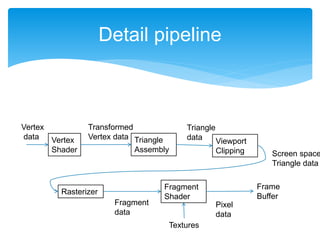
The document outlines a 5-day international graphics programming workshop focusing on cocos-2d-x, highlighting an overview of OpenGL, its installation and setup, and sample shader program creation. It is designed for teaching game programming using cocos-2d-x, a multi-platform framework compatible with various operating systems. The content also includes practical coding examples, shader operations, and project setup instructions tailored for developing 2D games.













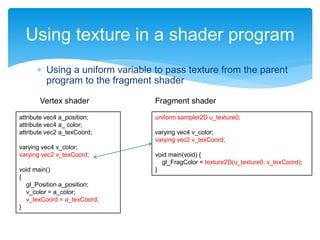
![Using a shader in cocos-2d-x
void ShaderNode::onDraw(const Mat4 &transform, uint32_t flags)
{
GLfloat vertices[6] = {
0, 0, 0.5f, 0, 0.5f, 0.5f
};
auto glProgramState = getGLProgramState();
// Pass the position parameter to the vertex shader’s attribute variable
glProgramState->setVertexAttribPointer(
"a_position", 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 0, vertices);
glProgramState->apply(transform);
// Draw a triangle
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 3);
CC_INCREMENT_GL_DRAWN_BATCHES_AND_VERTICES(1, 3);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphicsworkshop2014-1-140729010944-phpapp01/85/Trident-International-Graphics-Workshop-2014-1-5-15-320.jpg)







![ To draw a rectangle, draw 2 triangles
Draw a rectangle
GLfloat vertices[12] = {
// x y
0.0f, 0.0f, // First triangle
0.5f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f,
0.5f, 0.5f, // Second triangle
0.0f, 0.5f,
0.0f, 0.0f
};
// snip
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 6);
Y
X
0.5
0.50](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphicsworkshop2014-1-140729010944-phpapp01/85/Trident-International-Graphics-Workshop-2014-1-5-23-320.jpg)
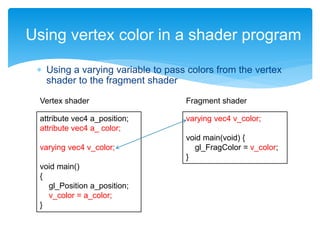
![Add color to a vertex
Position x
y
Color R
G
B
A
Position x
y
Color R
G
B
Position x
y
Color R
G
B
A
GLfloat vertices[18] = {
// x y R G B A
0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f
};
glProgramState->setVertexAttribPointer("a_position”,
2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 24, vertices);
glProgramState->setVertexAttribPointer("a_color",
4, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 24, vertices + 2);
Stride
float x 6 = 24 bytes
Stride
float x 6 = 24 bytes
Offset
float x 2 = 8 bytes
vertices
vertices + 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphicsworkshop2014-1-140729010944-phpapp01/85/Trident-International-Graphics-Workshop-2014-1-5-26-320.jpg)



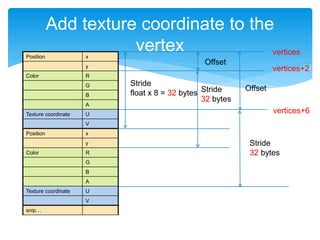
![Cont’d
bool NewShaderNode::initWithVertex(const std::string &vert, const std::string &frag,
Texture2D* texture)
{
// snip…
getGLProgramState()->setUniformTexture("u_texture0", texture);
// snip…
}
// snip…
void NewShaderNode::onDraw(const Mat4 &transform, uint32_t flags)
{
GLfloat vertices[48] = {
// x y R G B A U V
0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.0f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f
};
// snip…
glProgramState->setVertexAttribPointer("a_position”, 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 32, vertices);
glProgramState->setVertexAttribPointer("a_color”, 4, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 32, vertices + 2);
glProgramState->setVertexAttribPointer("a_texCoord”, 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 32, vertices + 6);
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 6);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphicsworkshop2014-1-140729010944-phpapp01/85/Trident-International-Graphics-Workshop-2014-1-5-31-320.jpg)