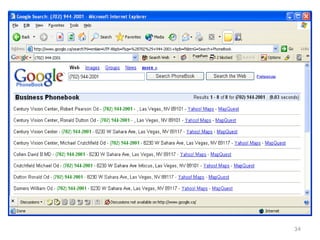
This chapter discusses using Google search techniques to find security vulnerabilities on websites. It covers both basic operators like +, -, and " to refine searches, as well as advanced operators like allintext:, filetype:, and intitle: to search specific fields. The goal is to quickly find sensitive information like login credentials, passwords, or internal documents through structured searches. A variety of example searches are provided to demonstrate how different operators can reveal website details and potentially sensitive data.