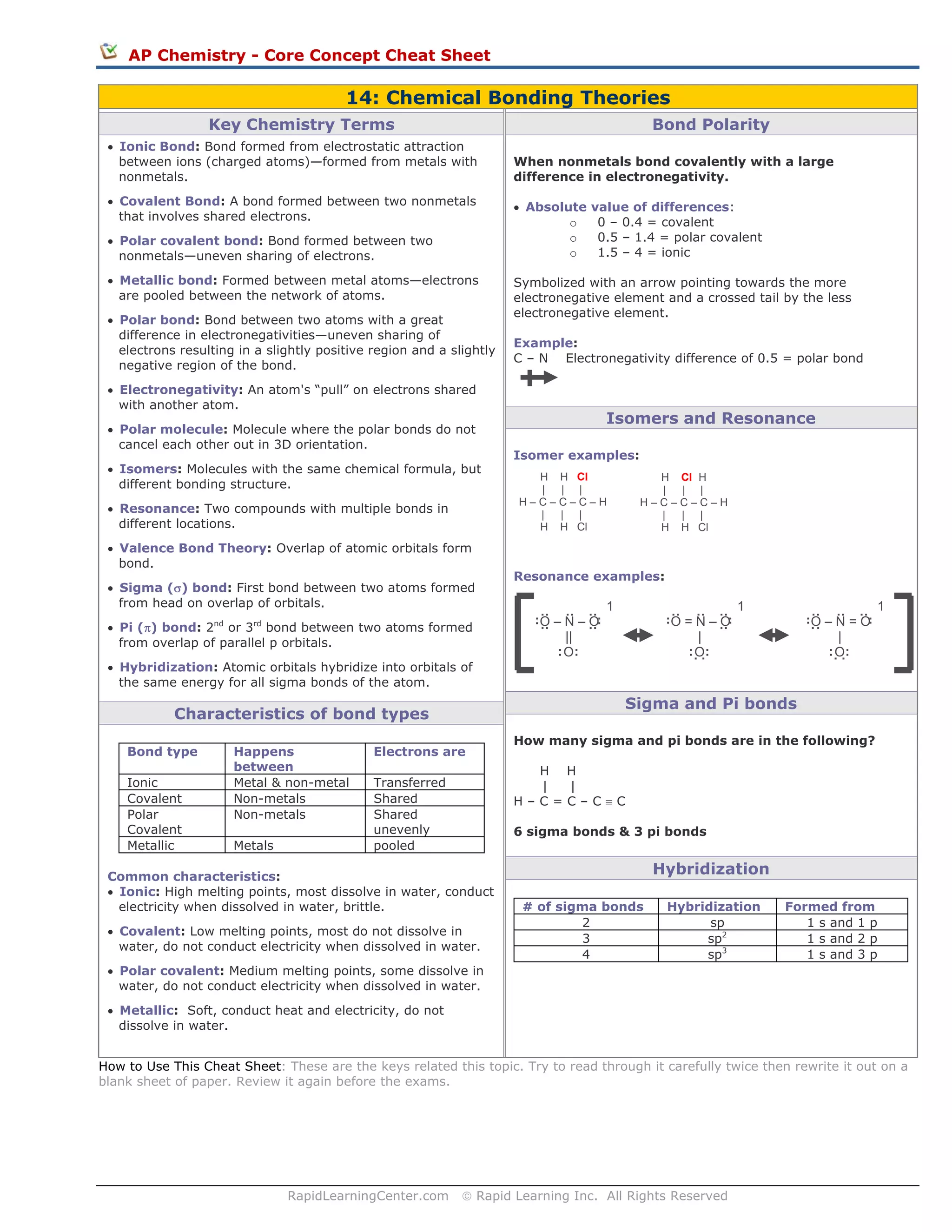
This document provides an overview of key concepts in chemical bonding theories, including different types of bonds (ionic, covalent, polar covalent, metallic) and how they are formed. It also discusses bond polarity, electronegativity, isomers, resonance structures, sigma and pi bonds, and hybridization. Common characteristics of different bond types are outlined such as melting points, solubility, and conductivity. Examples are given to illustrate concepts like bond polarity, isomers, resonance structures, and counting sigma and pi bonds.