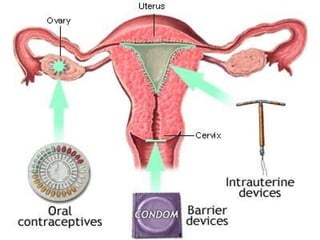
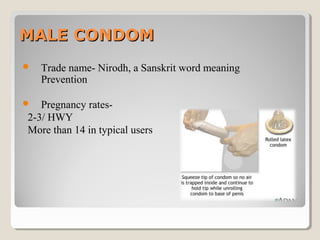
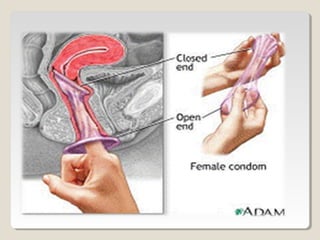
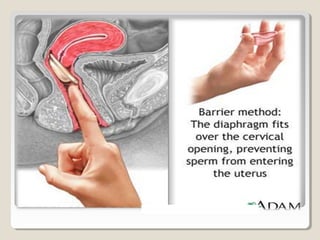
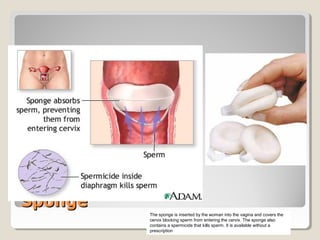
This document discusses various barrier contraceptive methods. It describes barrier methods as preventing pregnancy by blocking the egg and sperm from meeting and notes they have higher failure rates than hormonal methods due to design and human error. The main barrier methods discussed are male condoms, female condoms, diaphragms, vaginal sponges, and spermicides. Advantages and disadvantages of each method are provided.