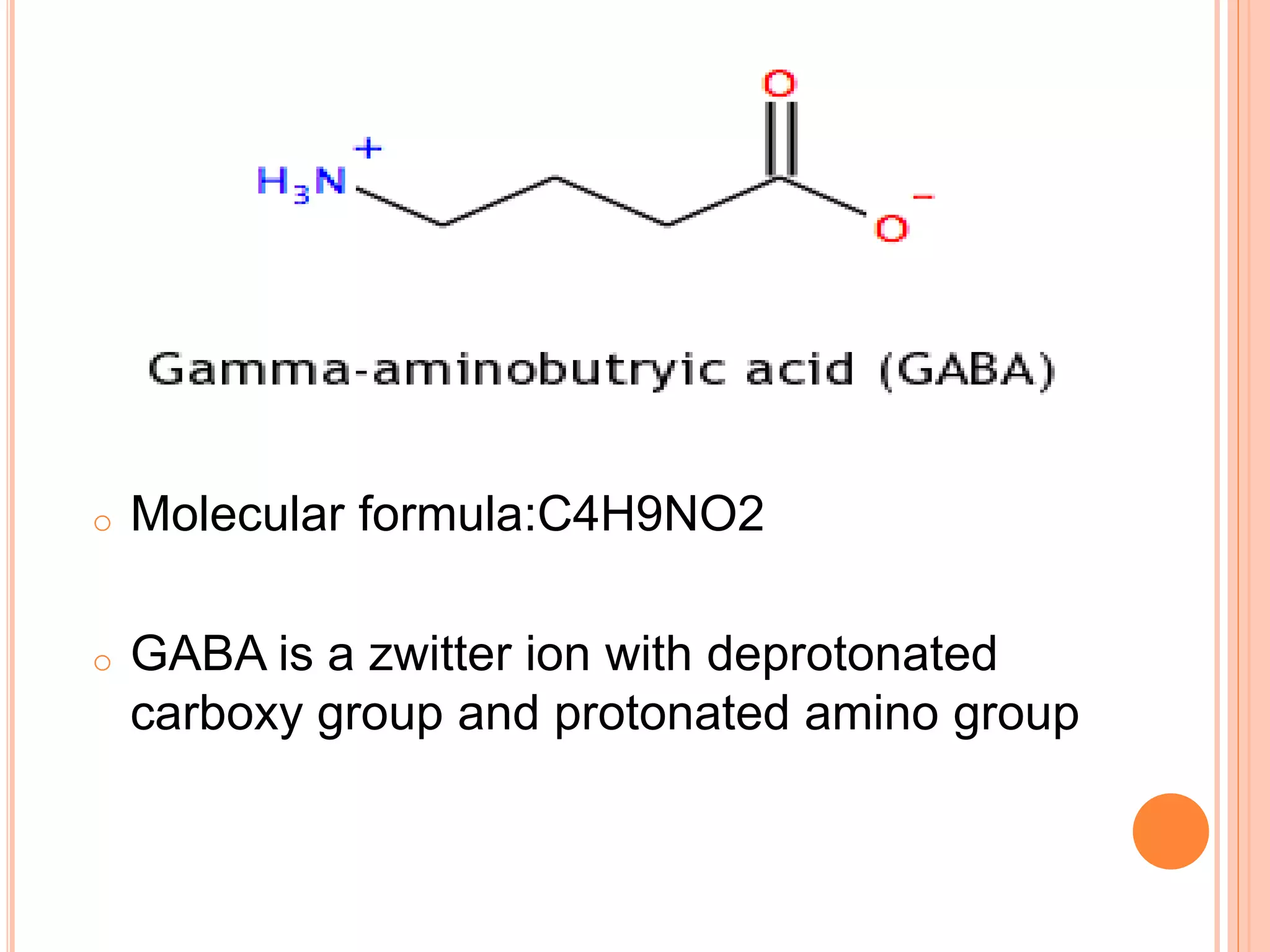
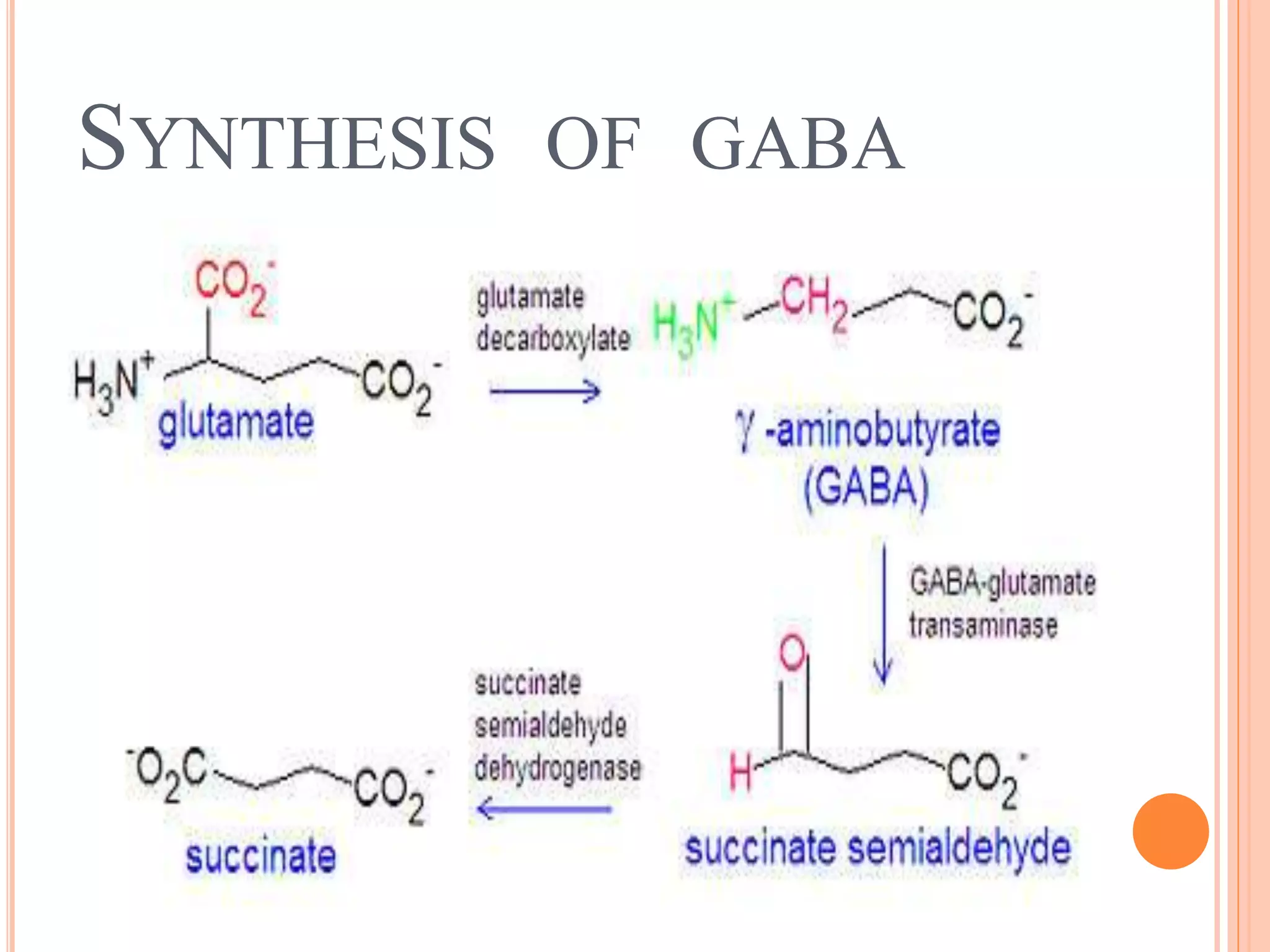
GABA is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mammalian central nervous system. It is synthesized in neurons and stored in synaptic vesicles until released into the synaptic cleft via calcium-dependent exocytosis. Upon binding to GABA receptors on postsynaptic neurons, GABA elicits inhibitory responses by increasing chloride ion conductance through ionotropic GABA-A receptors or by decreasing calcium conductance and increasing potassium conductance through metabotropic GABA-B receptors. GABA is then removed from the synaptic cleft via reuptake into presynaptic neurons and glial cells to terminate its action.