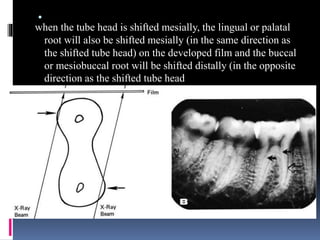
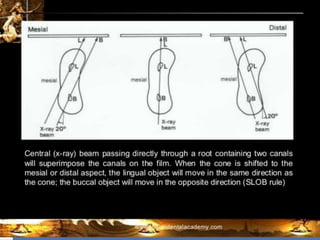
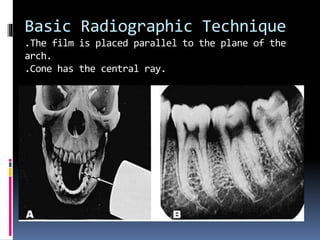
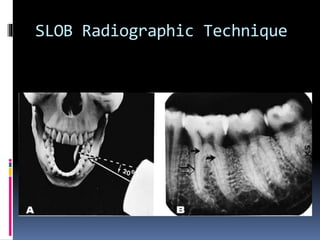
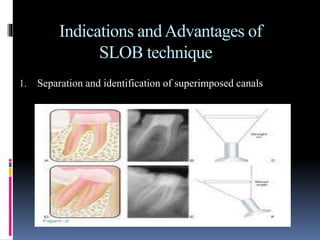
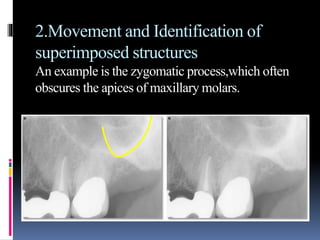
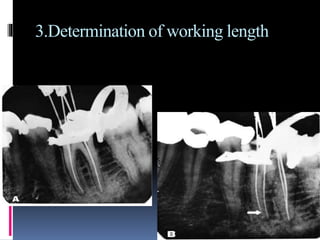
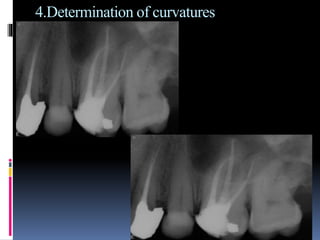
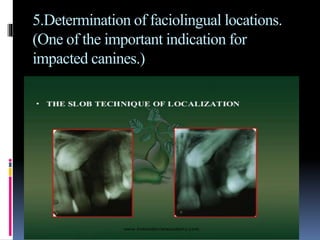
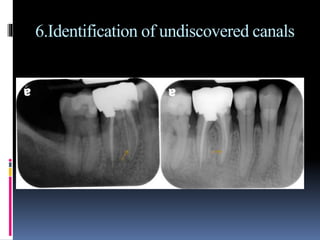
The document discusses the SLOB (Same Lingual, Opposite Buccal) technique, which is used in dental radiography. The SLOB technique involves shifting the X-ray tube head to separate superimposed structures on a radiograph. When the tube is shifted mesially, the lingual root will shift in the same direction and the buccal root will shift in the opposite direction. The SLOB technique has advantages like separating superimposed canals and structures, aiding in working length determination and identifying undiscovered canals. However, it can also cause decreased clarity and increased superimposition of structures at more oblique angles.