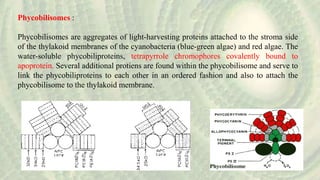
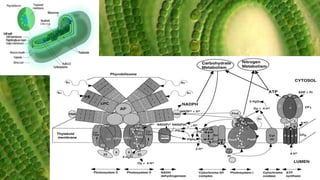
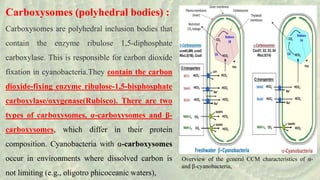
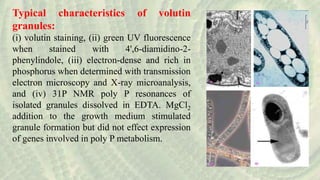
Cyanoprokaryotes, commonly known as blue-green algae, are prokaryotic organisms characterized by the absence of a nuclear membrane and membrane-bound organelles. They consist of around 150 genera and 2,500 species, with significant diversity in India. Key features include various types of pigments, a specialized cell structure, and reproduction methods that exclude sexual reproduction, with nitrogen storage using cyanophycin and carbon fixation occurring in carboxysomes.