Bacteriophages and plasmids
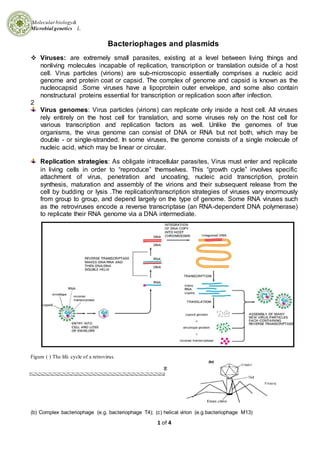
- 1. Molecularbiology& Microbial genetics L. 1 of 4 Bacteriophages and plasmids Viruses: are extremely small parasites, existing at a level between living things and nonliving molecules incapable of replication, transcription or translation outside of a host cell. Virus particles (virions) are sub-microscopic essentially comprises a nucleic acid genome and protein coat or capsid. The complex of genome and capsid is known as the nucleocapsid .Some viruses have a lipoprotein outer envelope, and some also contain nonstructural proteins essential for transcription or replication soon after infection. 2 Virus genomes: Virus particles (virions) can replicate only inside a host cell. All viruses rely entirely on the host cell for translation, and some viruses rely on the host cell for various transcription and replication factors as well. Unlike the genomes of true organisms, the virus genome can consist of DNA or RNA but not both, which may be double - or single-stranded. In some viruses, the genome consists of a single molecule of nucleic acid, which may be linear or circular. Replication strategies: As obligate intracellular parasites, Virus must enter and replicate in living cells in order to “reproduce” themselves. This “growth cycle” involves specific attachment of virus, penetration and uncoating, nucleic acid transcription, protein synthesis, maturation and assembly of the virions and their subsequent release from the cell by budding or lysis .The replication/transcription strategies of viruses vary enormously from group to group, and depend largely on the type of genome. Some RNA viruses such as the retroviruses encode a reverse transcriptase (an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase) to replicate their RNA genome via a DNA intermediate. Figure ( ) The life cycle of a retrovirus. (b) Complex bacteriophage (e.g. bacteriophage T4); (c) helical virion (e.g.bacteriophage M13)
- 2. Molecularbiology& Microbial genetics L. 2 of 4 Bacteriophages, or phages, any virus that infects bacteria; many (perhaps most, or all) bacteria are susceptible to one or more types of phage. A given phage may specifically infect bacteria of only one species or strain, or it may have a wider host range. Phages are often said to be virulent or temperate. A virulent phage lyses (kills) the bacterial host cell. A temperate phage can form a more or less stable relationship with a bacterium; in most cases the phage genome (the prophage) integrates in the bacterial chromosome, but in some cases (e.g. phage P1) it remains a circular, extrachromosomal ‘plasmid’. Under certain conditions a temperate phage may be induced to enter the lytic cycle – in which case virions are formed and cell lysis occurs; thus, a prophage may retain the potential for virulence, and in a population of lysogenic bacteria (i.e. bacteria which are hosts to a temperate phage), spontaneous induction may occur in a small number of cells. Phages commonly consist of nucleic acid enclosed within a protein coat called a capsid. However, certain phages contain lipid, either within the virion or as an outer envelope and certain phages contain components such as fucose or spermidine. Bacteriophages have played an important role in the history of both virology and molecular biology. They have important tools in the original identification of DNA as the genetic material, and many more fundamental concepts of molecular biology. Many studies have been carried out to investigate the use of phages against the bacteria that cause certain human diseases. Phage-encoded endolysins (enzymes that cleave the bacterial cell-wall polymer peptidoglycan) have also been considered as therapeutic agents. Some phages are also used as cloning vectors.
- 3. Molecularbiology& Microbial genetics L. 3 of 4 Plasmids are small, extrachromosomal DNA molecules that are stably inherited from one generation to another in the extra-chromosomal state. Usually closed circles of either single-stranded or double-stranded DNA (mostly). Plasmids are widely distributed throughout prokaryotes and range in size from approximately 1500 bp to over 300 kbp. Plasmids are commonly dispensable, i.e. not essential to their host cells, and not all cells contain plasmids; for example, plasmids are commonly absent in bacteria of the genera, Brucella and Rickettsia. The replication of the plasmid is often coupled to that of the host cell in which it is maintained, with plasmid replication occurring at the same time as the host genome is replicated. They contain an origin of replication (ori), which enables them to be replicated independently, although this normally relies on polymerases and other components of the host cell’s machinery. Features encoded by plasmids: Collectively, the plasmids encode a vast range of functions. In many cases they encode resistance to particular antibiotics or groups of antibiotics and/or to other inimical agents – such as mercury (or other heavy metal) ions. In certain pathogenic bacteria (e.g. Bacillus anthracis, causal agent of anthrax) the toxin(s) and/or other virulence factors are plasmid-encoded. (In some pathogens the virulence factors are phage-encoded.) Some plasmids encode products (such as particular enzymes) which enhance the metabolic potential of a cell; for example, the Cit plasmid in some strains of Escherichia coli enables those strains to use citrate as the sole source of carbon and energy (an ability which is lacking in wild-type strains of E. coli). Again, the TOL plasmid confers on certain strains of Pseudomonas the ability to metabolize toluene and xylene. Certain plasmids (e.g. ColE1) encode a colicin or other type of bacteriocin. In the archaean Halobacterium, structural components of gas vacuoles are plasmid- encoded. Size: In size, plasmids typically range from about several kilobases to several hundred kilobases. In DNA technology, the small circular plasmids can be inserted into cells by transformation more readily than large plasmids; moreover, small plasmids are less susceptible to damage by shearing forces. In general, linear plasmids are poorly transformable e.g. in normal cells of E. coli – although linear forms of DNA can be transformed by using a method such as the lambda (λ) red recombination system. Copy number: The copy number is characteristic for a given plasmid, in a particular host cell, under given conditions. Plasmids are referred to as ‘low-copy-number’ if they occur singly, or in a few copies, in each cell; the f plasmid is one example. Multicopy plasmids are normally present in appreciably higher numbers – e.g. >10 copies; the ColE1 plasmid (often 10–30 copies) is one example. Factors which influence copy number include the plasmid’s specific type of replication control system and its mode of partition (segregation to daughter cells during cell division). Compatibility: Inc groups: Different types of plasmid can occur in the same cell: those plasmids which have different modes of replication and partition are said to exhibit compatibility; such plasmids are able to co-exist – stably – within the same cell. On the other hand, plasmids with similar or identical systems of replication/partition are incompatible: they are not able to co-exist, stably, in the same cell. This is the basis of the incompatibility groups (the so-called Inc groups): a given Inc group consists of those plasmids which have similar or identical replication/partition systems and which cannot co-exist, stably, in the same cell.
- 4. Molecularbiology& Microbial genetics L. 4 of 4 Engineered plasmids: Plasmids have been engineered in order to carry out a great diversity of functions. For example, plasmids are widely used as cloning vectors, as expression vectors and as vehicles for introducing genetic material into cells. They are also used in studies on gene expression and on the mechanisms of intracellular signaling. Experimental elimination of plasmids: In some cases there is a need for plasmid- free cells. Various approaches have been used to eliminate plasmids from a bacterial population: e.g. curing. Plasmid stability: Plasmid-borne features are often lost from a population at a higher frequency than would be expected for the normal processes of mutation. The extent of this instability varies from one plasmid to another. Naturally-occurring plasmids are usually (but not always) reasonably stable. Artificially constructed plasmids on the other hand are often markedly unstable. Naming genes and DNA: Traditionally, recombinant plasmids tend to bear the initials of their creator(s) followed by a number that may indicate the numerical order in which the plasmids were produced, or perhaps has some deeper meaning. For example, the name of the plasmid pBR322 can be dissected into the following components: p – Plasmid, BR – named by Paco Bolivar and Ray Rodrigues, who developed the plasmid and 322 – the number of the plasmid within their stock collection. Plasmids and phages provide an important extra dimension to the flexibility of the organism’s response to changes in its environment, whether those changes are hostile (e.g. the presence of antibiotics) or potentially favorable (the availability of a new substrate). This extra dimension therefore consists of characteristics that are peripheral to the replication and production of the basic structure of the cell – they are the optional extras. Their role in contributing these additional characteristics is particularly significant because of the relative ease with which they can be transferred between strains or between different species Many DNA sequences can replicate independently of the rest of the genome. Such sequences have widely different degrees of independence from their host cells. Of these, virus chromosomes are the most independent because they have a protein coat that allows them to move freely from cell to cell. The viruses are closely related to plasmids and transposable elements, which are DNA sequences that lack a coat and are therefore more host cell- dependent and confined to replicate within a single cell and its progeny. Transposable elements are DNA sequences that differ from viruses in being able to multiply only in their host cell and its progeny; like plasmids, they cannot exist stably outside of cells. Unlike plasmids, they normally replicate only as an integral part of a chromosome. Some transposable elements, however, are closely related to retroviruses and can move from place to place in the genome by the reverse transcription of an RNA intermediate. Both viruses and transposable elements can be viewed as parasites.
