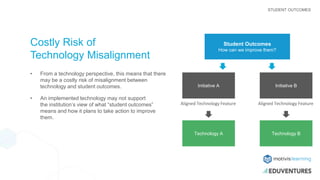
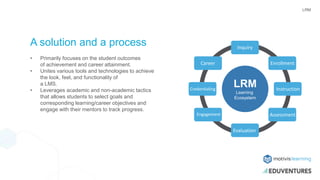
The document discusses improving student outcomes in higher education through enhanced teaching quality, student relationships, and institutional technologies, emphasizing the importance of aligned technological solutions. It highlights the challenges institutions face in defining student outcomes and the role of Learning Relationship Management (LRM) systems in facilitating these improvements. Moreover, the presenters share their expertise and the Motivis Learning approach to creating individualized learning environments that track and support student progress effectively.