermediate conductor:When using thermocouple to measure temperature, it is necessary to introduce connecting wires and instruments into the circuit. Will the connecting wires and instruments affect the thermoelectric potential in the circuit?The law of intermediate conductor states that when the third conductor is connected in the thermocouple temperature measuring circuit, as long as the temperature at both ends of the third conductor is the same, there is no effect on the total thermal potential of the circuit. 3, law of intermediate temperatureIn the thermocouple temperature measuring circuit, C is the temperature of a certain point on the thermoelectric pole. The thermoelectric potential (T, t0) of the thermocouple at the contact temperature of 0 is equal to the algebraic sum of the thermoelectric potential (T, TC) and
- 18. (T, t0) of the thermocouple at the contact temperature of C and 0, that is, EAB (T, t0) = EAB (T, TC) + EAB (TC, t0)TABT, tEABABT, tTCTEABEAB This law is the theoretical basis of the reference terminal temperature calculation correction method. In the actual thermocouple temperature measuring circuit, the thermoelectric potential with the reference terminal temperature not 0 ℃ can be corrected by using the thermocouple property. 3、 Structure of thermocouple In order to meet the temperature measurement requirements and conditions of different production objects, the structure of thermocouples includes common type thermocouple, armored type thermocouple and thin film thermocouple.Inside 1. ordinary thermocouple: the common structure thermocouple is the most widely used in the industry. It is generally composed of thermal electrode, insulating sleeve, protective tube and junction box.Common thermocouple can be divided into fixed thread connection, fixed flange connection, movable flange connection, no fixed device and other forms according to the connection form when it is installed. 2Armored thermocouple: armored thermocouple is also called thermowell.It is a solid combination of thermocouple wire, insulating material and metal sleeve. The main advantages of armored thermocouple are small thermal capacity, fast dynamic response, high mechanical strength and good flexibility. It can be installed on the device with complex structure, so it is widely used in many industrial sectors. 3Membrane thermocoupleThin film thermocouple is a kind of special thermocouple made of two kinds of thin film thermoelectric materials, which are evaporated to the insulating substrate by vacuum plating and chemical coating,The thermal contact of thin film thermocouple can be made very small (can be thin to 0.01- 0.1 μ m), has the characteristics of small thermal capacity, fast reaction speed and so on. The thermal response time reaches the microsecond level, which is
- 19. suitable for the surface temperature of small area and the dynamic temperature measurement with rapid change. 4、 Compensation wire of thermocouple and compensation method of cold end temperature When the thermocouple material is selected, the thermoelectric EMF is only related to the temperature of the hot end and the cold end.Therefore, only when the cold end temperature is constant, the thermoelectric potential of the thermocouple has a single value function relationship with the hot end temperature.The graduation table of thermocouple is based on the cold end temperature of 0 ℃, but in the actual use process, the cold end temperature is often not 0 ℃, so the cold end temperature must be treated to eliminate the influence of cold end temperature. Then, when the hot end temperature is, the relationship between the thermoelectric potential (T, 0) corresponding to the graduation table and the thermoelectric potential (T, t0) actually generated by the thermocouple can be obtained according to the intermediate temperature law as follows: (T, 0) = EAB (T, t0) + EAB (T0, 0)TEABEABEAB It can be seen that (T0, 0) is a function of cold junction temperature 0, so it is necessary to treat the cold junction temperature of thermocouple.EABT 1. thermocouple compensation wire: In the actual temperature measurement, it is necessary to transmit the potential signal output by the thermocouple to the display instrument or control instrument in the control room tens of meters away from the site, so that the cold end temperature 0 is relatively stable.Thermocouples are generally made short, generally 350-2000mm, and wires are needed to extend the cold end of the thermocouple.In the project, a kind of compensation wire is used, which is usually made of two kinds of cheap metal wires with different properties. In the temperature range of 0-100 ℃, the
- 20. compensation wire and the matched thermocouple are required to have the same thermoelectric characteristics.T 2. cold end temperature correction method: The cold end of the thermocouple can be extended to the place where the temperature is relatively stable by using the compensation wire, but as long as the cold end temperature 0 is not equal to 0 ℃, the measured potential value (0) of the thermocouple loop needs to be corrected.When the working end temperature is, the relationship between the thermoelectric potential (T, 0) corresponding to the graduation table and the thermoelectric potential (T, t0) actually generated by the thermocouple can be obtained according to the intermediate temperature law as follows: (T, 0) = EAB (T, t0) + EAB (T0, 0)TEABTTTEABEABEAB It can be seen that the corrected value of the measured potential value (T, t0) is (T0, 0).(T0, 0) is a function of the reference end temperature 0, the corrected thermoelectric potential is (, 0), and the actual temperature value to be measured can be found out from the graduation table.In the worldEABEABEABTEABTT For example, a nichrome nickel silicon thermocouple is used to measure the furnace temperature.It is known that the cold end temperature is 0 = 30 ℃, and the measured thermal potential (0) is 33.29mv, and the temperature of the heating furnace is calculated.TEABT,T solution(30,0) 1.203 MV was obtained by checking the graduation table of Ni Cr Ni Si thermocouple.According to equation (15-13), EAB (, 0) = EAB (T, t0) + EAB (T0, 0) = 33.29 + 1.203 = 34.493mv, and from the graduation table of Ni Cr Ni Si thermocouple = 829.5 ℃.EABTT 3Cold end 0Constant temperature method at constant temperature: In laboratory and precise measurement, the cold end is usually put into a 0 ℃ thermostat or a container filled with ice water mixture to keep the cold end temperature at
- 21. 0 ℃, which is also called ice bath method.This is an ideal compensation method, but it is very inconvenient to use in industry. 4. cold end temperature automatic compensation method (compensation bridge method): The compensation bridge method uses the unbalanced voltage generated by the unbalanced bridge as the compensation signal to automatically compensate the change value of the thermal potential caused by the temperature of the cold end not being 0 ℃ or the change in the measurement process of the thermocouple.The compensation bridge is composed of three resistances 1, 2, 3 which are wound by manganese copper wire with smaller temperature coefficient of resistance, and the resistances Cu which are wound by copper wire with larger temperature coefficient of resistance and the regulated power supply.The compensation bridge and the cold end of the thermocouple are in the same ambient temperature. When the thermoelectric potential (T, t0) changes due to the change of the cold end temperature, the resistance value of Cu changes with the change of the cold end temperature. If the resistance of the bridge arm and the bridge current are properly selected, the unbalanced voltage AB generated by the bridge can compensate the thermoelectric potential change due to the change of the cold end temperature 0, so as to achieve the purpose of automatic compensation.UabRRRREABRUT