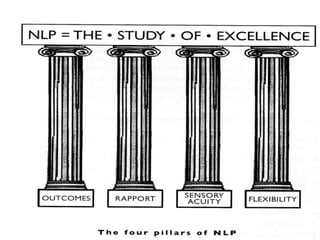
NLP involves the neurological processes of how we experience the world through our senses, the linguistic representation of our experiences, and training ourselves to think and act in new positive ways. The document also provides guidance on using feedback constructively, delivering positive messages, setting outcomes with students, and using stories and guided fantasies to impart metaphors.