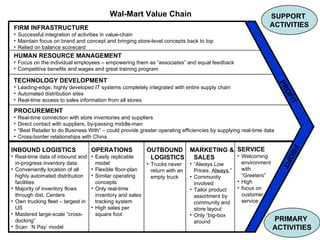
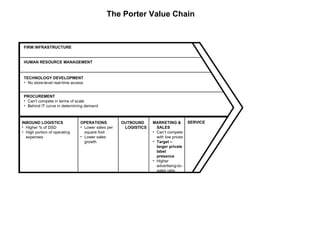
Wal-Mart has a highly integrated and efficient value chain. They focus on welcoming customers, low prices, and tailoring products to local communities. Wal-Mart collects real-time data on store inventories, sales, and supplier relationships to efficiently manage procurement, logistics, and operations across their large network. They invest heavily in technology and training employees to maintain low costs and drive profitability.