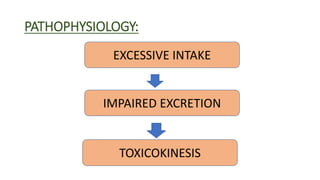
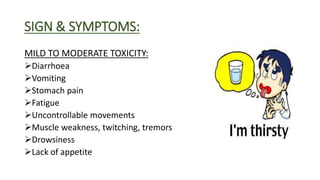
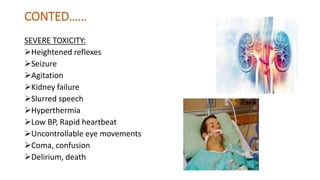
Lithium toxicity occurs when there are excessive levels of lithium in the blood. Symptoms range from mild like nausea and weakness to severe including seizures, coma and even death. Management involves stopping lithium intake, intravenous fluids to hydrate the patient, monitoring vital signs and blood lithium levels, and potentially interventions like dialysis. Nurses play an important role in monitoring patients on lithium therapy, educating them on signs of toxicity, and ensuring safe lithium levels through regular blood tests.