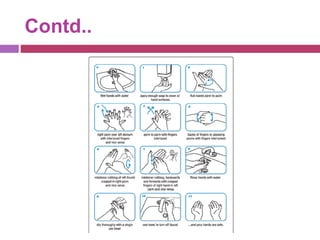
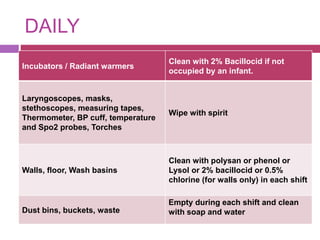
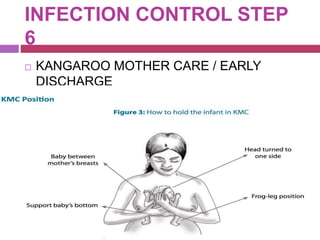
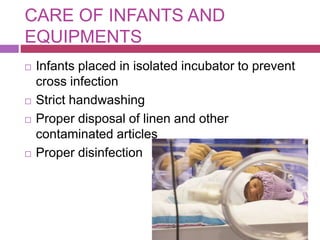
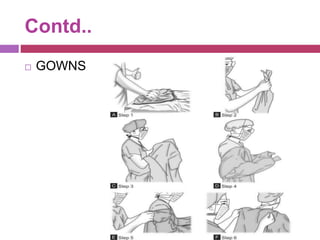
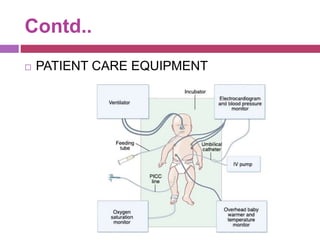
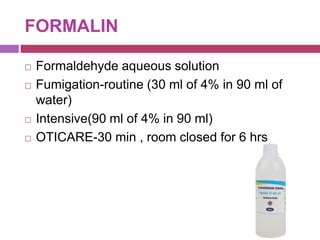
This document outlines infection control policies and procedures for a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU). It discusses why neonates are susceptible to infections, common infections seen in NICUs, and aseptic techniques. It then describes 8 steps for infection control: 1) preventing entry of microbes, 2) preventing proliferation of microbes, 3) preventing spread between babies, 4) protecting babies, 5) breastmilk protocols, 6) kangaroo mother care, 7) decreasing baby susceptibility, and 8) overall infection control protocols. Specific policies are provided for environmental cleaning, hand hygiene, equipment disinfection, waste disposal, and surveillance. The role of the infection control committee is also summarized.