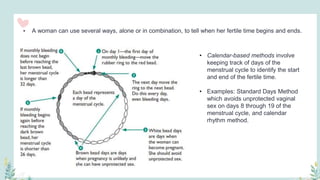
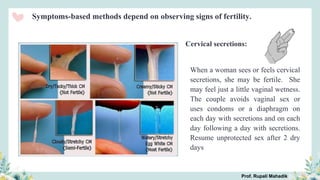
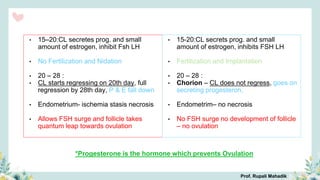
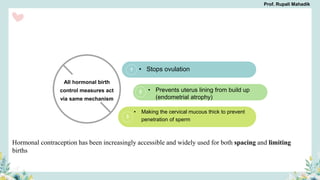
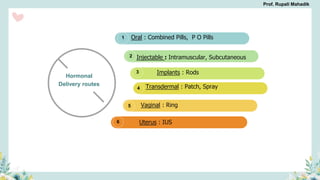
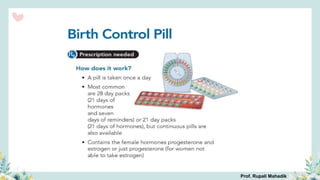
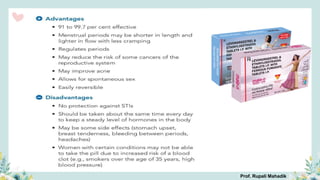
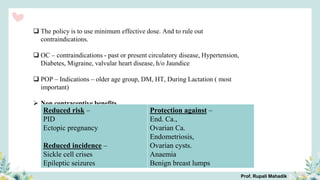
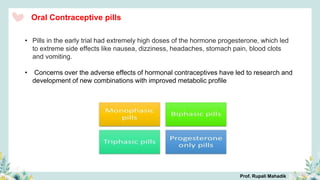
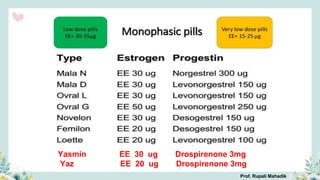
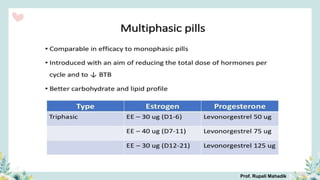
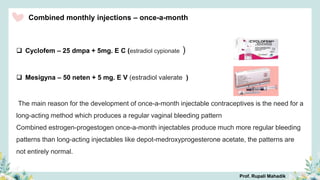
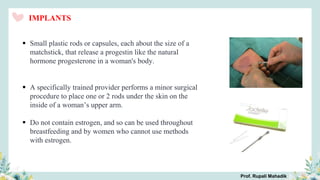
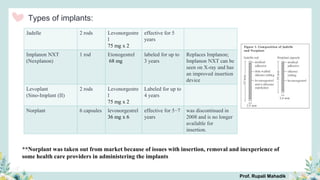
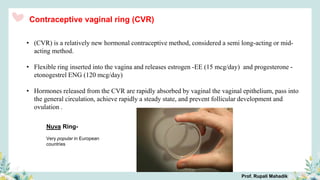
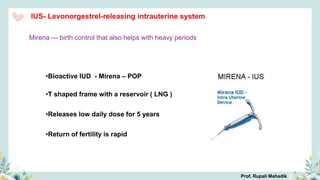
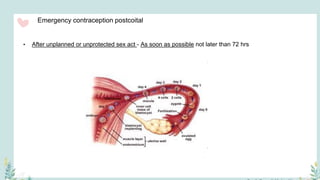
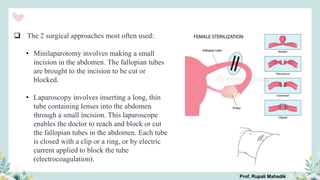
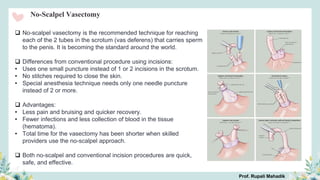
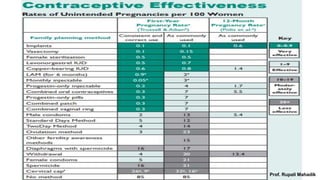
India has a historical family planning program, established in 1952, aimed at controlling population growth and enhancing maternal and newborn health. Contraceptive methods include temporary, permanent, and natural options, with varying effectiveness and procedures for use; they are crucial for reducing maternal and child mortality. Despite challenges in consistent use of contraceptives, education and access to services are vital for improving reproductive health outcomes.