This document provides information about Morse code. It discusses:
- What Morse code is and how it works using dots and dashes
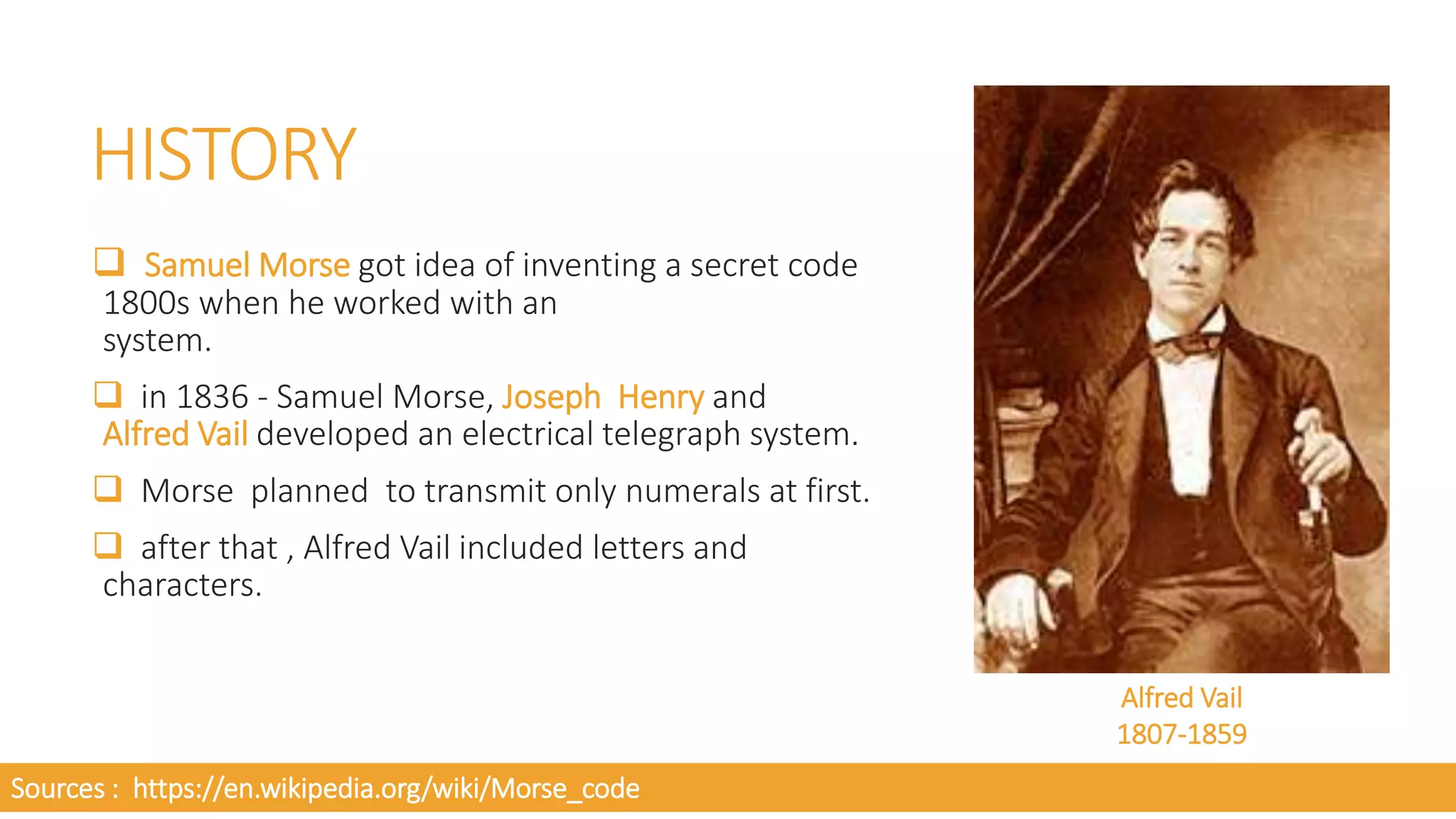
- The history and key people involved in its invention and development, including Samuel Morse, Joseph Henry, and Alfred Vail
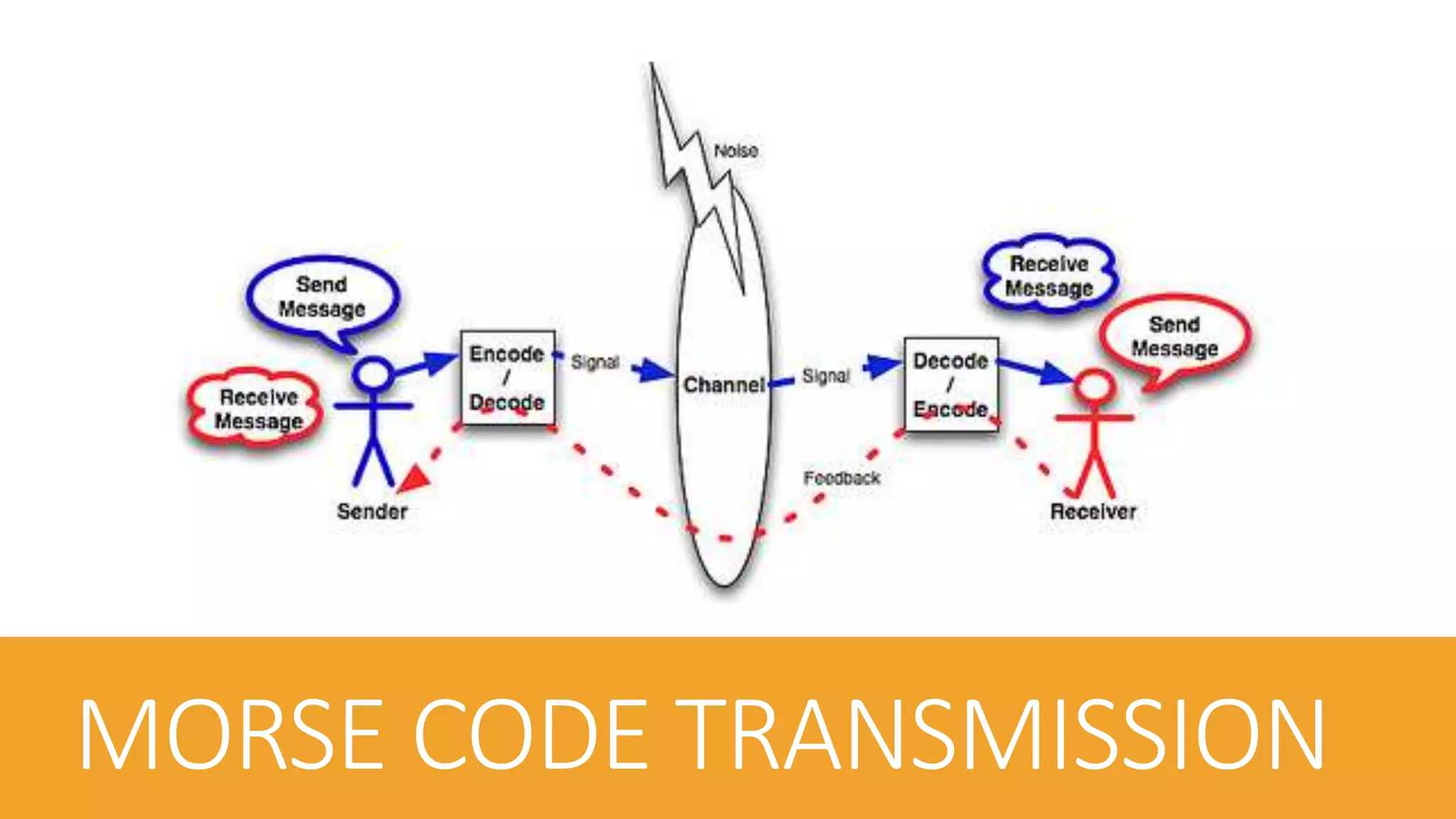
- How Morse code was transmitted through electrical telegraph wires, lights, sounds and its timing
- Changes made to Morse code over time, including the development of the American and Continental Morse codes
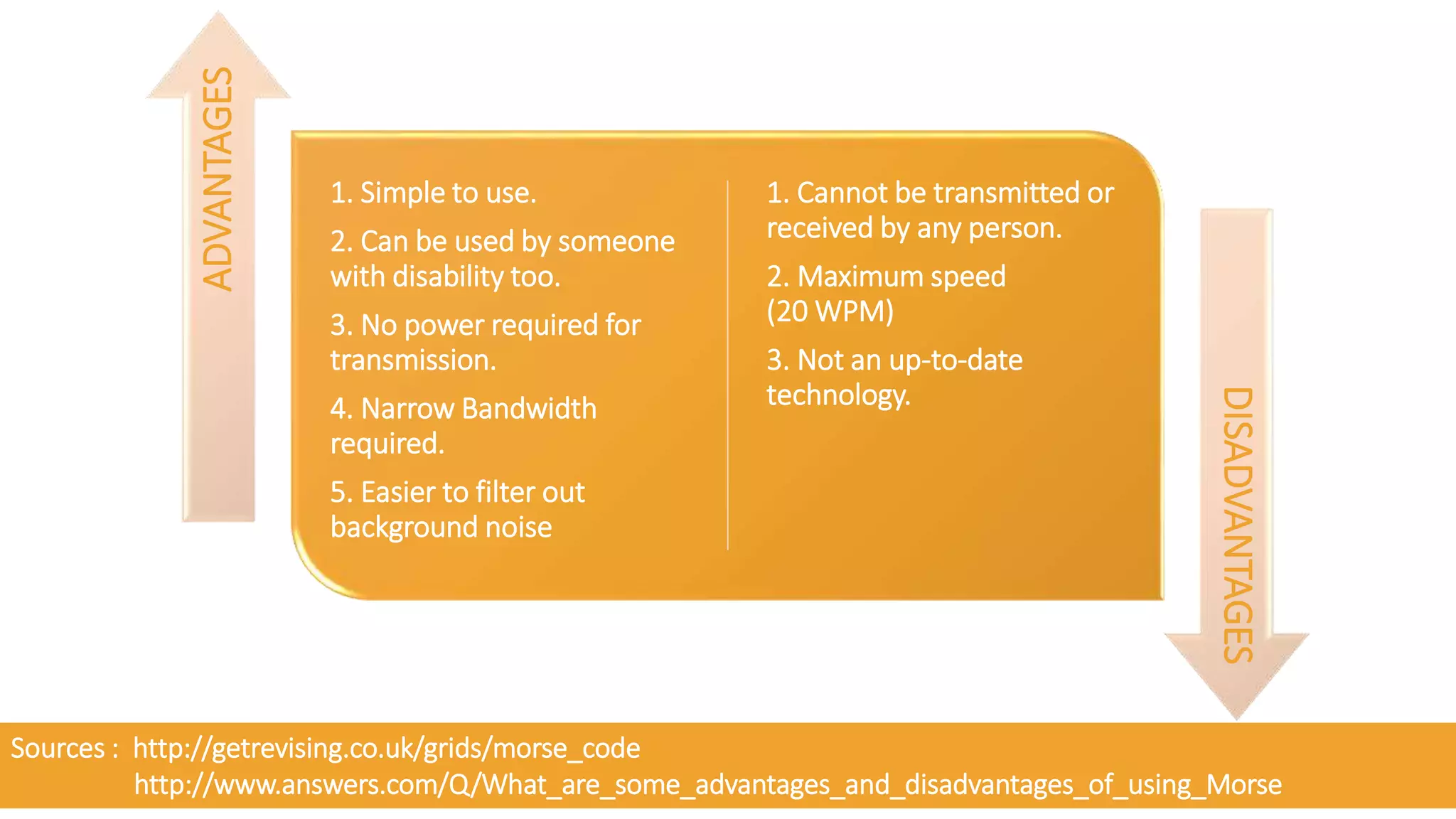
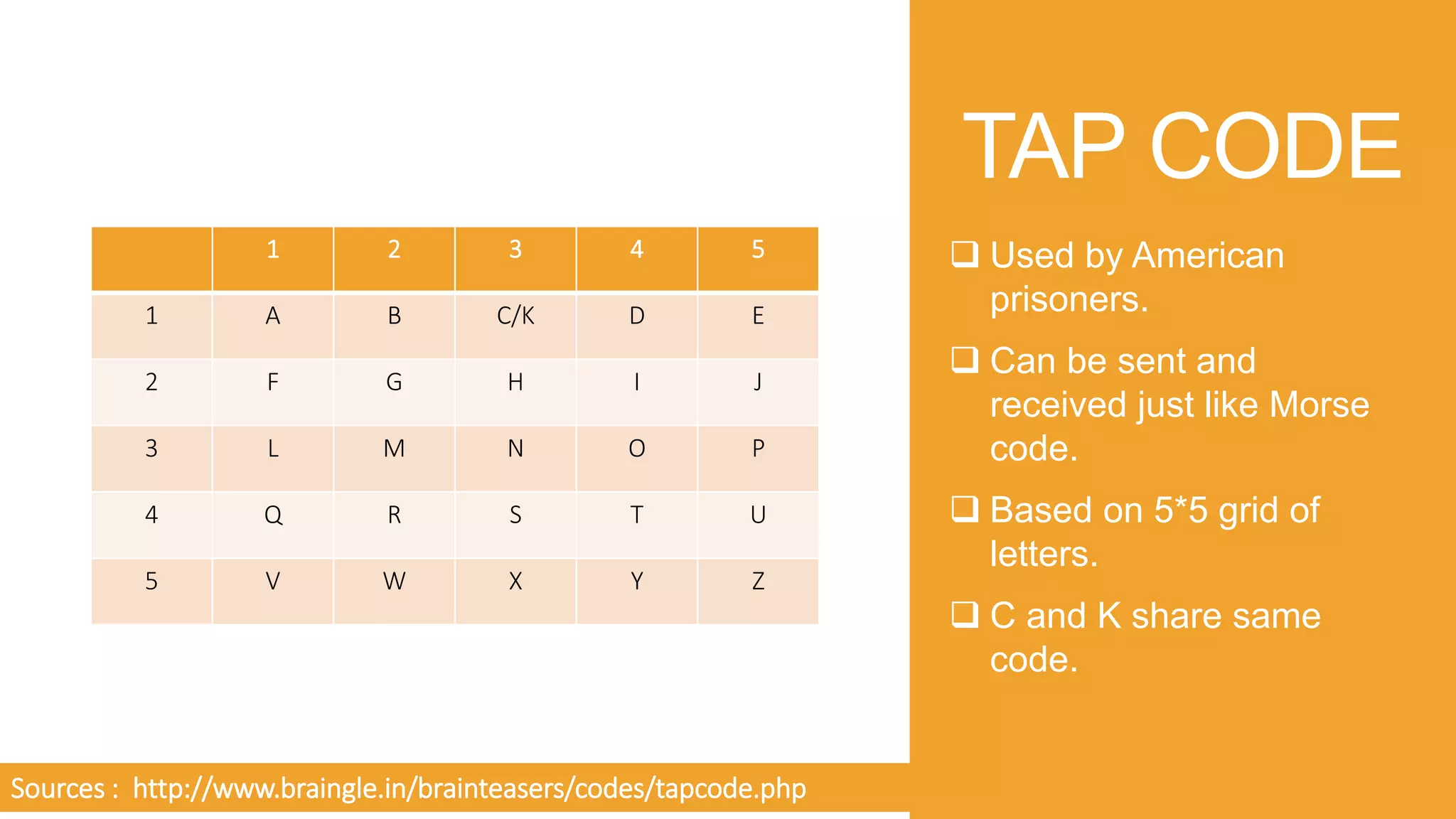
- Applications of Morse code such as in early radio communication and during World War 2, and current uses like in ham radio
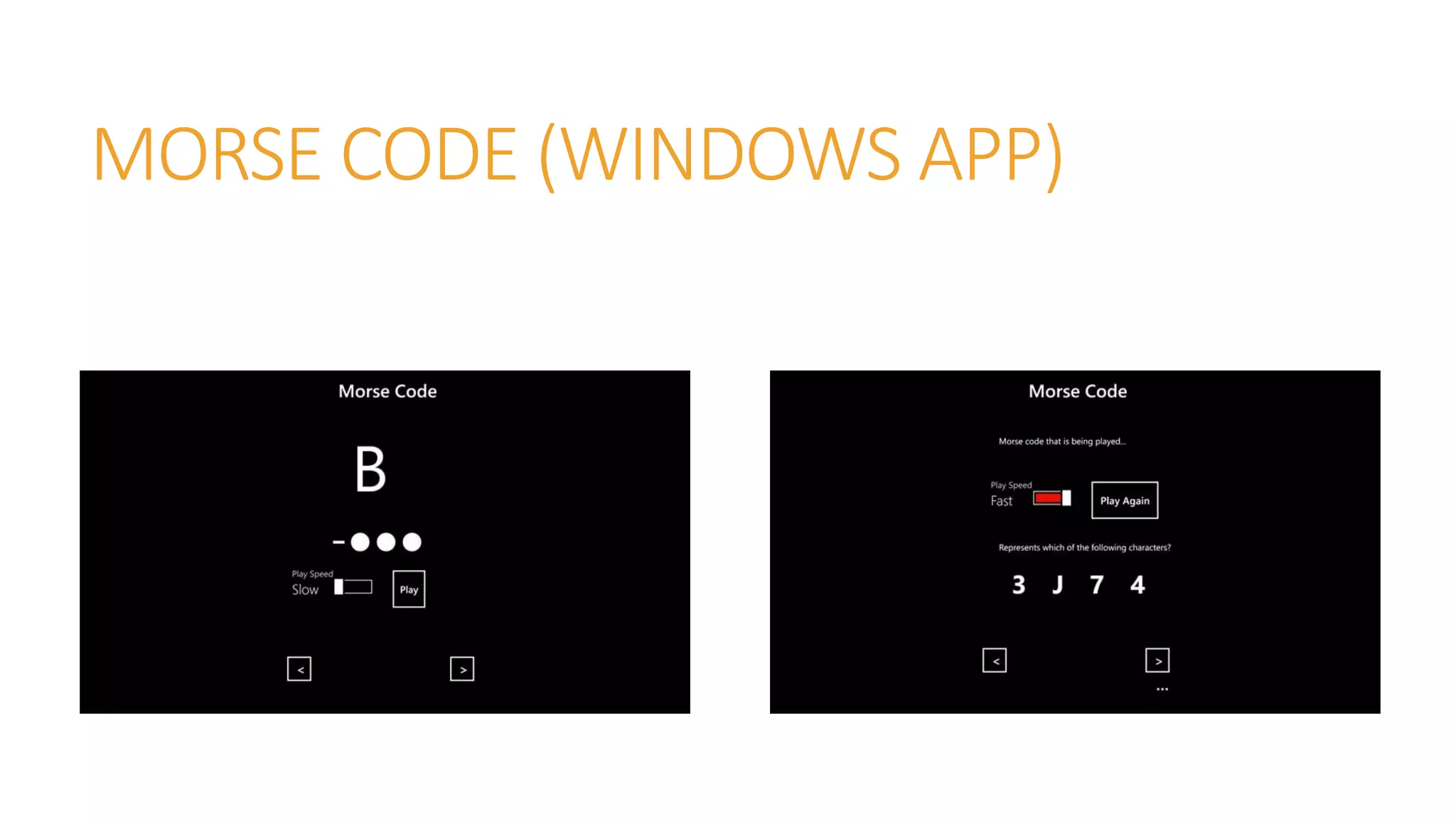
- Mobile apps that can be used to learn and translate Morse code



















![THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN THE MORSE AND THE CONTINENTAL CODES
Morse Continental Morse Continental
C . . . C _ . _ . 1 . _ _ . 1 . _ _ _ _
F . _ . F . . _ . 2 . . _ . . 2 . . _ _ _
J _ . _ . J . _ _ _ 3 . . . _ . 3 . . . _ _
L ___[long dash] L . _ . . 5 _ _ _ 5 . . . . .
O . . O _ _ _ 6 . . . . . . 6 _ . . . .
P . . . . . P . _ _ . 7 _ _ . . 7 _ _ . . .
Q . . _ . Q _ _ . _ 8 _ . . . . 8 _ _ _ . .
R . . . R . _ . 9 _ . . _ 9 _ _ _ _ .
X . _ . . X _ . . _ 0 _______ 0 _ _ _ _ _
Y . . . . Y _ . _ _
Z . . . . Z _ _ . .
Sources : http://jhbunnell.com/morsecode.shtml
http://www.vk5sw.com/Beginner's%20Morse%20Code.htm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/morsecode-160721092248/75/Morse-code-24-2048.jpg)