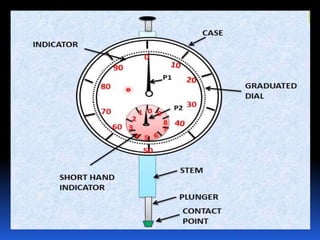
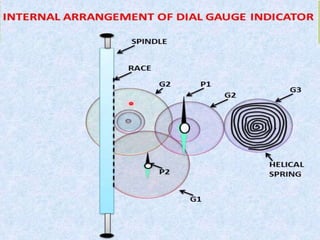
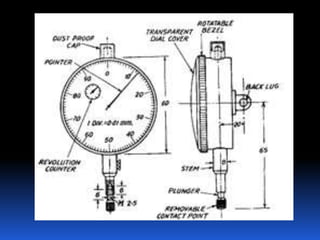
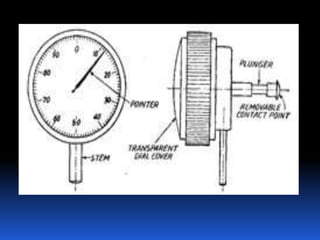
Dial gauges are precision measurement tools used in manufacturing. They have a circular dial body, graduated dial, pointer, gear train, and lever or plunger. There are several types of dial gauges differentiated by their size, connection method, and dial face features. Common types include balanced reading gauges with positive and negative numbers on the dial, continuous gauges with numbers running in one direction, and plunger gauges which use a rack and pinion mechanism. Dial gauges are used to measure small linear distances and detect errors in geometric forms, deformation, positional errors of surfaces, and other precision measurements in manufacturing applications.