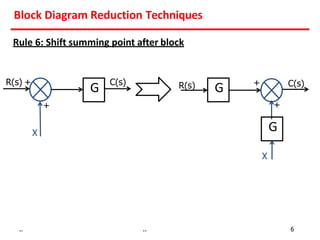
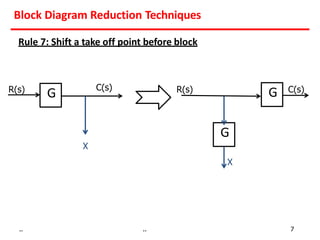
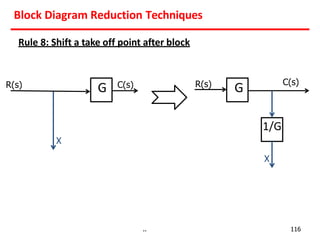
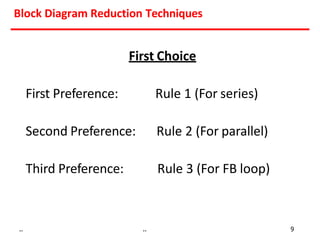
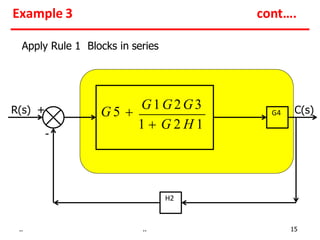
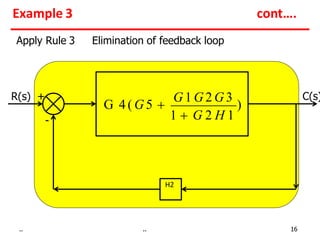
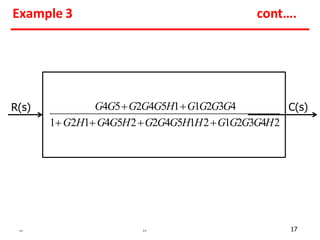
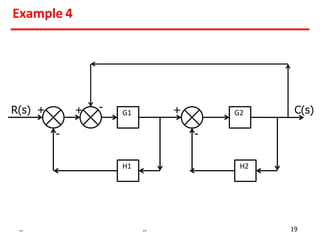
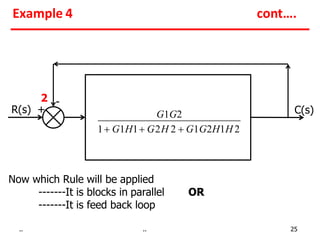
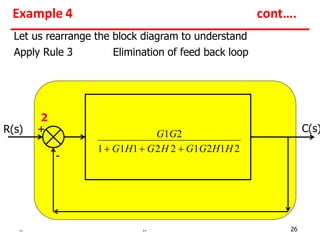
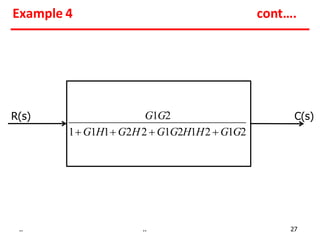
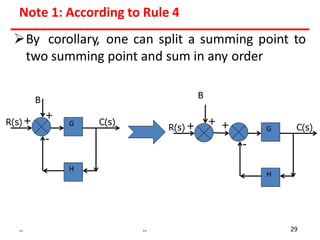
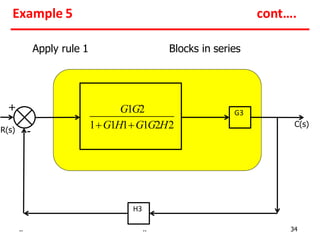
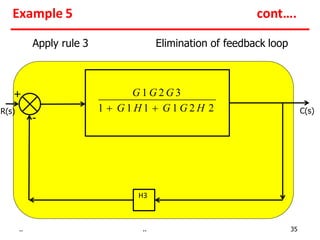
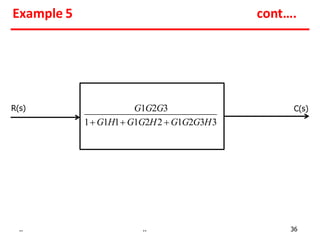
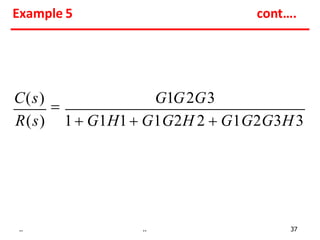
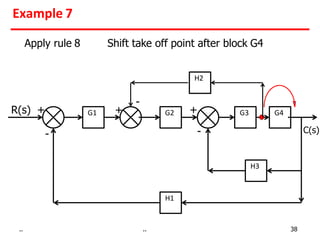
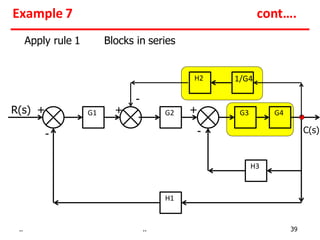
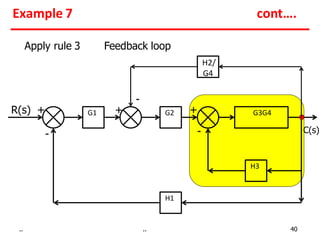
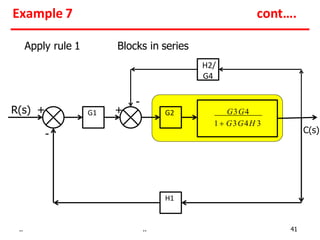
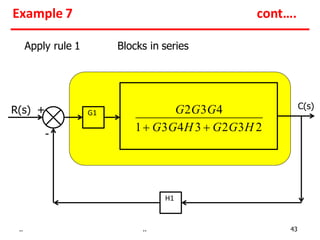
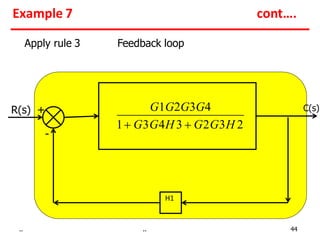
The document describes 8 rules for reducing block diagrams:
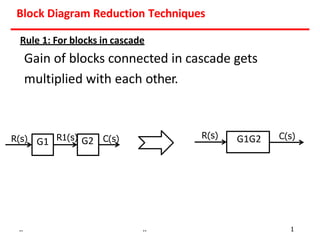
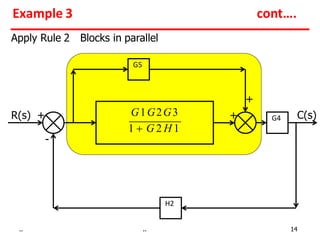
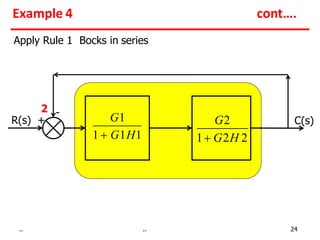
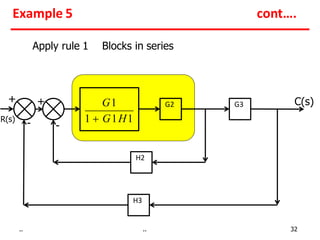
1) Gains of blocks in cascade are multiplied. Gains of blocks in parallel are added.
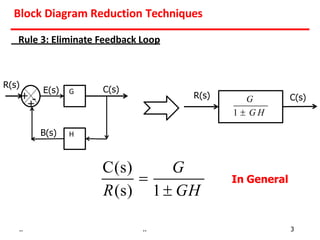
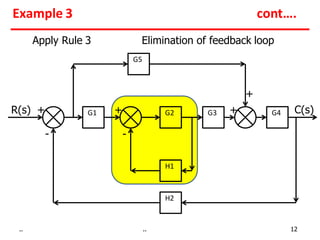
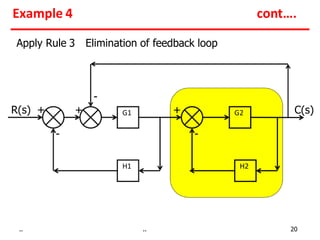
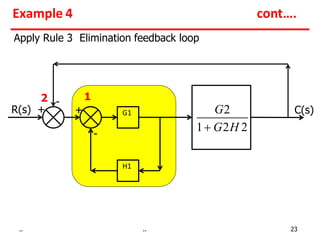
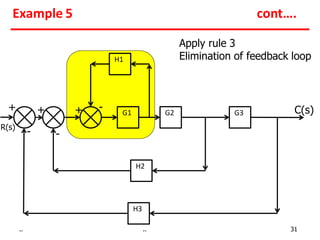
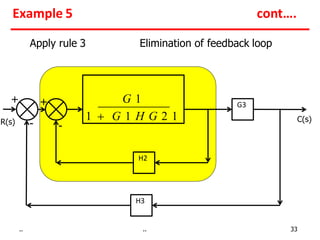
2) Feedback loops can be eliminated by expressing the output in terms of the input and the loop gain.
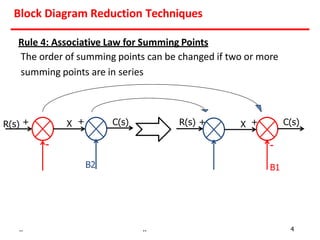
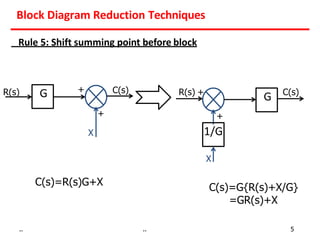
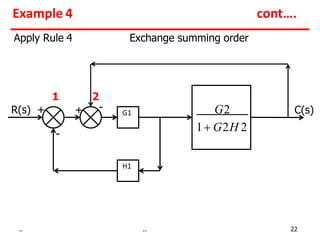
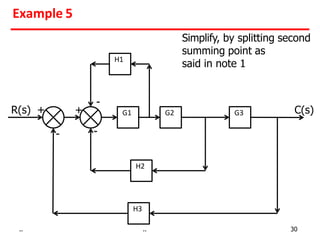
3) Summing points can be rearranged or split using associative laws. Summing points can also be shifted before or after blocks.
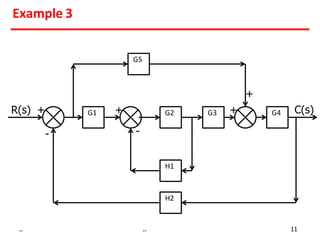
Examples show applying the rules to reduce complex block diagrams into simplified expressions relating the output to the input.