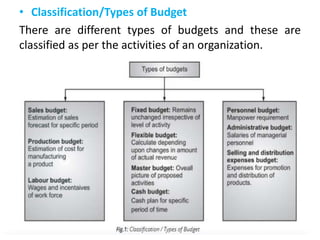
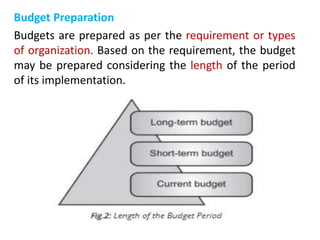
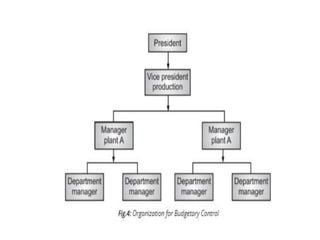
The document discusses budget preparation and implementation. It defines a budget as a financial plan for a defined period in the future. Budgets are used for planning, control, coordination, communication, performance evaluation, and motivation. There are different types of budgets such as long-term, short-term, and current budgets. Budget preparation involves determining revenue, expenses, capital equipment requests, and developing sections for these items. Effective budget implementation requires considering the actual financial position, utility and quantity of items, and product costs. Organization and control are also important aspects of managing the budgetary process.