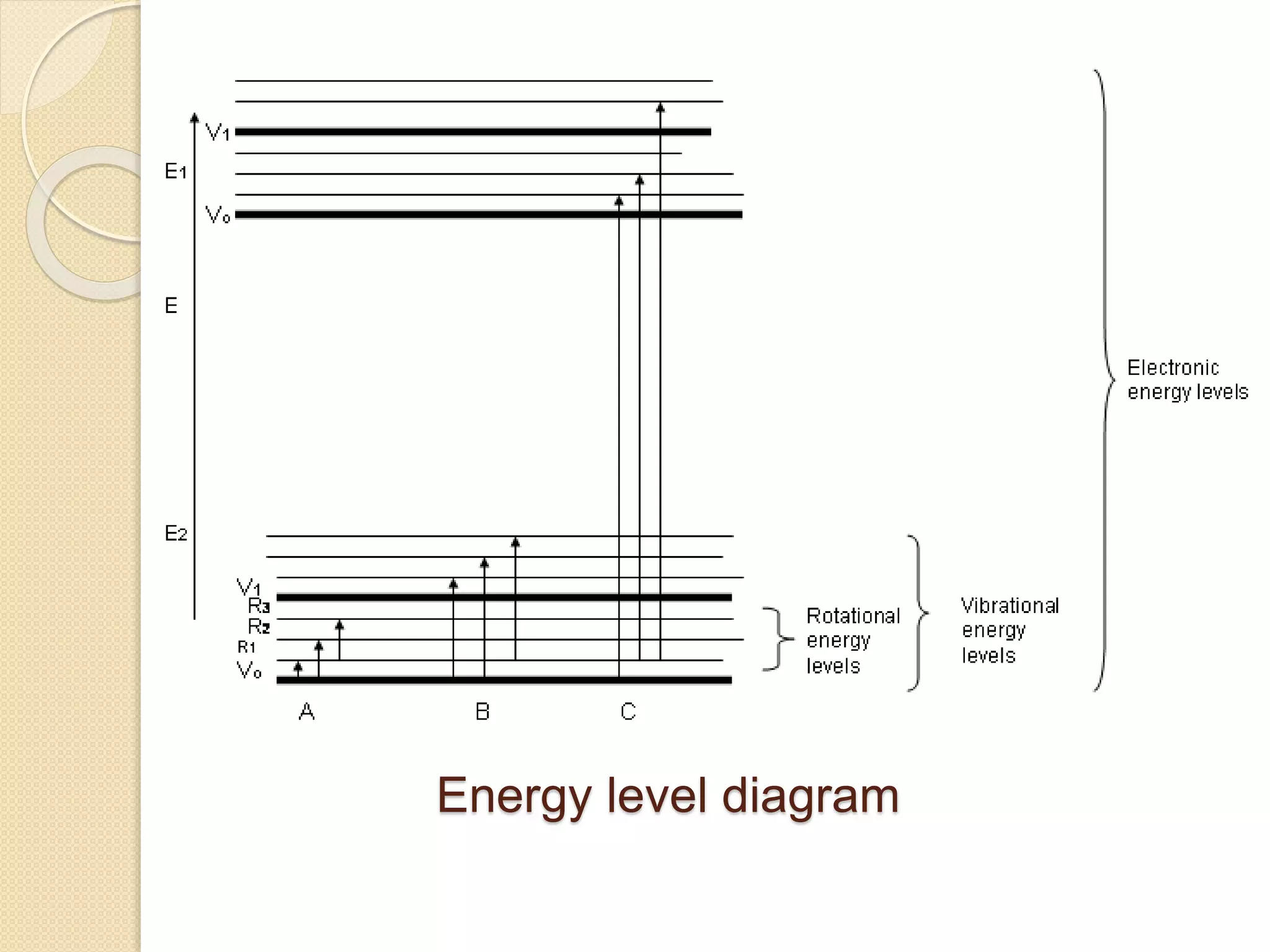
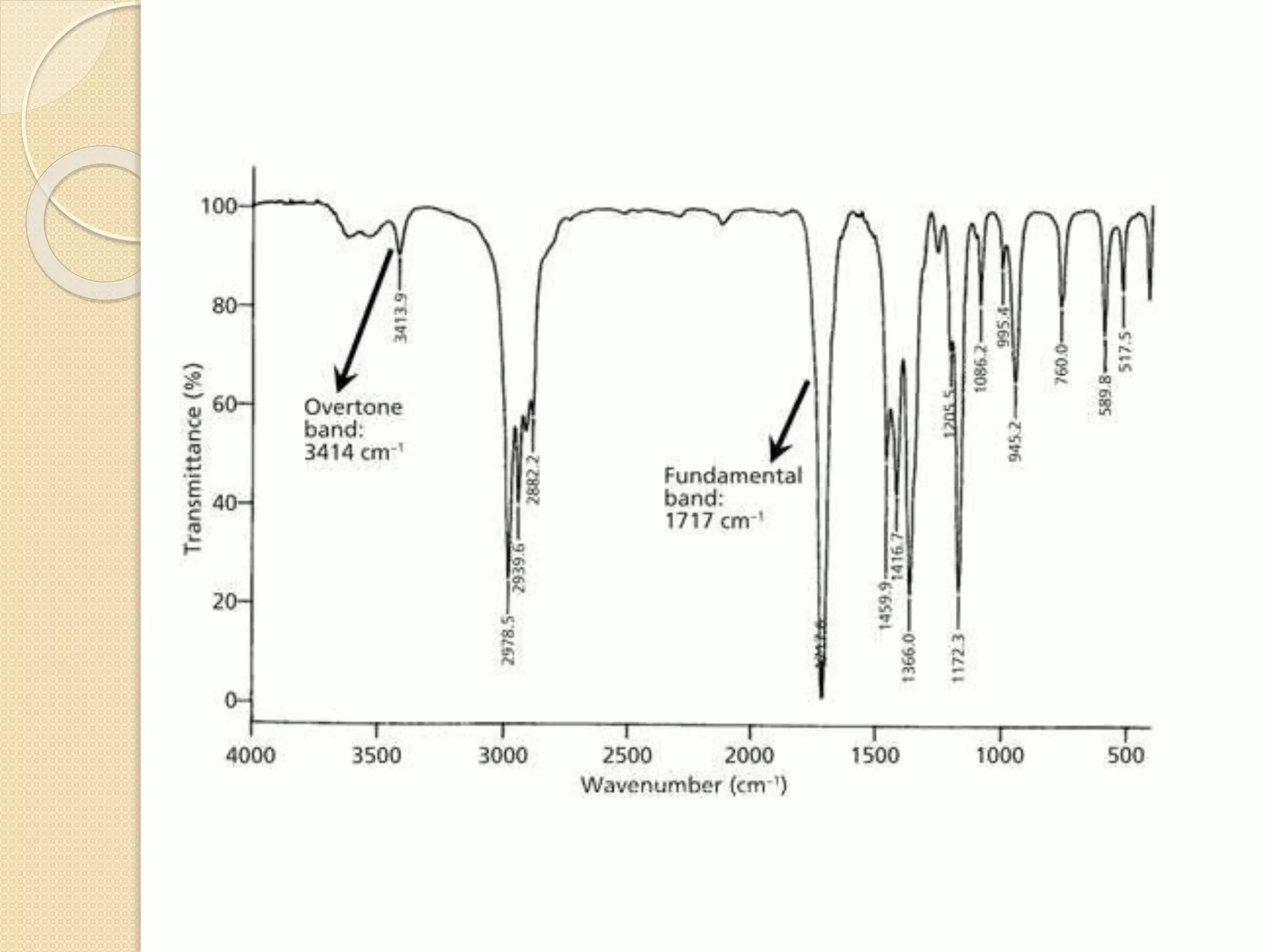
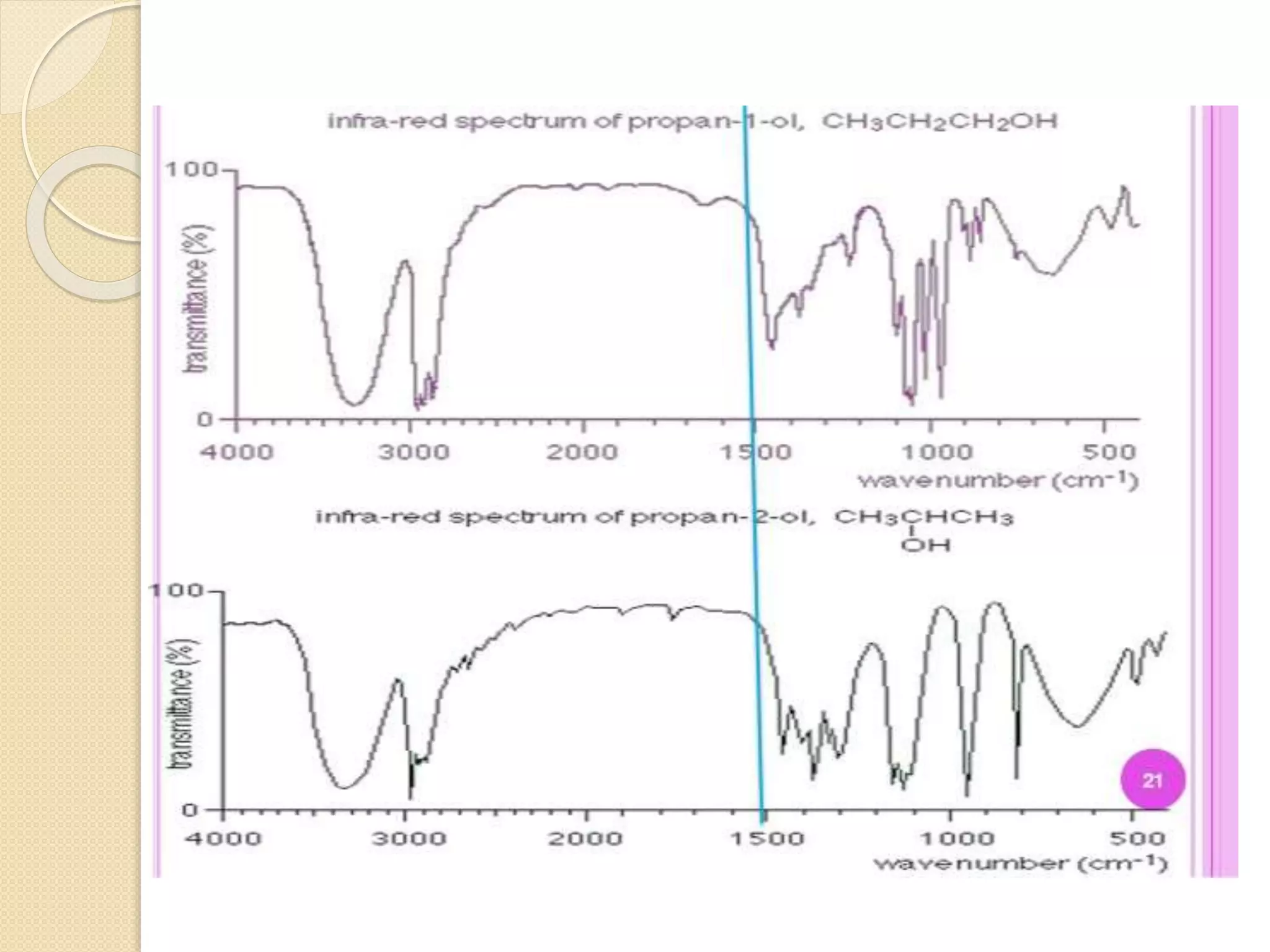
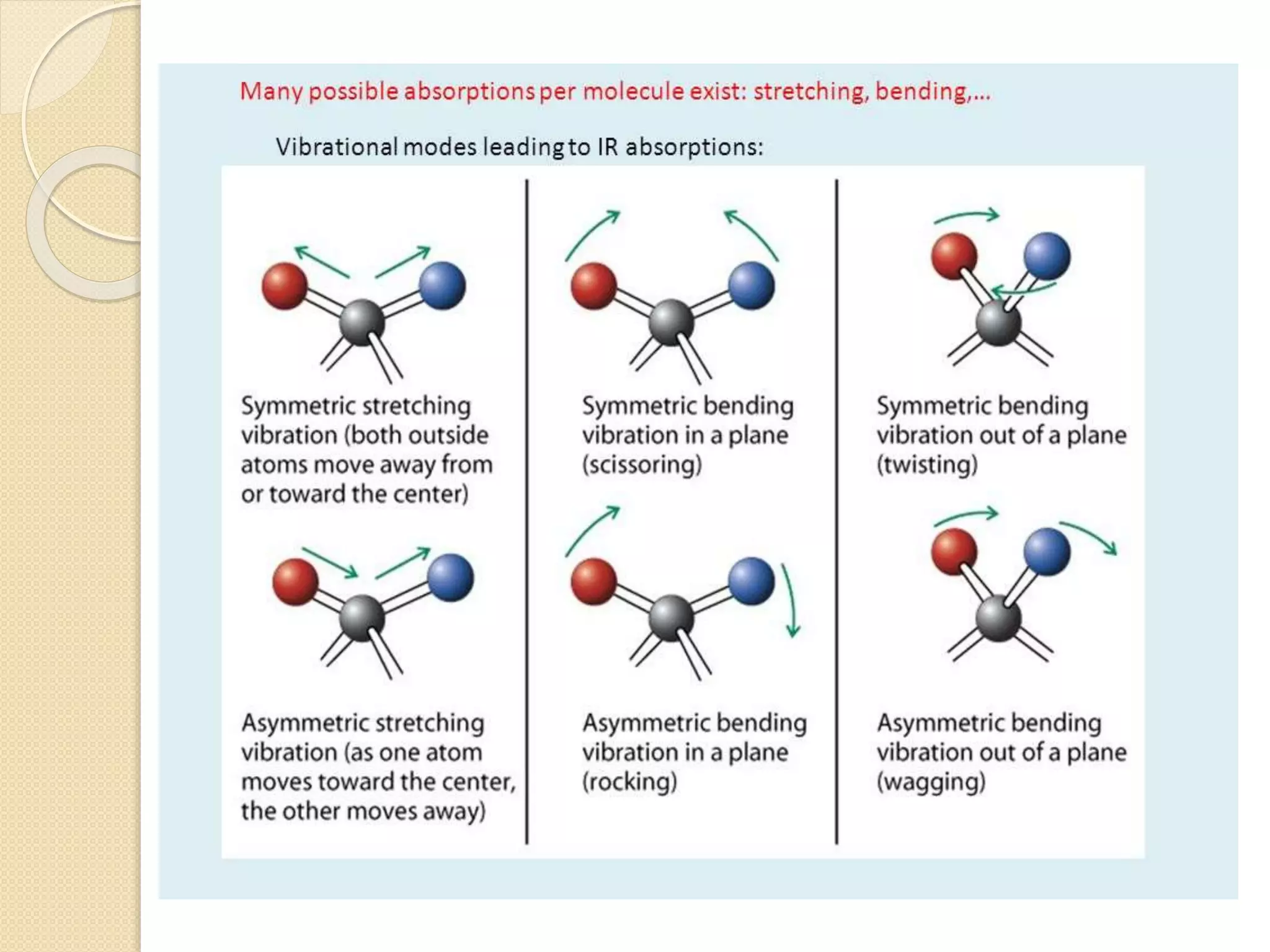
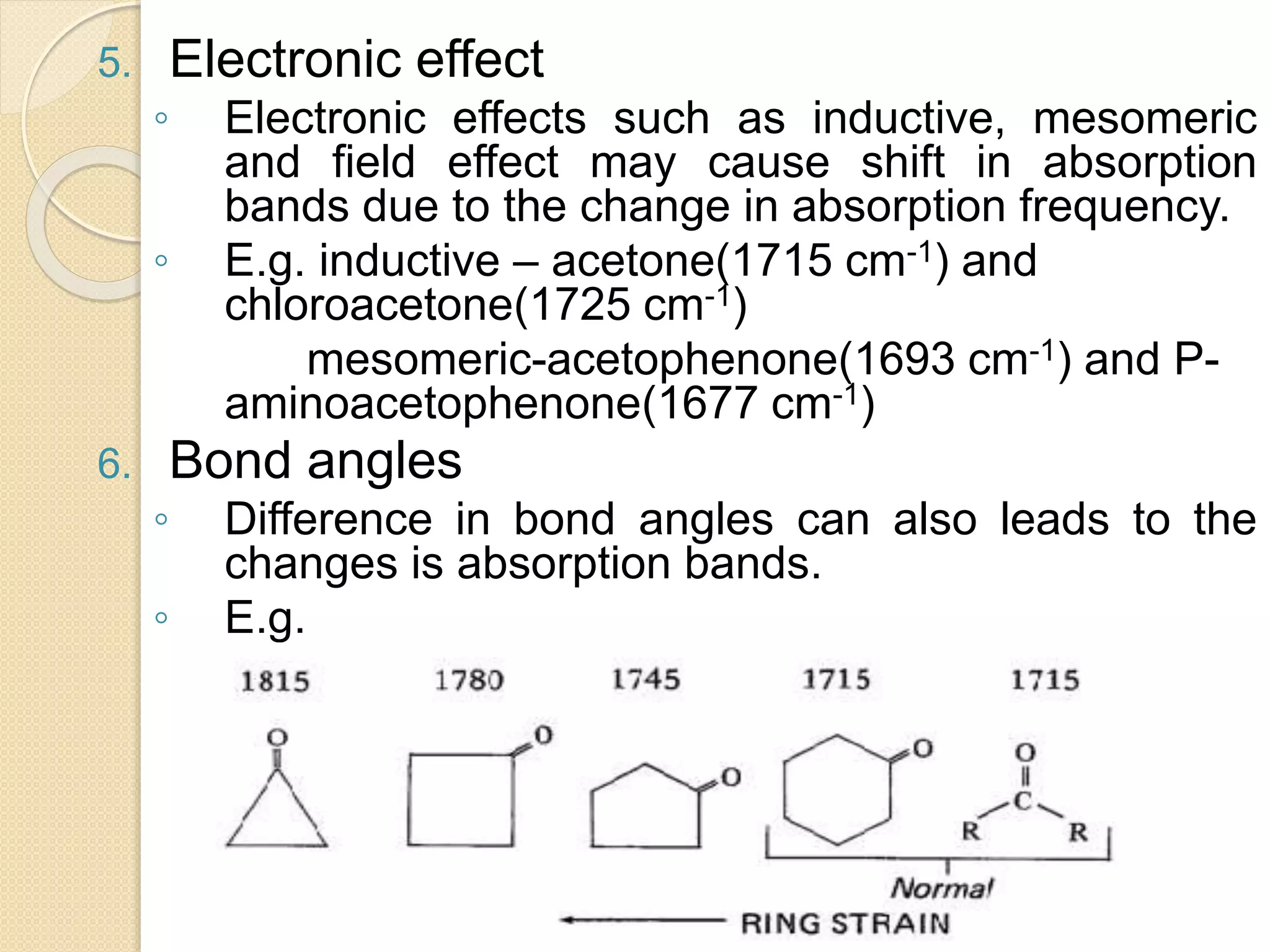
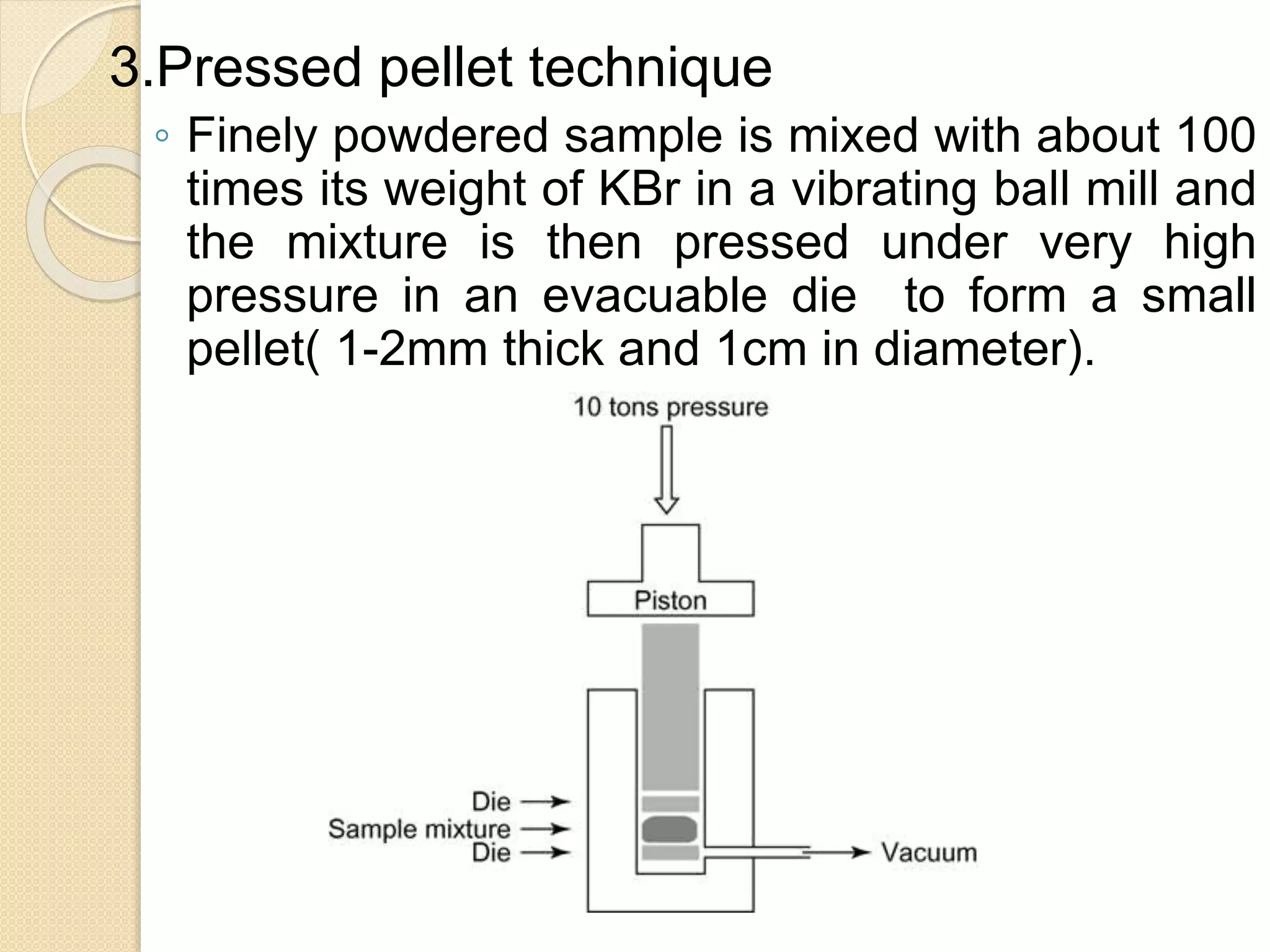
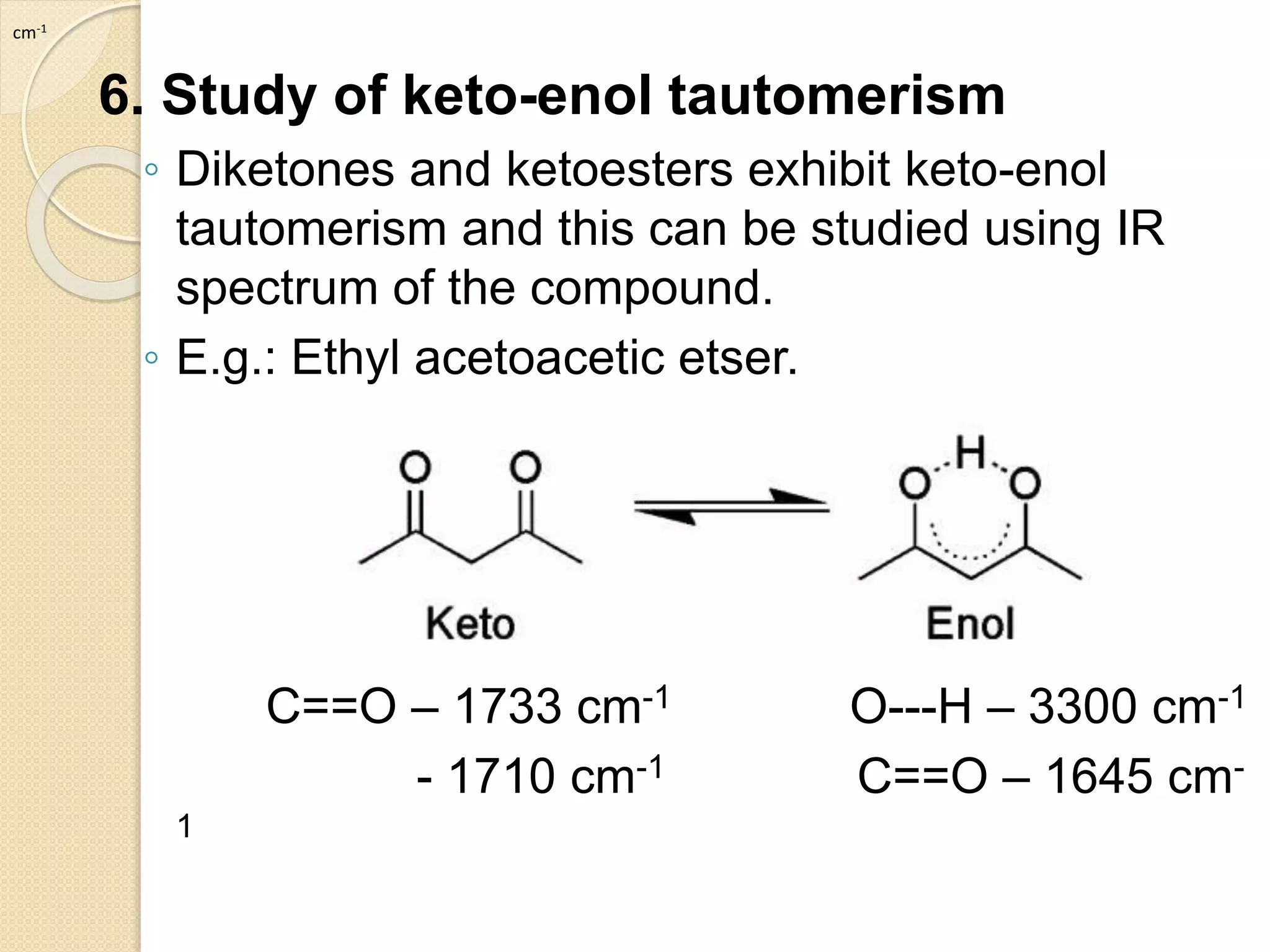
Infrared spectroscopy involves using infrared radiation to study molecular vibrations. When the frequency of infrared radiation matches the natural vibrational frequency of a molecule, absorption occurs, exciting the molecule to a higher vibrational state. Each bond in a molecule has characteristic vibrational frequencies that depend on the masses of the atoms and strength of the bonds. Infrared spectroscopy can be used to identify organic compounds based on their unique absorption frequencies, determine functional groups present, and study reactions and phenomena like hydrogen bonding and keto-enol tautomerism.