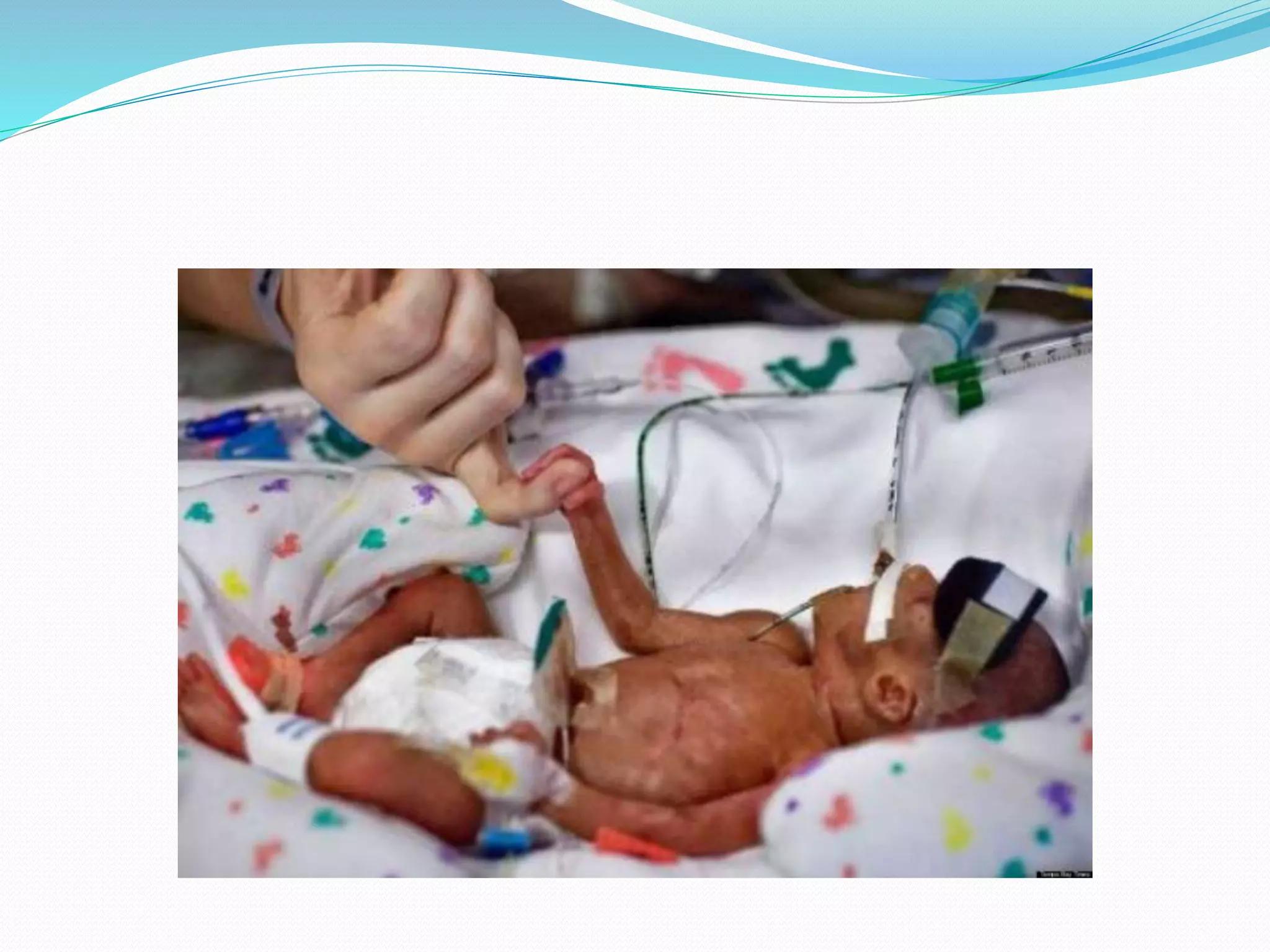
The document discusses infection prevention strategies in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs), highlighting the inherent risks faced by neonates such as low birth weight and prematurity. It emphasizes the importance of hand hygiene, proper staffing, environmental cleanliness, and strategic design to reduce the rate of infections. Key measures include limiting antibiotic use, adhering to aseptic techniques, and promoting breast milk feeding for enhanced immunity.