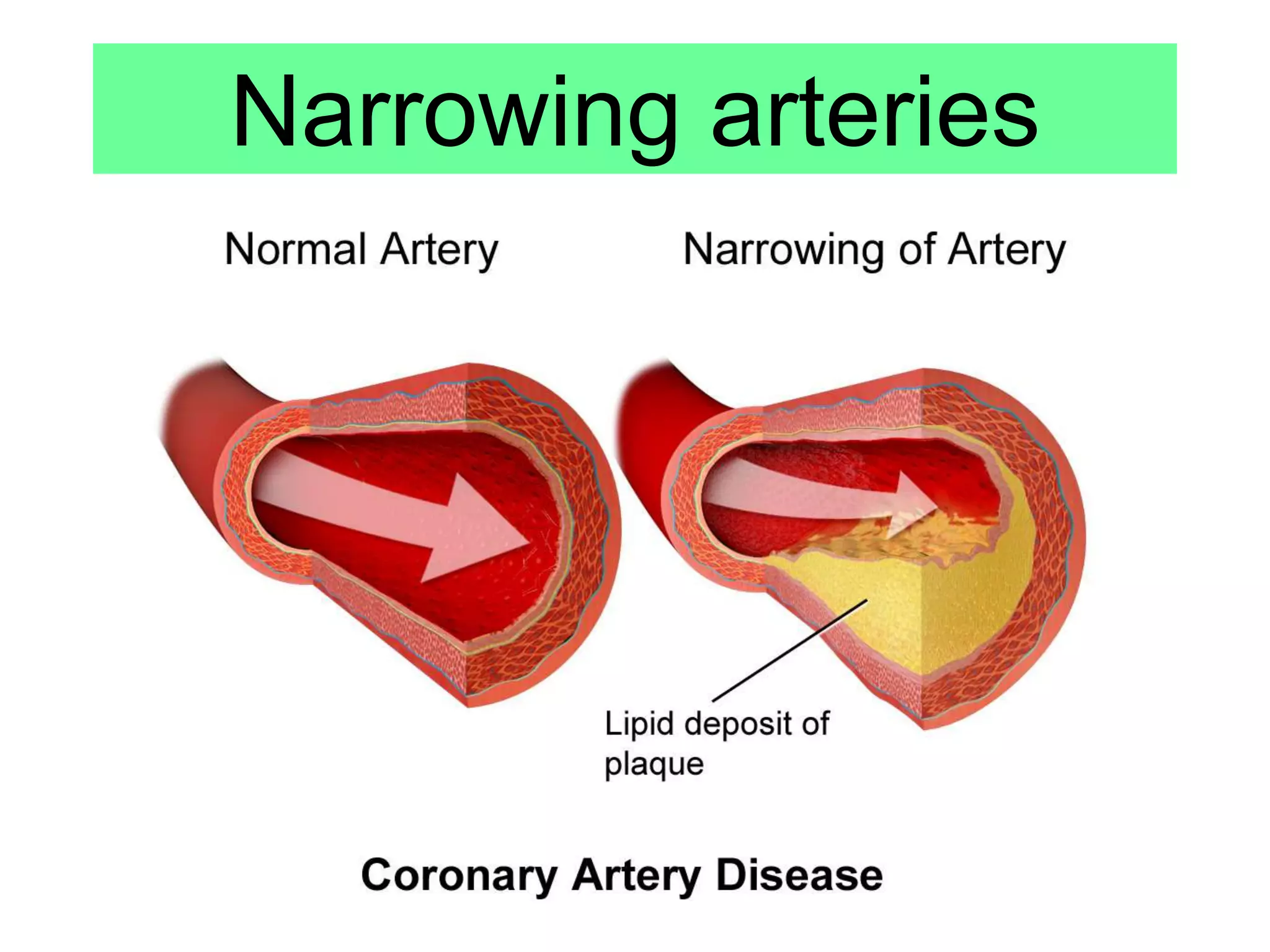
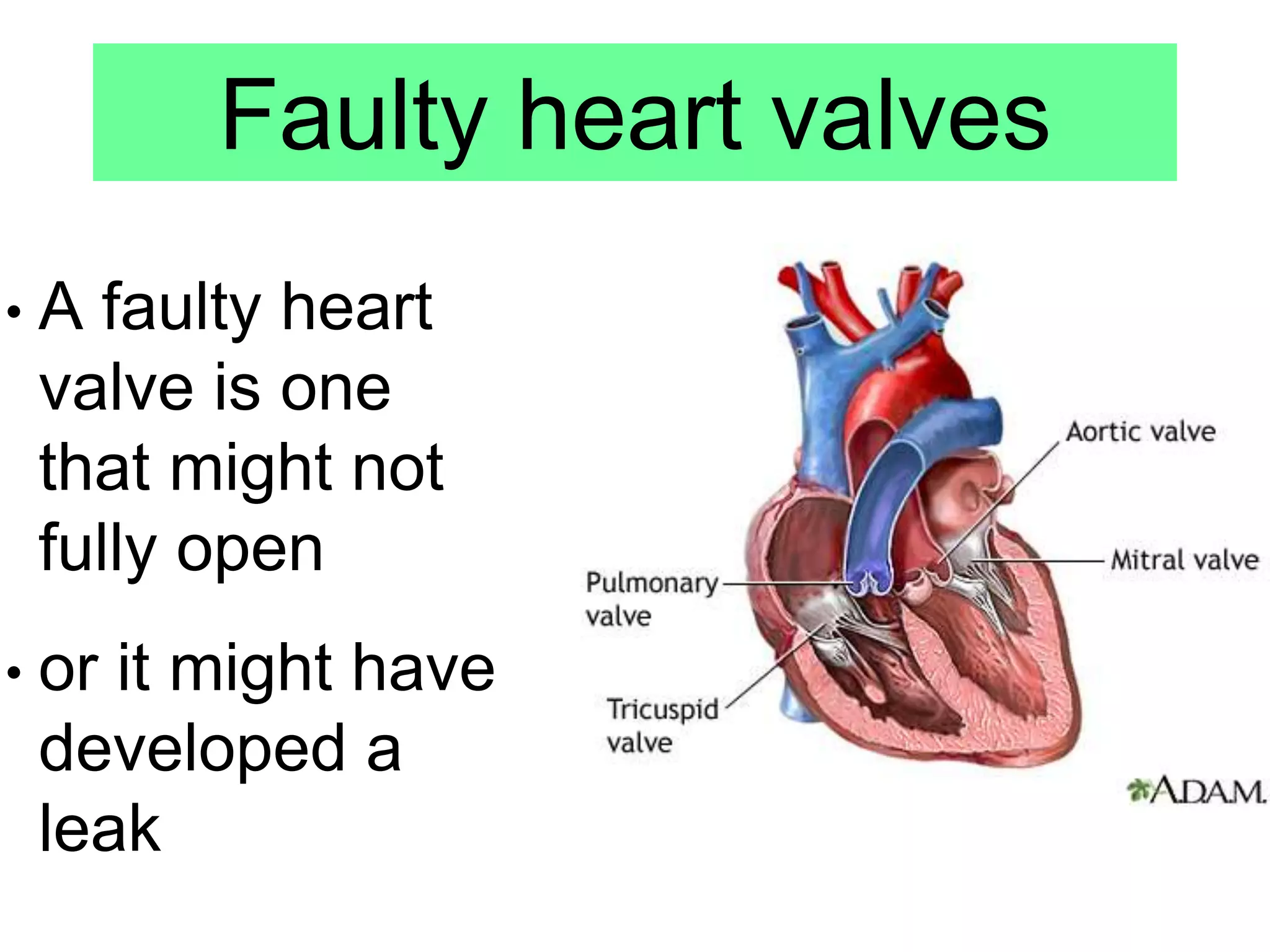
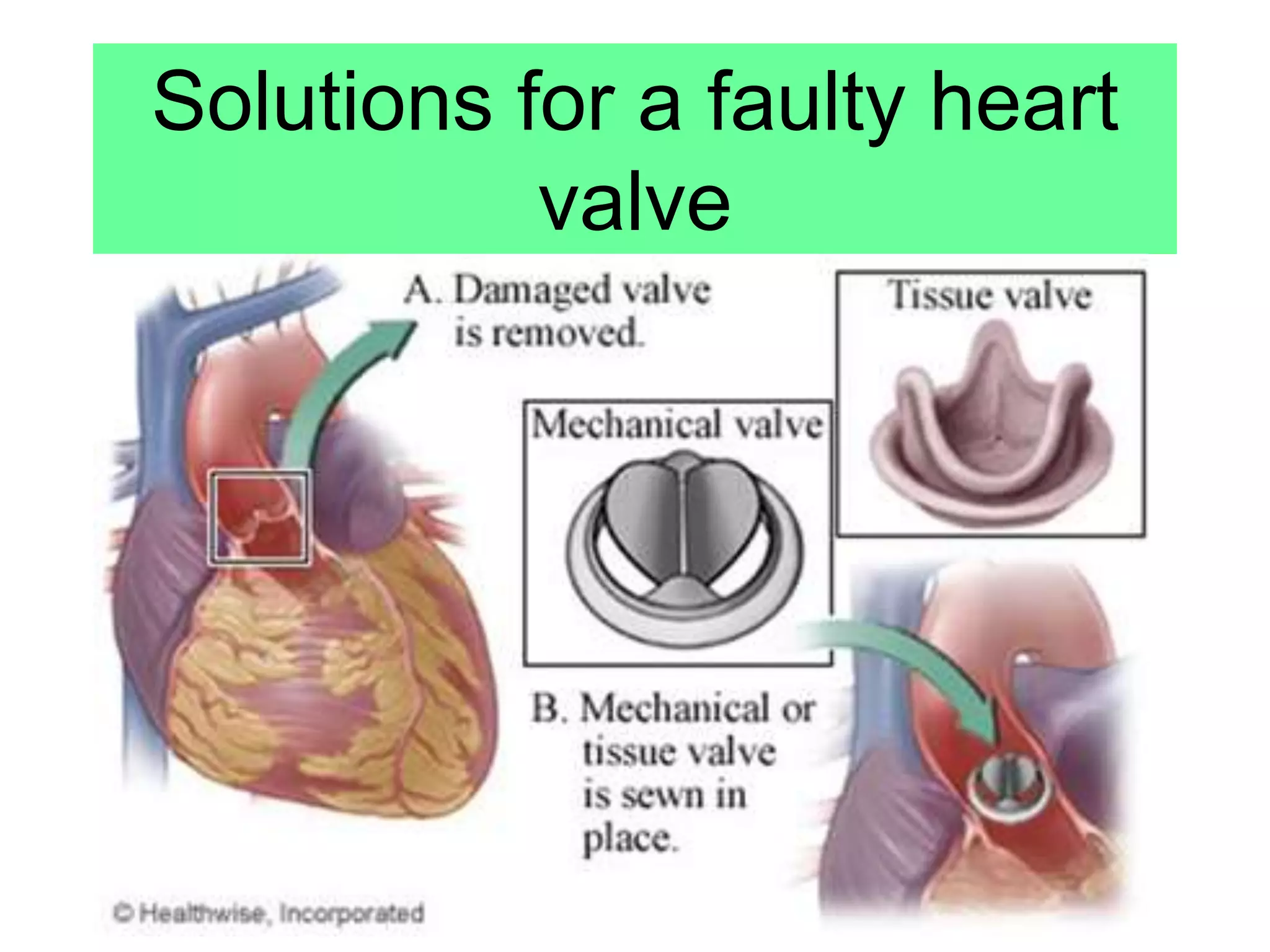
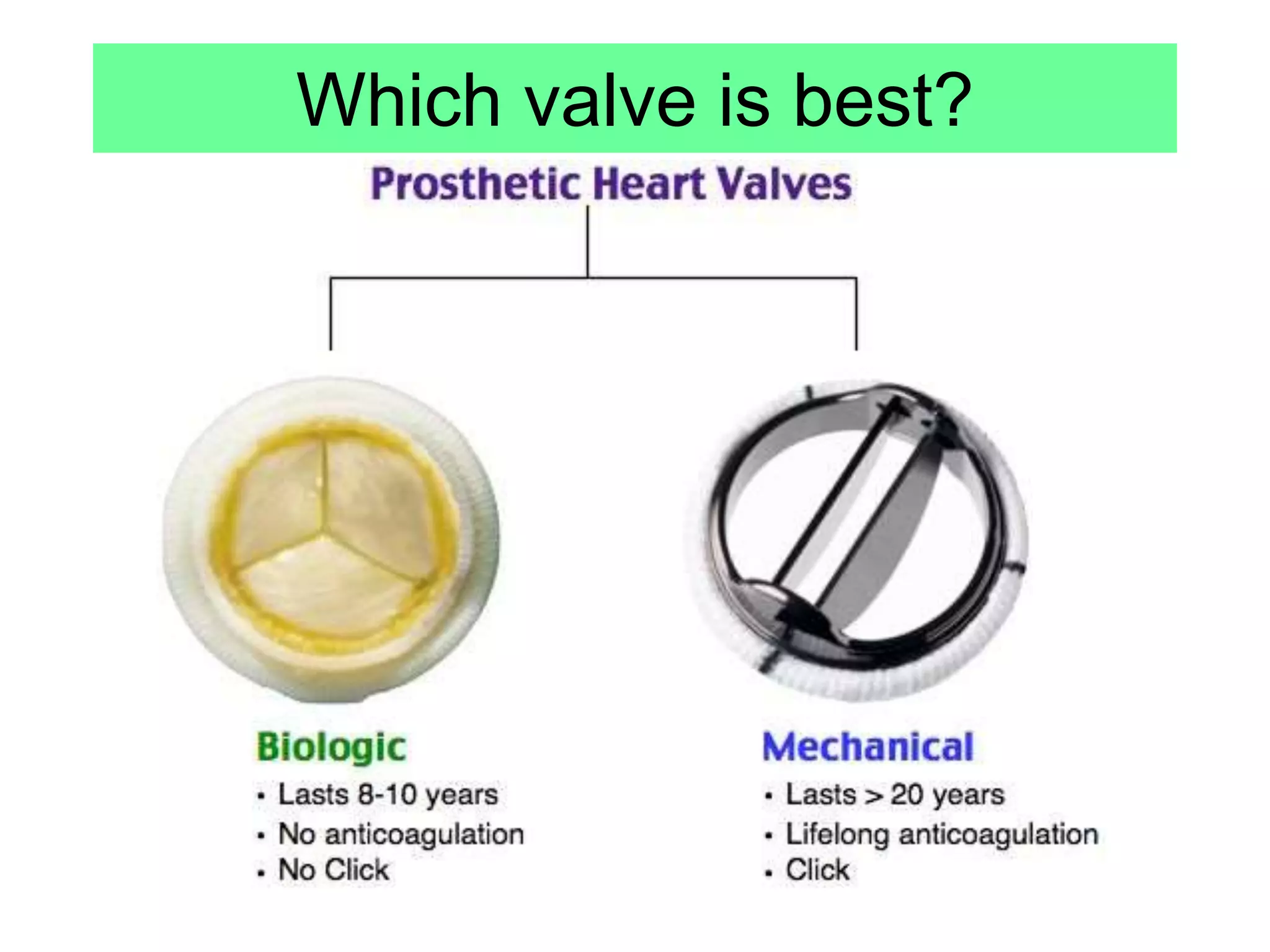
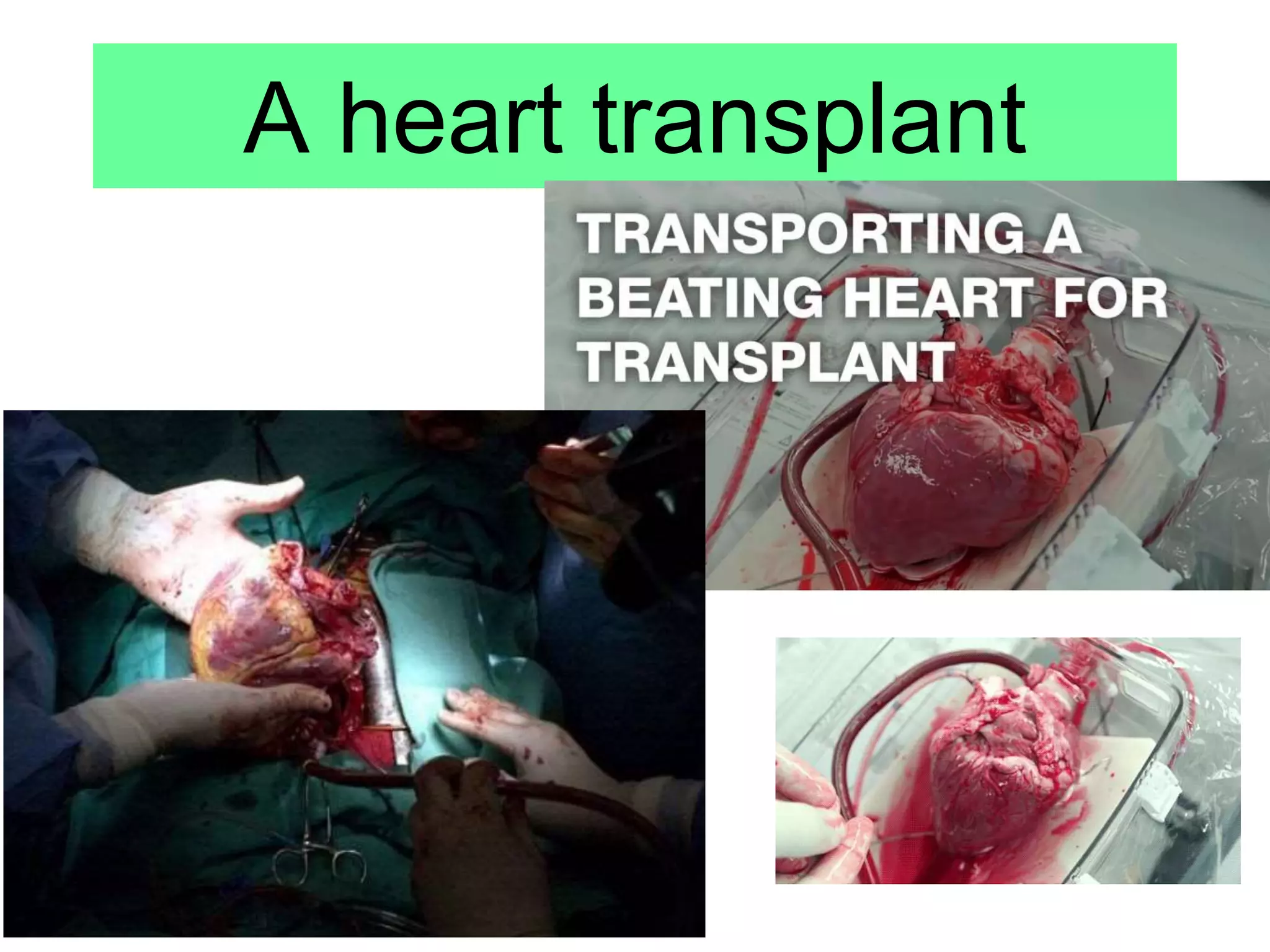
Noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) are long-duration diseases, including cardiovascular diseases, cancer, chronic respiratory diseases, and diabetes, which account for 63% of all global deaths annually. Cardiovascular issues, such as coronary heart disease, arise from narrowed arteries due to fatty deposits, leading to reduced blood flow and potential heart attacks, treatable with stents, statins, valve replacements, or transplants. The document emphasizes understanding and evaluating treatment methods for various heart conditions.