Using screencasts to teach undergraduate programming
•
1 like•212 views
King's Learning Institute, King's College London, 2017
Report
Share
Report
Share
Download to read offline
Recommended
Anna Levick, New College Pontefract alternative approaches to assessing & p...

Anna Levick, New College Pontefract alternative approaches to assessing & p...JISC Regional Support Centre
More Related Content
What's hot
Anna Levick, New College Pontefract alternative approaches to assessing & p...

Anna Levick, New College Pontefract alternative approaches to assessing & p...JISC Regional Support Centre
What's hot (20)
Are you talking to me? Lecture capture as a tool to improve learning.

Are you talking to me? Lecture capture as a tool to improve learning.
Training in audio visual techniques and powerpoint class 3

Training in audio visual techniques and powerpoint class 3
Anna Levick, New College Pontefract alternative approaches to assessing & p...

Anna Levick, New College Pontefract alternative approaches to assessing & p...
Miller - Best Practices for Using Videos in Courses

Miller - Best Practices for Using Videos in Courses
Screencasting for Staff and Student Development - MAME 2010

Screencasting for Staff and Student Development - MAME 2010
Similar to Using screencasts to teach undergraduate programming
Similar to Using screencasts to teach undergraduate programming (20)
Ready, Set, Record: Being Present and Engaging Students Online Using YouTube

Ready, Set, Record: Being Present and Engaging Students Online Using YouTube
Creating effective student-edited, self reflective essays

Creating effective student-edited, self reflective essays
Lesson 1 1 screencast o-matic description and uses

Lesson 1 1 screencast o-matic description and uses
EMMA Summer School - Mathy Vanbuel - Choosing to implement video in your MOOC...

EMMA Summer School - Mathy Vanbuel - Choosing to implement video in your MOOC...
Presentation on ShotCut - How to edit video and audio

Presentation on ShotCut - How to edit video and audio
More from Martin Chapman
More from Martin Chapman (20)
Principles of Health Informatics: Artificial intelligence and machine learning

Principles of Health Informatics: Artificial intelligence and machine learning
Principles of Health Informatics: Clinical decision support systems

Principles of Health Informatics: Clinical decision support systems
Mechanisms for Integrating Real Data into Search Game Simulations: An Applica...

Mechanisms for Integrating Real Data into Search Game Simulations: An Applica...
Using AI to understand how preventative interventions can improve the health ...

Using AI to understand how preventative interventions can improve the health ...
Using AI to autonomously identify diseases within groups of patients

Using AI to autonomously identify diseases within groups of patients
Using AI to understand how preventative interventions can improve the health ...

Using AI to understand how preventative interventions can improve the health ...
Principles of Health Informatics: Evaluating medical software

Principles of Health Informatics: Evaluating medical software
Principles of Health Informatics: Usability of medical software

Principles of Health Informatics: Usability of medical software
Principles of Health Informatics: Social networks, telehealth, and mobile health

Principles of Health Informatics: Social networks, telehealth, and mobile health
Principles of Health Informatics: Communication systems in healthcare

Principles of Health Informatics: Communication systems in healthcare
Principles of Health Informatics: Terminologies and classification systems

Principles of Health Informatics: Terminologies and classification systems
Principles of Health Informatics: Representing medical knowledge

Principles of Health Informatics: Representing medical knowledge
Principles of Health Informatics: Informatics skills - searching and making d...

Principles of Health Informatics: Informatics skills - searching and making d...
Principles of Health Informatics: Informatics skills - communicating, structu...

Principles of Health Informatics: Informatics skills - communicating, structu...
Principles of Health Informatics: Models, information, and information systems

Principles of Health Informatics: Models, information, and information systems
Using AI to understand how preventative interventions can improve the health ...

Using AI to understand how preventative interventions can improve the health ...
Using Microservices to Design Patient-facing Research Software

Using Microservices to Design Patient-facing Research Software
Recently uploaded
TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...

TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
Recently uploaded (20)
HMCS Max Bernays Pre-Deployment Brief (May 2024).pptx

HMCS Max Bernays Pre-Deployment Brief (May 2024).pptx
Micro-Scholarship, What it is, How can it help me.pdf

Micro-Scholarship, What it is, How can it help me.pdf
Fostering Friendships - Enhancing Social Bonds in the Classroom

Fostering Friendships - Enhancing Social Bonds in the Classroom
TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...

TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...
Python Notes for mca i year students osmania university.docx

Python Notes for mca i year students osmania university.docx
Food safety_Challenges food safety laboratories_.pdf

Food safety_Challenges food safety laboratories_.pdf
ICT role in 21st century education and it's challenges.

ICT role in 21st century education and it's challenges.
Kodo Millet PPT made by Ghanshyam bairwa college of Agriculture kumher bhara...

Kodo Millet PPT made by Ghanshyam bairwa college of Agriculture kumher bhara...
On National Teacher Day, meet the 2024-25 Kenan Fellows

On National Teacher Day, meet the 2024-25 Kenan Fellows
Jual Obat Aborsi Hongkong ( Asli No.1 ) 085657271886 Obat Penggugur Kandungan...

Jual Obat Aborsi Hongkong ( Asli No.1 ) 085657271886 Obat Penggugur Kandungan...
Vishram Singh - Textbook of Anatomy Upper Limb and Thorax.. Volume 1 (1).pdf

Vishram Singh - Textbook of Anatomy Upper Limb and Thorax.. Volume 1 (1).pdf
UGC NET Paper 1 Mathematical Reasoning & Aptitude.pdf

UGC NET Paper 1 Mathematical Reasoning & Aptitude.pdf
ICT Role in 21st Century Education & its Challenges.pptx

ICT Role in 21st Century Education & its Challenges.pptx
Salient Features of India constitution especially power and functions

Salient Features of India constitution especially power and functions
Mixin Classes in Odoo 17 How to Extend Models Using Mixin Classes

Mixin Classes in Odoo 17 How to Extend Models Using Mixin Classes
Using screencasts to teach undergraduate programming
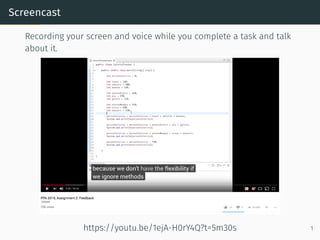
- 1. Screencast Recording your screen and voice while you complete a task and talk about it. https://youtu.be/1ejA-H0rY4Q?t=5m30s 1
- 2. Primary use: Assignment Feedback i Record my screen while I complete an assignment and discuss what I’m doing. • This is the only form in which assignment solutions are released (at least initially), so students don’t just look at a completed piece of code and assume they know what it does, or could replicate it. Instead, they must also look at the steps associated with constructing a solution. • I tailor which areas I pay attention to in the video according to trends of problems I’ve seen emerge from students while they’ve completed the assignment. This makes the feedback much more personal, and thus (hopefully) useful. 2
- 3. Editing Video is mostly unedited and unplanned. Mistakes I make end up being good points of learning for the students. If edits are ever required, a simple editing programming is usually sufficient to cut or reorder video segments (e.g. iMovie, MovieMaker). • Allows you to cut from screen recording to slides or images. 3
- 4. YouTube Release videos via YouTube. • I can see how many students have viewed a video, and how they rate it, so I can get a broad understand of how many students have engaged with the feedback and whether it was useful for them. • The YouTube format is widely accessible (e.g. different devices, speed, captions, etc.), and also enables comments, through which students can ask additional questions. • Can add bookmarks to help students navigate longer content, overlay information directly onto the video. • Limit privacy to link only. 4
- 5. Other use: Assignment Hints https://youtu.be/169Omxnk4NY?t=1m26s 5
- 6. Other use: Supplement Lecture i https://youtu.be/Ka9KPCKFNWk?t=19m54s 6
- 7. Other use: Supplement Lecture ii • Content can supplement a lecture • A lecture given by a colleague that you wish to add your take on. • After a lecture, to go over topics again, if necessary, and potentially provide a more useful resource than lecture capture. 7
- 8. Other use: Assignment Specification https://youtu.be/ZpbGd8NvRTw?t=36m6s https://martinchapman.co.uk/teaching/screencasts 8
