Differences Between Gram Positive and Gram Negative Cell Walls
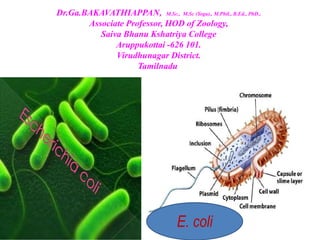
- 1. Dr.Ga.BAKAVATHIAPPAN, M.Sc., M.Sc (Yoga)., M.Phil., B.Ed., PhD., Associate Professor, HOD of Zoology, Saiva Bhanu Kshatriya College Aruppukottai -626 101. Virudhunagar District. Tamilnadu E. coli
- 2. • Escherichia coli • also known as E. coli is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus Escherichia that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. • Theodor Escherich, the German physician who discovered Escherichia coli. • Most E. coli strains are harmless, but some serotypes (EPEC, ETEC etc) can cause serious food poisoning in their hosts. • The harmless strains are part of the normal micro-biota of the gut, and can benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2. • E. coli is expelled into the environment within faecal matter. The bacterium grows massively in fresh faecal matter under aerobic conditions for 3 days, but its numbers decline slowly afterwards.
- 10. Some of the differences between Fimbriae and Pili are as follows: Characteristics Fimbriae Pili Definition Fimbriae are tiny bristle-like fibres arising from the surface of bacterial cells. Pili are hair like microfibers that are thick tubular structure made up of pilin. Length Thin and Shorter than pili, Less rigid. Thicker and Longer than fimbriae, Rigid Number No. of fimbriae are 200-400 per cell. No of pili are less 1-10 per cell. Made up of Fimbrillin protein Pilin protein. Found in Both gram positive and gram negative bacteria. Only gram negative bacteria. Function Responsible for cell to surface attachment. Specialized for attachment i.e. enable the cell to adhere the surfaces of other bacteria. Responsible for bacterial conjugation. Two basic function of pili. They are gene transfer and attachment.
- 12. Pili differ from flagella in being shorter and thinner, straight and less ligid. But they are in large number. The sex pili make contact between two cells. Since they posses hollow core, they act as conjugation tube. The tip of pilus recognises the female (F–) cell through which the genetic material of donor (F+) cell passes to the recipient (female) cell.
- 16. Plasmid A plasmid is a small, circular piece of DNA that is different than the chromosomal DNA. It replicates independently of chromosomal DNA. Plasmids are mainly found in bacteria There are five main types of plasmids: fertility F-plasmids, resistance plasmids, virulence plasmids, degradative plasmids, and Col plasmids. Fertility plasmids, also known as F-plasmids, contain transfer genes that allow genes to be transferred from one bacteria to another through conjugation. Bacteria that have the F-plasmid are known as F positive (F+), and bacteria without it are F negative (F–). Resistance or R plasmids contain genes that help a bacterial cell defend against environmental factors such as poisons or antibiotics. Some resistance plasmids can transfer themselves through conjugation. Virulence plasmids, which turn the bacterium into a pathogen. e.g. Ti plasmid in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Degradative plasmids, which enable the digestion of unusual substances, e.g. toluene and salicylic acid. Col plasmids contain genes that make bacteriocins (also known as colicins), which are proteins that kill other bacteria and thus defend the host bacterium.
- 17. • Plasmids are used in genetic engineering to amplify, or produce many copies of, certain genes. • In molecular cloning, a plasmid is a type of vector. • A vector is a DNA sequence that can transport foreign genetic material from one cell to another cell, where the genes can be further expressed and replicated. • Plasmids are useful in cloning short segments of DNA. • Also, plasmids can be used to replicate proteins, such as the protein that codes for insulin, in large amounts.
- 26. • Both gram positive and gram negative cell walls contain an ingredient known as peptidoglycan (also known as murein). • Peptidoglycan is a polysaccharide made of two glucose derivatives, N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and N- acetylmuramic acid (NAM), alternated in long chains. The chains are cross-linked to one another by a tetrapeptide that extends off the NAM sugar unit, allowing a lattice-like structure to form. The four amino acids that compose the tetrapeptide are: L-alanine, D-glutamine, L-lysine or meso- diaminopimelic acid (DPA), and D-alanine.
- 27. • The cell walls of gram negative bacteria are more complex than that of gram positive bacteria, with more ingredients overall. They do contain peptidoglycan as well, although only a couple of layers, representing 5-10% of the total cell wall. What is most notable about the gram negative cell wall is the presence of a plasma membrane located outside of the peptidoglycan layers, known as the outer membrane. This makes up the bulk of the gram negative cell wall. • It differs from the cell membrane by the presence of large molecules known as lipopolysaccharide (LPS), which are anchored into the outer membrane and project from the cell into the environment. LPS is made up of three different components: 1) the O-antigen or O-polysaccharide, which represents the outermost part of the structure , 2) the core polysaccharide, and 3) lipid A, which anchors the LPS into the outer membrane. LPS is known to serve many different functions for the cell.
- 28. • The cell walls of gram positive bacteria are composed predominantly of peptidoglycan. In fact, peptidoglycan can represent up to 90% of the cell wall, with layer after layer forming around the cell membrane. The NAM tetrapeptides are typically cross-linked with a peptide interbridge and complete cross-linking is common. All of this combines together to create an incredibly strong cell wall. • The additional component in a gram positive cell wall is teichoic acid, a glycopolymer, which is embedded within the peptidoglycan layers. Teichoic acid is believed to play several important roles for the cell, such as generation of the net negative charge of the cell, which is essential for development of a proton motive force.