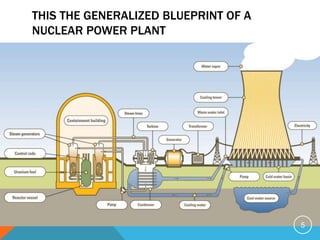
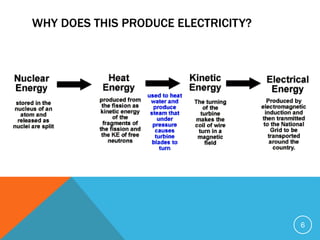
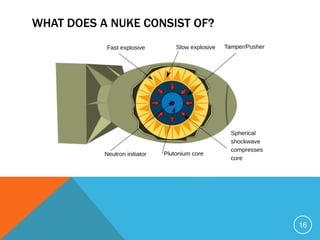
Nuclear power generates electricity through nuclear fission reactions that produce heat to power steam turbines. A nuclear power plant has a reactor core that sustains a controlled nuclear chain reaction to heat water and produce steam. This turns turbines that generate electricity. Nuclear power has advantages like reducing greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels. However, it also has disadvantages like radioactive waste, safety risks from accidents, high construction costs, and potential military applications.