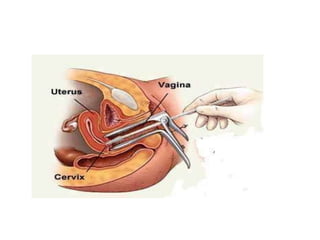
This document discusses vaginal swabs and vaginal discharge. It notes that physiological vaginal discharge is usually white and increases during ovulation, pregnancy, and with oral contraceptive use. Pathological vaginal discharge can be caused by conditions like candidal infection, bacterial vaginosis, trichomoniasis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, cervical ectropion, and various cancers. The document outlines the procedures for collecting vaginal, endocervical, and rectal swabs, including pre-procedure preparation, the collection process, and post-procedure steps.