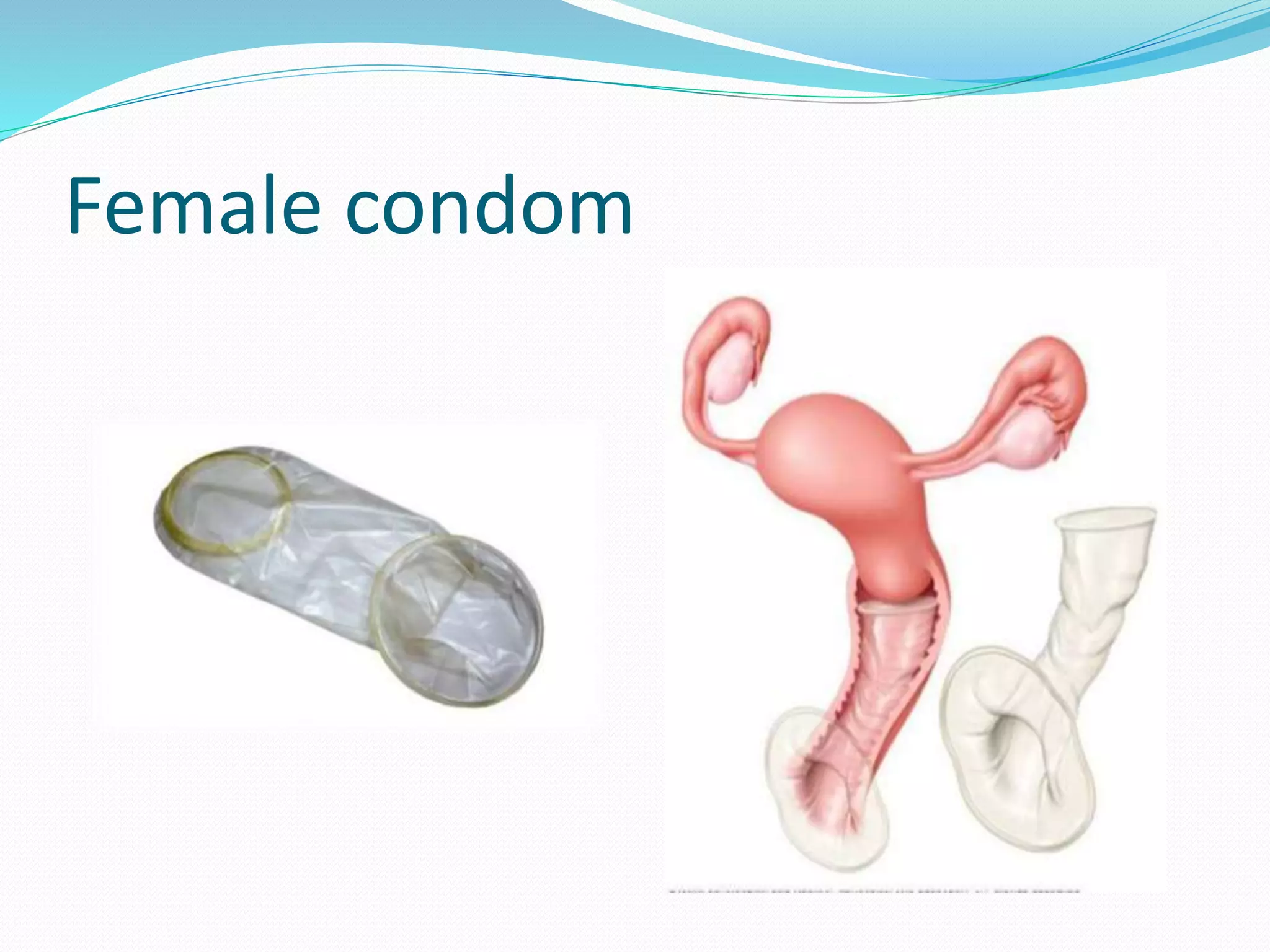
This document provides information on various contraceptive methods including barrier methods like condoms, diaphragms, and vaginal sponges. It describes how each method works, advantages and disadvantages, proper usage, and failure rates. Barrier methods prevent pregnancy by blocking sperm from entering the uterus. Condoms are the most commonly used barrier method and can be male or female condoms. Diaphragms are shallow cups that cover the cervix while sponges are small foam devices inserted into the vagina. Spermicides are chemical methods that can be used with barriers to kill sperm.