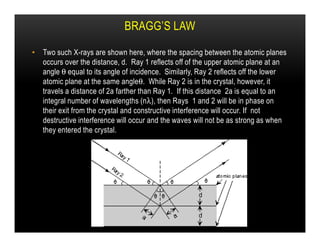
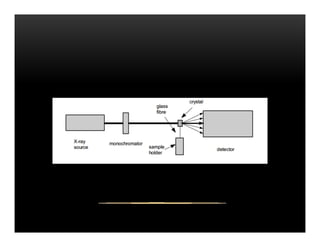
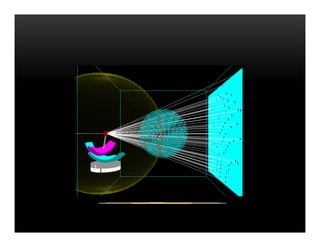
X-ray crystallography uses diffraction of X-rays by the periodic crystal structure of molecules to determine their structure. Crystals of the molecule are bombarded with X-rays, which produce a diffraction pattern. Analysis of this pattern reveals the location of atoms within the crystal unit cell. Researchers first crystallize molecules and collect diffraction data, then use computers to process the data and deduce the molecular structure. This technique has provided insights into materials science, biology, and medicine by revealing atomic-scale structures.


![• If the waves are out of phase, being off by a non-integer number
of wavelengths, then destructive interference will occur and the
amplitude of the waves will be reduced.
• In an extreme case, if the waves are out of phase by an odd
multiple of ½ λ [(2n+1)/2 λ ], the resultant wave will have no
amplitude and thus be completely destroyed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xraycrystallography-231126144640-bd2b73cb/85/X-RAY-CRYSTALLOGRAPHY-pdf-3-320.jpg)