Agrobacterium mediated gene transfer - LIKE NEVER BEFORE!!
- 1. Shovan Das B.Sc (Agriculture) Bidhan Chandra Krishi Viswavidyalaya AGROBACTERIUM MEDIATED GENE TRANSFER
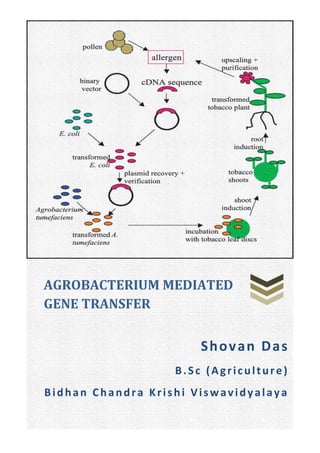
- 2. 1 Transferring of gene is necessary to incorporate foreign genes or modified genes (of that organism) into an organism. This process is called transformation and the produced individual is called transgenic. There are various methods of gene transfer, agrobacterium mediated transfer is one among them. Methods of gene transfer: Direct transfer: Directly transfer gene into an organism. 1. Physical methods: Micro injection, macro injection, pressure, biolistic-gene gun/particle bombardment, electroporation, silicon carbide fibres, laser mediated, liposome encapsulation, 2. Chemical methods: Polyethylene glycol (PEG) method, diethyl amino ethyl (DEAE) dextran mediated, calcium phosphate precipitation, artificial lipids, proteins, dendrimers. Indirect transfer: 1. Biological methods: Agrobacterium tumifaciens mediated, Agrobacterium rhizogenes mediated, plant viruses. In plants: Meristem transformations, floral dip method, pollen transformation. So, agrobacterium mediated gene transfer is a biological method where gene is inserted indirectly by using a vector. Why agrobacterium? a. It successfully infects the host and transfers the target gene into it, high transformation efficiency. b. Simple and comparatively less expensive. c. Large number of dicots and few monocots (as they don’t produce phenolic) and gymnosperms response to agrobacterium. d. Transgenic crops obtained have better fertility percentage. About agrobacterium: Discovered by Smith and Townsend (1907). A soil-born gram negative bacterium causing induction of ‘crown gall' and ‘hairy root' diseases. It is rod shaped and motile, having 1-6 peritichous flagella. It is a phyto-pathogen, and it is regarded as Nature’s most effective plant genetic engineer. It is the natural expert of inter-kingdom gene transfer. There are three strains of agrobacterium – Strains Causes Agrobacterium tumefaciens Crown gall disease Agrobacterium rhizogenes Hairy root disease Agrobacterium radiobacter Avirulent strain Agrobacterium Mediated Gene Transfer Crown gall in sugar beet caused by agrobacterium
- 3. 2 Agrobacterium contains a chromosome & a plasmid. Both chromosomes & plasmid contains different genes which help in the transfer of the foreign DNA into host. The plasmid is Ti (tumour inducing) plasmid or Ri (root inducing) plasmid. Only the T-DNA part of plasmid is inserted into the host cell, where the foreign gene recombined. Chromosomal genes: Chromosomal genes Function/s Chv A& B Major role in exopolysaccharide production. psc A T-DNA transport. chv E Glucose and galactose transport. chvD, ilv, miaA and att Have virulence property. Ti Plasmid: Ti plasmid is a large conjugative plasmid or mega plasmid of about 200 kb. Ti plasmid is a circular vector containing various regions which have different functions – T-DNA region: T-DNA is 23 kb long containing various genes which have regulatory sequences recognised by plant cells. It initiates at right border (RB) and terminates at left border (LB). These are not transferred intact to the plant genome, but are involved in the transfer process. The RB is rather precise, but the LB can vary by about 100 nucleotides. Deletion of the RB repeat abolishes T-DNA transfer, but the LB seems to be nonessential. At least RB should present in plasmid for successful transformation. This region has genes for auxin, cytokinin & opine synthesis. Auxin & cytokinin are useful for plant (they stimulate the growth of that definite plant part, which results the formation of tumour or crown gall). But opines are not useful to plants, rather it is used by the bacterium for C & N source. Genes present in T-DNA and their functions are – Gene Product Function ocs Octopine synthase Opine synthesis nos Nopaline synthase Opine synthesis trns1 (iaaH, auxA) Tryptophan-2-mono-oxygenase Auxin synthesis
- 4. 3 trns2 (iaaM, auxB) Indoleacetamide hydrolase Auxin synthesis trnr (ipt, cyt) Isopentyltransferase Cytokinin synthesis trnL Unknown Unknown, mutations affect tumour size frs Fructopine synthase Opine synthesis mas Mannopine synthase Opine synthesis ags Agropine synthase Opine synthesis Opine catabolism region: Genes are carried on this region allow the bacterium to utilize opines as nutrient. Origin of replication (Ori): Replication of DNA of that plasmid starts from here. Virulence region: Virulence region (30 kb) consists of 24 genes which code for proteins that prepare the T-DNA and the bacterium for transfer. Virulence genes are located in 8 operons from virA to virH. vir A,F,G are monocistronic operons, whereas vir B,C,D,E,H are polycistronic. Operons Function/s virA Chemoreceptor (senses acitosyringone & alpha hydroxy acitosyringone), activator of virG. It is activated after binding with phenolic compound and cause auto-phosphorylation due to auto-kinase activity on histidine residue of vir A. virB Transmembrane complex (conjugational pores between plant cell and bacteria). VirB11 has ATPase activity and generate ATP needed for the delivery of T-DNA into the plant cells. virC Host-range specificity. Helps in DNA transfer (VirC1 specifically binds to overdrive sequence and stimulates the transfer process. Agrobacterium tumefaciens uses type IV secretion system [T4SS] to transfer T-DNA complex to its host cells. T4SS also known as mating pair formation apparatus is a cell envelope spanning complex. T4SS form a pore or channel). virD Site-specific endonuclease, essential for cleavage of super coiled stranded substrate. VirD1 has topoisomerase activity and VirD2 has endonuclease activity. virE T-DNA processing and protection (it bind to the single stranded DNA and protect it from nuclease action). virF Host range specificity. It directs the T-complex (virD4, virB1, virB2, T4SS) protein for destruction in proteosomes. virG Positive regulator of vir B, C, D, E, F. (virA cause phosphorylation to VirG protein and bind with virG forming dimer and then induce the expression of other operons. virH Encodes P-450 type monooxygenases protein. Associated with detoxification of a variety of compound. Agrobacterium tumeficiens strains generally produce octapine (arginine + alanine) or nopaline (arginine + glutamine). Agrobacterium rhizogenes produce either agropine or mannopine.
- 5. 4 Ri Plasmid: The Ri–plasmid contains a distinct segment of DNA which is transferred to plant genome during infection. The A. rhizogenes have Ri plasmid. Strains of A. rhizogenes are known to produce agrocinopine and few opines of the agropine group. Preparation of vectors: The preparation of vectors is essential for transferring the foreign DNA (target DNA/gene of interest) to the host (plant). There are two kinds of vectors are used for transfer – 1. Co-integrated Vectors: This is the type of vector where T-DNA region and virulence region are co-integrated. Three vectors are required in this system – Vectors / Plasmids Initially resides in Features & functions Disarmed Ti plasmid A. tumifaciens Oncogenes (phytohormone genes which produce auxin & cytokinin, as they are responsible for tumour formation) located in T-DNA region are replaced by exogenous DNA, so it is disarmed. They are pGV3850 vector with left & right border of T-DNA region. Intermediate vectors E. coli (then transferred to agrobacterium through conjugation) These are small pBR322 based plasmids containing a T- DNA region with foreign DNS included. They are replicated in E.coli and are transferred into agrobacterium by conjugation. They have only origin pf replication for E. coli (OriE), so they can’t replicate in agrobacterium. They also need DNA segments homologous to the disarmed T- DNA to permit recombination to form a co-integrated T- DNA structure. Helper vectors E. coli (stays here, are not transferred). These are small plasmids contain transfer (tra) and mobilization (mob) genes, which allow the transfer of the intermediate vectors into Agrobacterium. A resulting co-integrated plasmid assembled by in vitro manipulation normally contains: the vir genes, the left and right T-DNA borders, an exogenous DNA sequence between the two T-DNA borders, and plant and bacterial selectable markers. These vectors were among the first types of modified and engineered Ti plasmids. There are several drawbacks of using co-integrated vectors, so that they are not widely used today.
- 6. 5 Drawbacks of co-integrated vectors: 1. Long homologies required between the Ti plasmid and the E. coli plasmids making them difficult to engineer and use. 2. Relatively inefficient gene transfer compared to the binary vectors. 2. Binary Vectors: Binary vector was developed by Hoekma et al (1983) and Bevan in (1984). It utilizes the trans- acting functions of the vir genes of the Ti-plasmid and can act on any T-DNA sequence present in the same cell. Binary vector contains transfer apparatus (the vir genes) and the disarmed T-DNA containing the transgene on separate plasmids. The two different plasmids employed are – Vectors / Plasmids Initially resides in Feature & functions Small replicon E. coli (transferred to agrobacterium) It has an broad origin of replication (RK2) that permits the maintenance of the plasmid in a wide range of bacteria including E. coli and Agrobacterium. This plasmid typically contains: – Foreign DNA in place of T-DNA, – The left and right T-DNA borders (or at least the right T-border), – Markers for selection and maintenance in both E. coli and A. tumefaciens, – A selectable marker for plants. Ti plasmid (with vir region) A. tumifaciens It lacks the entire T-DNA region but contains an intact vir region. The T-DNA plasmid can be introduced into Agrobacterium by triparental mating or by a more simple transformation procedure, such as electroporation. These two plasmids resides separately in agrobacterium, they don’t need recombination. So here the adaptability is wide. The plant cells are co-cultivated with the Agrobacterium, to allow transfer of recombinant T-DNA into the plant genome and transformed plant cells are selected under appropriate conditions. Advantages of binary vectors: Small size due to the absence of border sequences needed to define T-DNA region and vir region. Ease of manipulation. Examples of binary vectors: pBIN19: one of the first binary vectors developed in 1980s and was widely used. pGreen: A newly developed vector with advanced features than pBIN19.
- 7. 6 T-DNA transfer and integration: Signal recognition by Agrobacterium: The wounded plant cells release certain chemicals, such as phenolic compounds and sugars. These chemicals are recognized by Agrobacterium as signals. This in turn results in a sequence of biochemical events in Agrobacterium that helps in transfer of T-DNA of Ti plasmid. Attachment to plant cell: Attachment of this bacterium to plant cells is a two-step process. It involves an initial attachment via polysaccharides (the product of att R locus). Subsequently, a mesh of cellulose fibres is produced by Agrobacterium. Several chromosomal virulence genes (chv genes) are involved in attachment of bacterial cells to the plant cells. Induction of virulence gene: virA (a membrane- linked sensor kinase) senses phenolic compounds (such as acetosyringone) and autophosphorylates, subsequently phosphorylating and, thereby, activating virG. This activated virG induces expression of other virulence gene of Ti plasmid to produce the corresponding virulence proteins (D, D2, E2, B). It has been also identified that certain sugars (e.g. glucose, galactose, xylose etc.) also induce virulence gene.
- 8. 7 Production of T-DNA strand: The right and left border sequence of T- DNA are identified by virD1/ virD2 protein complex and virD2 produces single stranded DNA (ss-T-DNA). After nicking, virD2 becomes covalently attached to the 5'end of ss-T- DNA strand and protect and export the ss-T-DNA to plant cells. Transfer of T-DNA out the bacterial cell: The ss- T-DNA – virD2 complex in association with virE2 is exported from bacterial cell by a ‘T-pilus' (a membrane channel secretary system). Transfer T-DNA into plant cell and integration: The single stranded T-DNA– virD2 complex and other vir proteins cross the plant plasma membrane. In the plant cells, T-DNA gets covered with vir E2. This covering of virE2 helps in protection of ss-T-DNA from degradation by nucleases. virD2 and virE2 interact with variety of plant proteins which influence the T-DNA transport and integration. The T-DNA – virD2 – virE2 – plant proteins complex enters the nucleus through nuclear pore complex (NPC). In the nucleus, T-DNA gets integrated into the plant genome by a process referred to as ‘illegitimate recombination'. This process is unlike homologous recombination as it does not depend on extensive region of sequence similarity.
