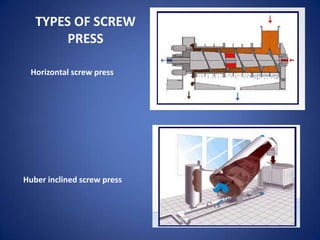
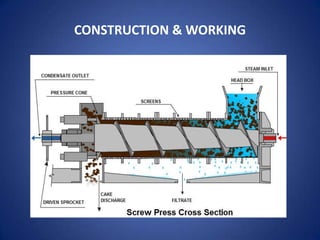
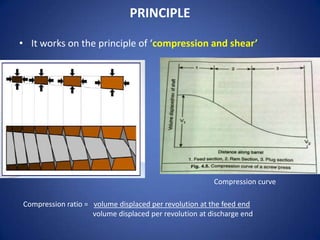
1. The document discusses screw presses, which are used to separate solids and liquids through compression and shear. It describes the types, construction, working principle, design considerations, and performance of screw presses.
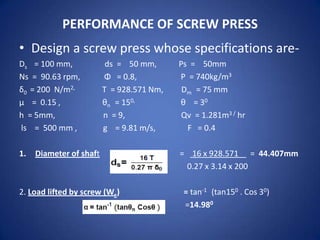
2. Key aspects of screw press design include the diameter of the shaft, load lifted by the screw thread, and pressure developed. Performance is determined by parameters like capacity, power requirement, oil yield, efficiency, and extraction loss.
3. Examples are provided to calculate screw press specifications and performance metrics like oil efficiency and effectiveness based on given operating conditions and extraction results.